|
Liam Deasy
Liam Deasy (6 May 1896 – 20 August 1974) was an Irish Republican Army officer who fought in the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. In the latter conflict, he was second-in-command of the Anti-Treaty forces for a period in late 1922 and early 1923. Before the anti-treaty and pro-treaty split, he was considered closely associated with Michael Collins Early life Deasy was born in Kilmacsimon, Bandon in County Cork on 6 May 1896, and educated in the local school at Ballinadee. He was the third son of William and Mary Deasy. Irish War of Independence In the War of Independence (1919–21, he was the Adjutant of the 3rd Cork Brigade (West Cork). He served under Tom Barry in one of the unit's best known action, the Crossbarry Ambush in March 1921. His younger brother, Pat, died in action at the Kilmichael Ambush in November 1920, an engagement which Liam Deasy himself was not present at. He also took part in the Tooreen ambush. Civil War He opposed the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmacsimon
Kilmacsimon () is a small village and townland situated on the banks of the River Bandon in County Cork, Ireland. Historical records list ''Killmcsimon'' in the Calendar of Patent Rolls of James I dated 1615. The village has a pub and a community and activity centre which opened in May 2014. The local rowing club hosts the Kilmacsimon Water Carnival every year towards the end of June. The more substantial village of Innishannon is 4 km to the north. The town of Bandon is 7 km to the west, and Cork city Cork ( ; from , meaning 'marsh') is the second-largest city in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, the county town of County Cork, the largest city in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland ... is 22 km to the north-east. References Towns and villages in County Cork {{Cork-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Barry (soldier)
Thomas Bernardine Barry (1 July 1897 – 2 July 1980), better known as Tom Barry, was a prominent guerrilla warfare, guerrilla leader in the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), Irish Republican Army (IRA) during the Irish War of Independence and the Irish Civil War. He is best remembered for orchestrating the Kilmichael Ambush, Kilmichael ambush, in which he and his column wiped out a 18-man patrol of Auxiliary Division, Auxiliaries, killing sixteen men. Born in County Kerry, Barry was the son of a former Royal Irish Constabulary constable. In 1915, at the age of seventeen, he joined the British Army and would go on to see action as a gunner in the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East during the World War I, First World War. Despite expressing some British patriotism during his early years, Barry's views slowly began to change towards Irish republicanism. In his memoir, Barry stated that this started shortly after he heard about the Easter Rising in 1916, though r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Free State Offensive
The Irish Free State offensive of July–September 1922 was the decisive military stroke of the Irish Civil War. It was carried out by the National Army (Ireland), National Army of the newly created Irish Free State against Irish Republican Army (1922-1969), anti-treaty strongholds in the south and southwest of Ireland. At the beginning of the Civil War in June 1922, the Irish Free State government, composed of the leadership faction who had accepted the Anglo-Irish Treaty, held the capital city of Dublin, where its armed forces were concentrated and some other areas of the midlands and north. The new National Army was composed of those units of the Irish Republican Army loyal to them, plus recent recruits, but was, at the start of the war, still relatively small and poorly armed. Much of the rest of the country, particularly the south and west, was outside of its control and in the hands of the anti-Treaty elements of the IRA, who did not accept the legitimacy of the new state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoin O'Duffy
Eoin O'Duffy (born Owen Duffy; 28 January 1890 – 30 November 1944) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier, police commissioner, politician and fascist. O'Duffy was the leader of the Monaghan Brigade of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a prominent figure in the Ulster IRA during the Irish War of Independence. In this capacity, he became Chief of Staff of the IRA in 1922. He accepted the Anglo-Irish Treaty and as a general became Chief of Staff of the National Army in the Irish Civil War, on the pro-Treaty side. He had been an early member of Sinn FĂ©in and was elected a Teachta Dála (TD) for Monaghan in the Second Dáil in 1921, supporting pro-Treaty Sinn FĂ©in in the split of 1922. In 1923 he became associated with Cumann na nGaedheal. He was appointed as the second Commissioner of the Garda SĂochána in 1922, the police force of the new Irish Free State, serving until 1933. In 1924, during the Irish Army Mutiny, he was appointed as General Officer Commanding of the Iri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
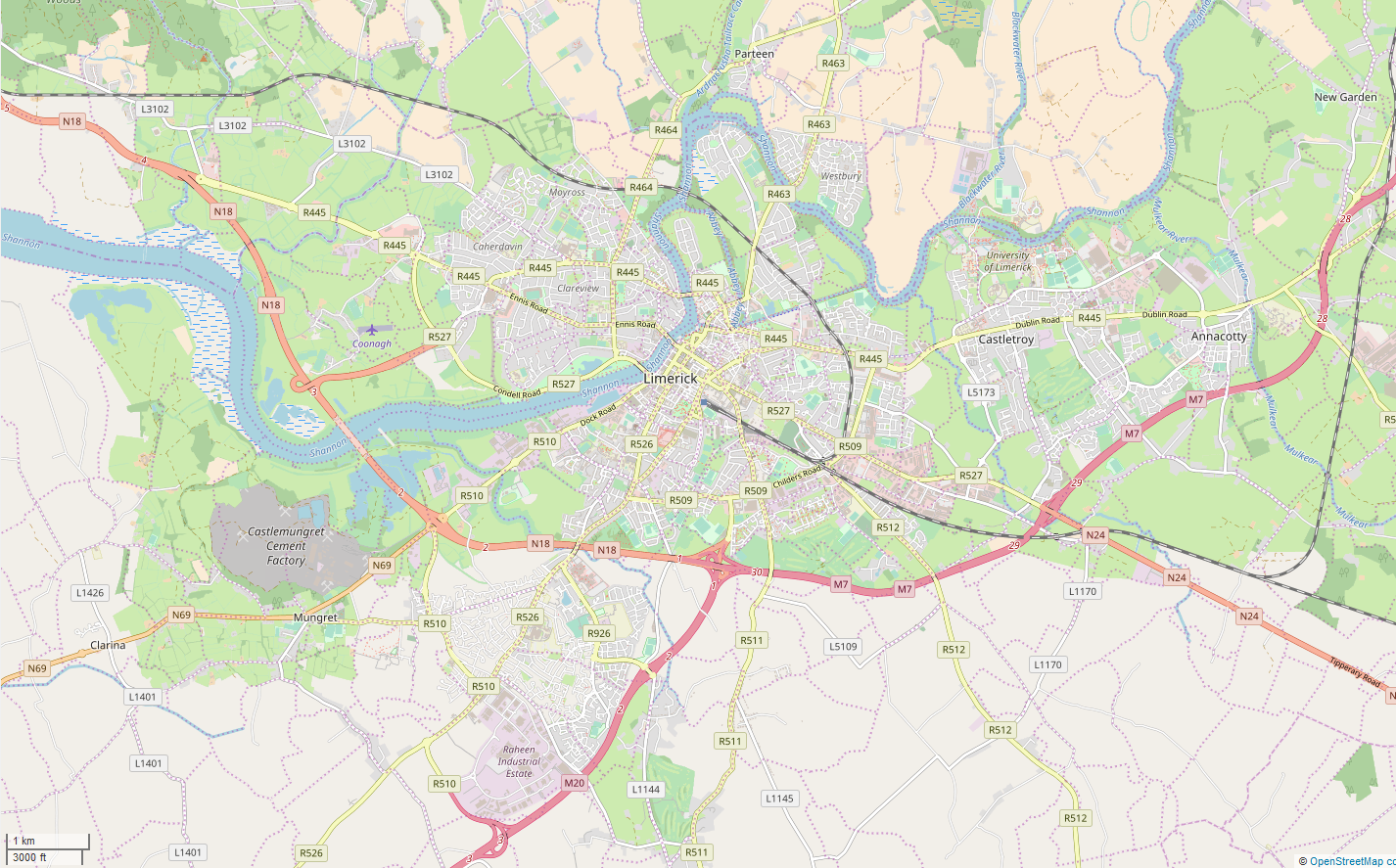
Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. With a population of 102,287 at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census, Limerick is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland, third-most populous urban area in Republic of Ireland, Ireland, and the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, fourth-most populous city on the island of Ireland. It was founded by Scandinavian settlers in 812, during the Viking Age. The city straddles the River Shannon, with the historic core of the city located on King's Island, Limerick, King's Island, which is bounded by the Shannon and Abbey River, Limerick, Abbey Rivers. Limerick is at the head of the Shannon Estuary, where the river widens before it flows into the Atlantic Ocean. Limerick City and County Council is the Local gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilmallock
Kilmallock () is a town in south County Limerick, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, near the border with County Cork, 30 km south of Limerick city. There is a Dominican Priory in the town and King John's Castle (Kilmallock), King's Castle (or King John's Castle). The remains of medieval walls which encircled the settlement are still visible. History Foundation and development Saint Mocheallóg (literally 'Mo - Ceallach - Og' meaning 'my young Ceallach') built a church in the area in the early 7th century, and the town's name derives from the Irish ''Cill Mocheallóg'' meaning "the church of Mocheallóg". This saint also established a hermitage or a small community of monks on Inishvickillane, Inisvickillane, one of the Blasket Islands off the coast of County Kerry. In St. Kieran's College, Kilkenny, an ancient statue of Mocheallóg was venerated, depicting him as a bearded man with a monk’s cowl. The town was of considerable importance in the late medieval period, ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
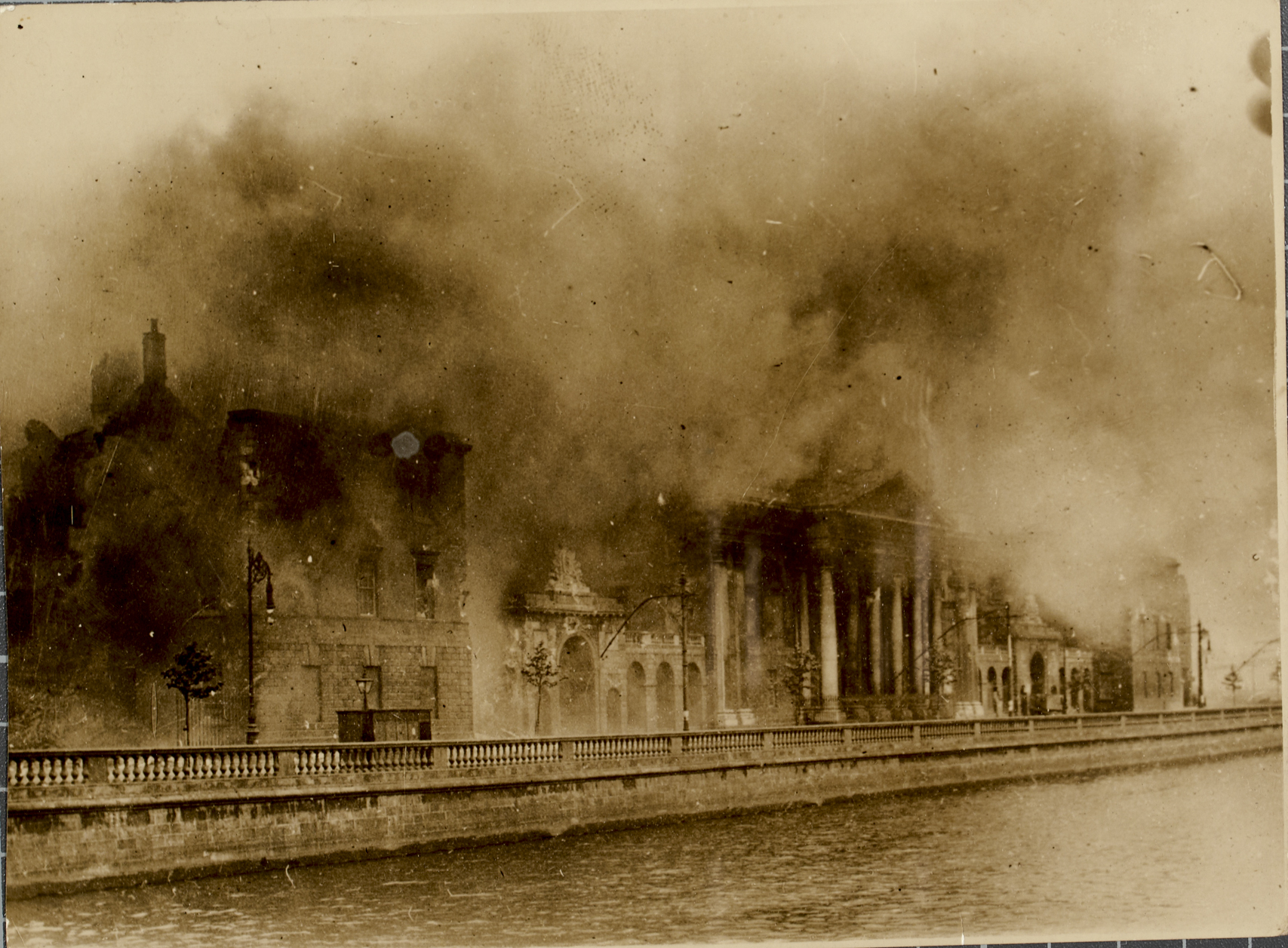
Four Courts
The Four Courts () is Ireland's most prominent courts building, located on Inns Quay in Dublin. The Four Courts is the principal seat of the Supreme Court, the Court of Appeal, the High Court and the Dublin Circuit Court. Until 2010 the building also housed the Central Criminal Court; this is now located in the Criminal Courts of Justice building. Court structure The original courts building on St Michael's Hill close to Christchurch cathedral housed four superior courts, of Chancery, King's Bench, Exchequer and Common Pleas, giving the building its familiar name. Under the Supreme Court of Judicature Act (Ireland) 1877, these four courts were replaced by two - the Court of Appeal, presided over by the Lord Chancellor, and the High Court of Justice, headed by the Lord Chief Justice - but the building has retained its historic name. Under the Courts of Justice Act 1924, courts were established for the new Irish Free State with the Supreme Court of Justice, presided ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
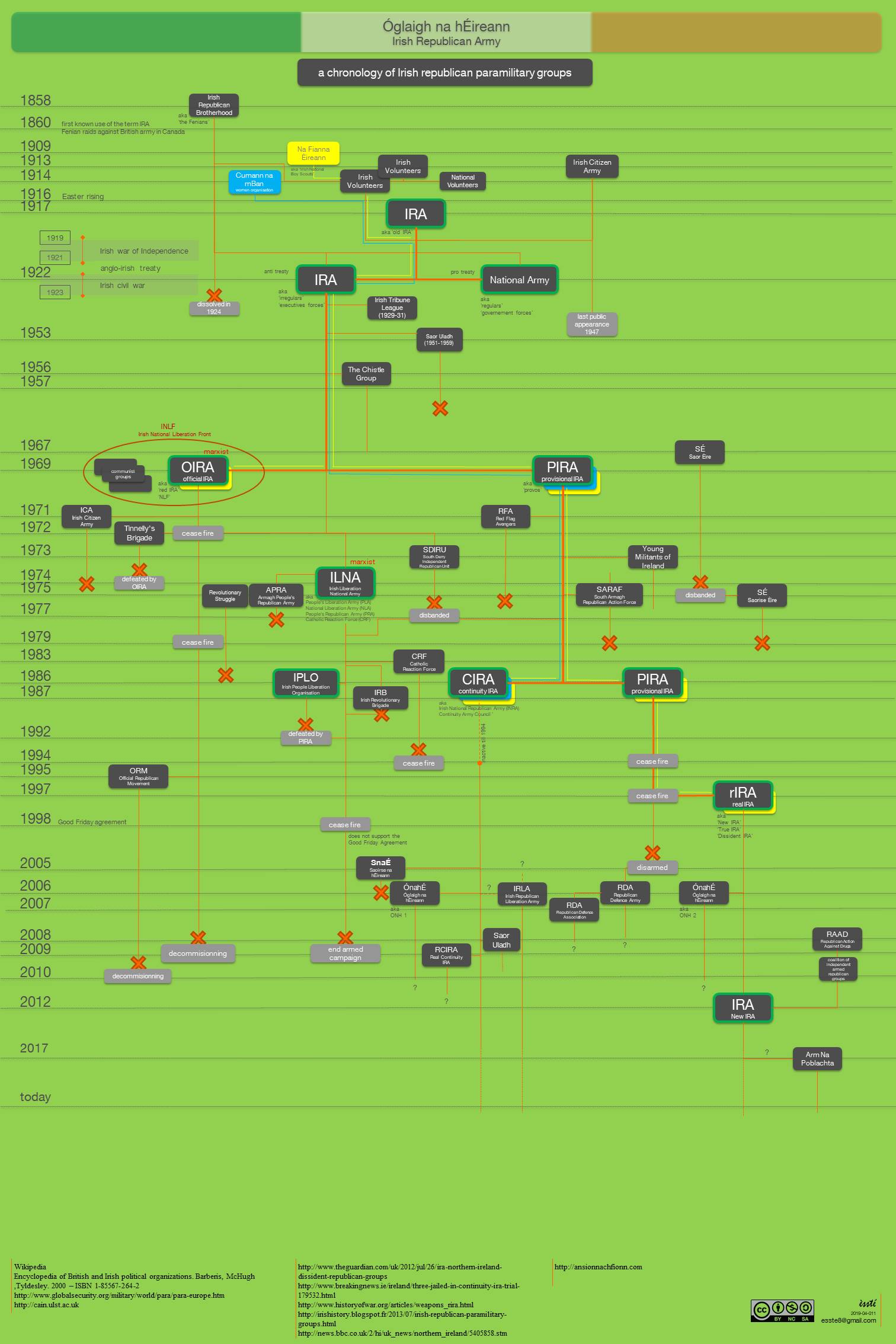
Irish Republican Army (1922-1969)
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various resistance organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dominantly Catholic and dedicated to anti-imperialism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British colonial rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions, to such a degree that many subsequent paramilitary organisations have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the forces of the Irish Republic – the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), Irish Republican Army (IRA) – and The Crown, British Crown forces. The Free State was established as a dominion of the British Empire. It comprised 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland. Northern Ireland, which was made up of the remaining six counties, exercised its right under the Treaty to opt out of the new state. The Irish Free State government consisted of the Governor-General of the Irish Free State, governor-general – the viceregal representative of the King – and the Executive Council of the Irish Free State, Executive Council (cabinet), which replaced both the revolutionary Government of the 2nd Dáil, Dáil Governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Collins (Irish Leader)
Michael Collins (; 16 October 1890 – 22 August 1922) was an Irish revolutionary, soldier and politician who was a leading figure in the early-20th century struggle for Irish independence. During the War of Independence he was Director of Intelligence of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) and a government minister of the self-declared Irish Republic. He was then Chairman of the Provisional Government of the Irish Free State from January 1922 and commander-in-chief of the National Army from July until his death in an ambush in August 1922, during the Civil War. Collins was born in Woodfield, County Cork, the youngest of eight children. He moved to London in 1906 to become a clerk in the Post Office Savings Bank at Blythe House. He was a member of the London GAA, through which he became associated with the Irish Republican Brotherhood and the Gaelic League. He returned to Ireland in January 1916 and fought in the Easter Rising. He was taken prisoner and held in the Frongoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liam Lynch (general)
William Fanaghan Lynch (; 20 November 1892 – 10 April 1923) was an Irish Republican Army officer during the Irish War of Independence of 1919–1921. During much of the Irish Civil War, he was chief of staff of the Irish Republican Army. On 10 April 1923, Lynch was killed whilst trying to escape an encirclement by Free State troops in south Tipperary. Early life Lynch was born in the townland of Baurnagurrahy, Anglesboro, County Limerick, near Mitchelstown, County Cork, on 20 November 1892. His father was Jeremiah Lynch and his mother was Mary Lynch (née Kelly), both of whom are buried in Brigown graveyard, Mitchelstown. During his first twelve years of schooling he attended Anglesboro National School. Lynch was living with his parents in Baurnagurrahy for the 1901 and 1911 censuses. In 1909, at the age of 17, he started an apprenticeship in O'Neill's hardware shop in Mitchelstown, where he joined the Gaelic League and the Ancient Order of Hibernians. Later he worked at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Éamon De Valera
Éamon de Valera (; ; first registered as George de Valero; changed some time before 1901 to Edward de Valera; 14 October 1882 – 29 August 1975) was an American-born Irish statesman and political leader. He served as the 3rd President of Ireland from 1959 to 1973, and several terms as the Taoiseach. He had a leading role in introducing the Constitution of Ireland in 1937, and was a dominant figure in Irish politics from the early 1930s to the late 1960s, when he served terms as both the head of government and head of state. De Valera was a commandant of the Irish Volunteers (Third Battalion) at Boland's Mill during the Easter Rising, 1916 Easter Rising. He was arrested and sentenced to death, but released for a variety of reasons, including his American citizenship and the public response to the British execution of Rising leaders. He returned to Ireland after being jailed in England and became one of the leading political figures of the Irish War of Independence, War of Inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |