|
Liberty Lake (Washington)
Liberty Lake is a lake in Spokane County in the U.S. state of Washington. The lake is located about south of the eponymous city, and is a popular fishing spot. The lake is part of the Spokane Valley–Rathdrum Prairie Aquifer. Besides the aquifer, the only outflow is a small unnamed stream that ends at a small ephemeral pond a little over 1 mile (1.9 km) to the North. Native fish species Liberty lake has a fishing season that lasts from March 1 to October 31. Early fishing in the month of March yields good results for the elusive brown trout. As the water warms, other fish such as the largemouth and smallmouth bass, and yellow perch become more prevalent. Other fish dwelling in the lake include black crappie, bluegill, brown bullhead, channel catfish, rainbow trout, and walleye. See also *Lake Saltese The Saltese Flats is a flat located in Spokane County, Washington, United States. The flats are occupied by the residual wetlands of the now-drained Saltese Lake. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open And Closed Lakes
Open and closed lakes refer to the major subdivisions of lakes – bodies of water surrounded by land. Exorheic, or open lakes drain into a river, or other body of water that ultimately drains into the ocean. Endorheic basins fall into the category of endorheic or closed lakes, wherein waters do not drain into the ocean, but are reduced by evaporation, and/or drain into the ground. Open lake An open lake is a lake where water constantly flows out under almost all climatic circumstances. Because water does not remain in an open lake for any length of time, open lakes are usually fresh water: dissolved solids do not accumulate. Open lakes form in areas where precipitation is greater than evaporation. Because most of the world's water is found in areas of highly effective rainfall, most lakes are open lakes whose water eventually reaches the sea. For instance, the Great Lakes' water flows into the St. Lawrence River and eventually the Atlantic Ocean. Open lakes typically have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Perch
The yellow perch (''Perca flavescens''), commonly referred to as perch, striped perch, American perch, American river perch or preacher is a freshwater perciform fish native to much of North America. The yellow perch was described in 1814 by Samuel Latham Mitchill from New York. It is closely related, and morphologically similar to the European perch (''Perca fluviatilis''); and is sometimes considered a subspecies of its European counterpart. Other common names for yellow perch include American perch, coontail, lake perch, raccoon perch, ring-tail perch, ringed perch, and striped perch. Another nickname for the perch is the Dodd fish. Latitudinal variability in age, growth rates, and size have been observed among populations of yellow perch, likely resulting from differences in day length and annual water temperatures. In many populations, yellow perch often live 9 to 10 years, with adults generally ranging from in length. The world record yellow perch (; ) was caught in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Coeur D'Alene
Lake Coeur d'Alene, officially Coeur d'Alene Lake ( ), is a natural dam-controlled lake in North Idaho, located in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. At its northern end is the city of Coeur d'Alene. It spans in length and ranges from 1 to wide with over of shoreline. The lake was named after the Coeur d'Alene people. Geology and geography Lake Coeur d'Alene, like other lakes surrounding the Spokane Valley and Rathdrum Prairie, was formed by the Missoula Floods, most recently 12,000 to 15,000 years ago. The Purcell Lobe of the Cordilleran Ice Sheet flowed south from Canada, carving the basin of present-day Lake Pend Oreille and damming the Clark Fork river. The impounded river repeatedly filled to form Glacial Lake Missoula and broke through the ice dam, resulting in massive floods that filled the Rathdrum Prairie area with sand, gravel, and boulders. Large eddy bars formed downstream from bedrock obstructions, thereby damming tributary valleys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shelley Lake
Shelley Lake is a small lake located entirely in the city of Spokane Valley, in the U.S. state of Washington. The lake is surrounded on three sides by the 248 lot gated community of Shelley Lake Estates. The lake is kept full by Saltese Creek, which is supplied by drainage canals from the Saltese Flats The Saltese Flats is a flat located in Spokane County, Washington, United States. The flats are occupied by the residual wetlands of the now-drained Saltese Lake. The term Saltese Flats is generally used to refer to both the flat and the occupyi .... Although an open lake, there are no above-ground outflows. See also * Liberty Lake References Lakes of Washington (state) Lakes of Spokane County, Washington {{SpokaneCountyWA-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Saltese
The Saltese Flats is a flat located in Spokane County, Washington, United States. The flats are occupied by the residual wetlands of the now-drained Saltese Lake. The term Saltese Flats is generally used to refer to both the flat and the occupying wetlands. The wetlands—which are overlooked by the Saltese Uplands—are primarily fed by Quinnamose and Saltese Creeks, and are also emptied by the latter. The wetlands were originally drained for farming, but the Spokane County Environmental Services are actively trying to restore them. The primary goal is to restore the wetlands, and increase late summer water flow into the Spokane River (via the Spokane Valley–Rathdrum Prairie Aquifer). History The area known as the Saltese Flats, was once a Lake (even larger than the nearby Liberty Lake), but was drained by Peter Morrison in the 1890s so he could grow Timothy hay on the dry lakebed. Starting in 1894, Morrison used hired laborers and horses to dig of drainage canals div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
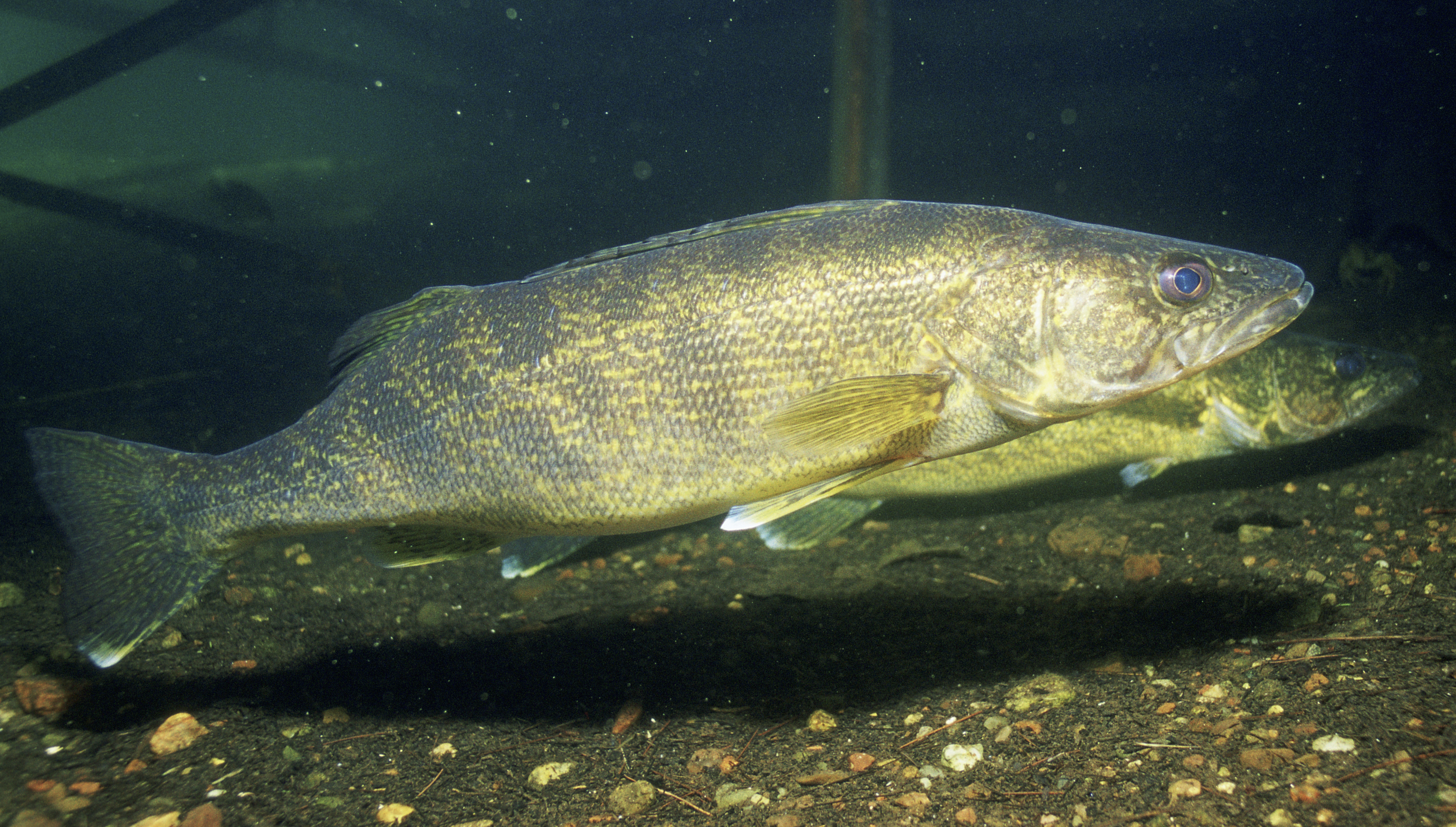
Walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relative of the European zander, also known as the pikeperch. The walleye is sometimes called the yellow walleye to distinguish it from the blue walleye, which is a color morph that was once found in the southern Ontario and Quebec regions, but is now presumed extinct. However, recent genetic analysis of a preserved (frozen) 'blue walleye' sample suggests that the blue and yellow walleye were simply phenotypes within the same species and do not merit separate taxonomic classification. In parts of its range in English-speaking Canada, the walleye is known as a pickerel, though the fish is not related to the true pickerels, which are members of the family ''Esocidae''. Walleyes show a fair amount of variation across watersheds. In general, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
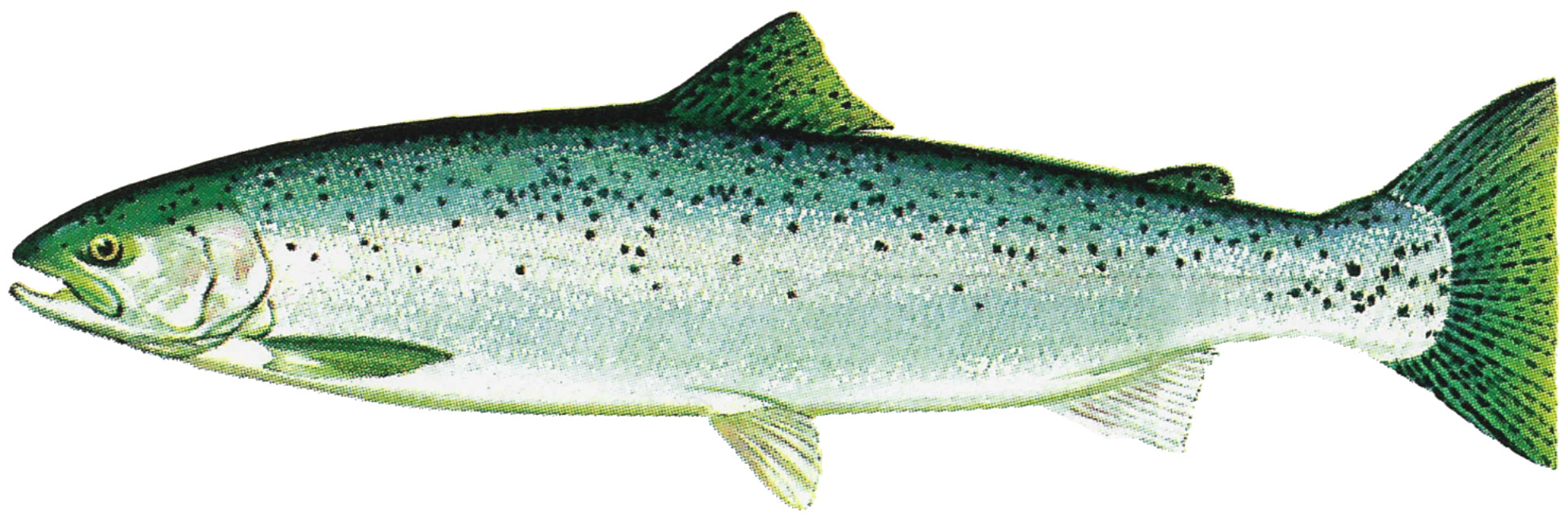
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Catfish
The channel catfish (''Ictalurus punctatus'') is North America's most numerous catfish species. It is the official fish of Kansas, Missouri, Iowa, Nebraska, and Tennessee, and is informally referred to as a "channel cat". In the United States, they are the most fished catfish species with around 8 million anglers targeting them per year. The popularity of channel catfish for food has contributed to the rapid expansion of aquaculture of this species in the United States. It has also been widely introduced in Europe, Asia and South America, and it is legally considered an invasive species in many countries. Distribution and habitat Channel catfish are native to the Nearctic, being well distributed in lower Canada and the eastern and northern United States, as well as parts of northern Mexico. They have also been introduced into some waters of landlocked Europe (Czech Republic and Romania) and parts of Malaysia and almost as many parts of Indonesia. They thrive in small and large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Bullhead
The brown bullhead (''Ameiurus nebulosus'') is a fish of the family Ictaluridae that is widely distributed in North America. It is a species of bullhead catfish and is similar to the black bullhead (''Ameiurus melas'') and yellow bullhead (''Ameiurus natalis''). It was originally described as ''Pimelodus nebulosus'' by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1819, and is also referred to as ''Ictalurus nebulosus''. The brown bullhead is also widely known as the "mud pout", "horned pout", "hornpout", or simply "mud cat", a name also used with the other bullhead species. The brown bullhead is important as a clan symbol of the Ojibwe people. In their tradition, the bullhead or is one of six beings that came out of the sea to form the original clans. Appearance The brown bullhead grows to be approximately in length and is a darker brown-green dorsally, growing lighter green and yellow towards the ventral surface. The belly is off-white or cream, and the fish has no scales. Additionally, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluegill
The bluegill (''Lepomis macrochirus''), sometimes referred to as "bream", "brim", "sunny", or "copper nose" as is common in Texas, is a species of North American freshwater fish, native to and commonly found in streams, rivers, lakes, ponds and wetlands east of the Rocky Mountains. It is the type species of the genus '' Lepomis'' (true sunfish), from the family Centrarchidae (sunfishes, crappies and black basses) in the order Perciformes ( perch-like fish). Bluegills can grow up to long and about . While their color can vary from population to population, they typically have a very distinctive coloring, with deep blue and purple on the face and gill cover, dark olive-colored bands down the side, and a fiery orange to yellow belly. They are omnivorous and will consume anything they can fit in their mouth, but mostly feed on small aquatic insects and baitfishes. The fish are important prey for bass, other larger sunfish, northern pike and muskellunge, walleye, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Crappie
The black crappie (''Pomoxis nigromaculatus'') is a freshwater fish found in North America, one of the two types of crappies. It is very similar to the white crappie in size, shape, and habits, except that it is darker, with a pattern of black spots. Taxonomy ''Pomoxis'', the genus name, is Greek: "poma, -atos" and "oxys" meaning sharp operculum. This references the fish's spined gill covers. The species name, ''nigromaculatus'', is derived from Latin and means "black-spotted". Description Black crappies are most accurately identified by the seven or eight spines on its dorsal fin (white crappies have five or six dorsal spines). Crappies have a deep and laterally compressed body. They are usually silvery-gray to green in color and show irregular or mottled black splotches over the entire body. Black crappies have rows of dark spots on their dorsal, anal, and caudal fins. The dorsal and anal fins resemble each other in shape. Both crappies have large mouths extending to below t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)