|
Lexical-functional Grammar
Lexical functional grammar (LFG) is a constraint-based grammar framework in theoretical linguistics. It posits several parallel levels of syntactic structure, including a phrase structure grammar representation of word order and constituency, and a representation of grammatical functions such as subject and object, similar to dependency grammar. The development of the theory was initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan in the 1970s, in reaction to the theory of transformational grammar which was current in the late 1970s. It mainly focuses on syntax, including its relation with morphology and semantics. There has been little LFG work on phonology (although ideas from optimality theory have recently been popular in LFG research). Some recent work combines LFG with Distributed Morphology in Lexical-Realizational Functional Grammar.Ash Asudeh, Paul B. Melchin & Daniel Siddiqi (2021). ''Constraints all the way down: DM in a representational model of grammar''. In ''WCCFL 39 Proceed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constraint-based Grammar
Model-theoretic grammars, also known as constraint-based grammars, contrast with generative grammars in the way they define sets of sentences: they state constraints on syntactic structure rather than providing operations for generating syntactic objects. A generative grammar provides a set of operations such as rewriting, insertion, deletion, movement, or combination, and is interpreted as a definition of the set of all and only the objects that these operations are capable of producing through iterative application. A model-theoretic grammar simply states a set of conditions that an object must meet, and can be regarded as defining the set of all and only the structures of a certain sort that satisfy all of the constraints. The approach applies the mathematical techniques of model theory to the task of syntactic description: a grammar is a theory in the logician's sense (a consistent set of statements) and the well-formed structures are the models that satisfy the theory. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature (linguistics)
In linguistics, a feature is any characteristic used to classify a phoneme or word. These are often binary or unary conditions which act as constraints in various forms of linguistic analysis. In phonology In phonology, segments are categorized into natural classes on the basis of their distinctive features. Each feature is a quality or characteristic of the natural class, such as voice or manner. A unique combination of features defines a phoneme. Examples of phonemic or distinctive features are: /- voice Advanced tongue root">ATR (binary features) and [ coronal consonant">CORONAL (a unary feature; also a place of articulation">place feature). Surface representations can be expressed as the result of rules acting on the features of the underlying representation. These rules are formulated in terms of transformations on features. In morphology and syntax In morphology (linguistics), morphology and syntax, words are often organized into lexical categories or word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apptek
Applications Technology (AppTek) is a U.S. company headquartered in McLean, Virginia that specializes in artificial intelligence and machine learning for human language technologies. The company provides both managed and professional services for natural language processing (NLP) technologies including automatic speech recognition (ASR), neural machine translation (MT), natural-language understanding (NLU) and neural speech synthesis. AppTek's automatic speech recognition covers over 45 languages and dialects. The neural MT engine covers over 1000 language pairs between languages. AppTek's Head of Science, Prof. Dr. -Ing Hermann Ney, was awarded the IEEE James L. Flanagan Speech and Audio Processing Award in 2019 and the ISCA Medal for Scientific Achievement in 2021 for his work in natural language processing. History AppTek was acquired in 1998 by Lernout & Hauspie (at the time a NASDAQ publicly traded company), AppTek organized a management buy-out and went private again in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Translation
Machine translation is use of computational techniques to translate text or speech from one language to another, including the contextual, idiomatic and pragmatic nuances of both languages. Early approaches were mostly rule-based or statistical. These methods have since been superseded by neural machine translation and large language models. History Origins The origins of machine translation can be traced back to the work of Al-Kindi, a ninth-century Arabic cryptographer who developed techniques for systemic language translation, including cryptanalysis, frequency analysis, and probability and statistics, which are used in modern machine translation. The idea of machine translation later appeared in the 17th century. In 1629, René Descartes proposed a universal language, with equivalent ideas in different tongues sharing one symbol. The idea of using digital computers for translation of natural languages was proposed as early as 1947 by England's A. D. Booth and Warr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsable
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject and predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a parse tree showing their syntactic relation to each other, which may also contain semantic information. Some parsing algor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Voice
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical sentences. In theoretical linguistics, a speaker's judgement on the well-formedness of a linguistic 'string'—called a grammaticality judgement—is based on whether the sentence is interpreted in accordance with the rules and constraints of the relevant grammar. If the rules and constraints of the particular lect are followed, then the sentence is judged to be grammatical. In contrast, an ungrammatical sentence is one that violates the rules of the given language variety. Linguists use grammaticality judgements to investigate the syntactic structure of sentences. Generative linguists are larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
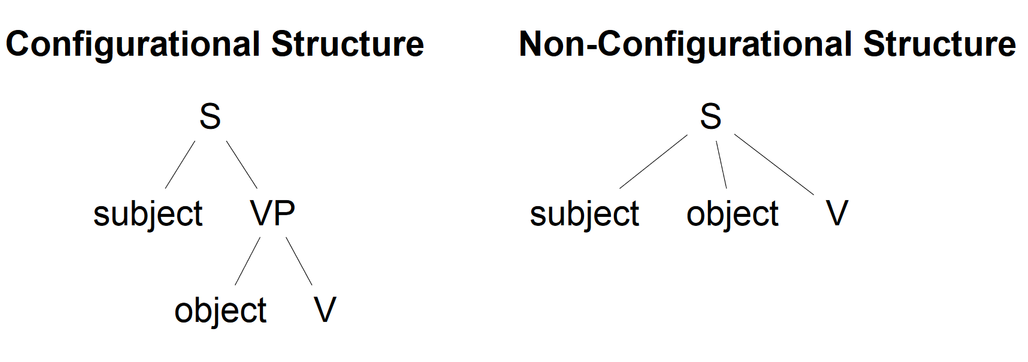
Non-configurational Language
In generative grammar, non-configurational languages are languages characterized by a flat phrase structure, which allows syntactically discontinuous expressions, and a relatively free word order. History of the concept of "non-configurationality" The concept of non-configurationality was developed by grammarians working within Noam Chomsky's generative linguistics, generative framework. Some of these linguists observed that the Syntactic Universals proposed by Chomsky and which required a rigid phrase structure were challenged by the syntax of some of the world's languages that had a much less rigid syntax than that of the languages on which Chomsky had based his studies. The concept was invented by Kenneth L. Hale, Ken Hale who described the syntax of Warlpiri language, Warlpiri as being non-configurational. However, the first to publish a description of non-configurationality was Chomsky himself in his 1981 lectures on Government and Binding, in which he referred to an unpublish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American professor and public intellectual known for his work in linguistics, political activism, and social criticism. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He is a laureate professor of linguistics at the University of Arizona and an institute professor emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Among the most cited living authors, Chomsky has written more than 150 books on topics such as linguistics, war, and politics. In addition to his work in linguistics, since the 1960s Chomsky has been an influential voice on the American Left, American left as a consistent critic of U.S. foreign policy, Criticism of capitalism, contemporary capitalism, and Corporate influence on politics in the United States, corporate influence on political institutions and the media. Born to Ashkenazi Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta-role
Theta roles are the names of the participant roles associated with a predicate: the predicate may be a verb, an adjective, a preposition, or a noun. If an object is in motion or in a steady state as the speakers perceives the state, or it is the topic of discussion, it is called a theme. The participant is usually said to be an argument of the predicate. In generative grammar, a theta role or θ-role is the formal device for representing syntactic argument structure—the number and type of noun phrases—required syntactically by a particular verb. For example, the verb ''put'' requires three arguments (i.e., it is trivalent). The formal mechanism for implementing a verb's argument structure is codified as theta roles. The verb ''put'' is said to "assign" three theta roles. This is coded in a theta grid associated with the lexical entry for the verb. The correspondence between the theta grid and the actual sentence is accomplished by means of a bijective filter on the grammar k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object (grammar)
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but are not limited to direct objects, indirect objects, and arguments of adpositions ( prepositions or postpositions); the latter are more accurately termed ''oblique arguments'', thus including other arguments not covered by core grammatical roles, such as those governed by case morphology (as in languages such as Latin) or relational nouns (as is typical for members of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area). In ergative-absolutive languages, for example most Australian Aboriginal languages, the term "subject" is ambiguous, and thus the term " agent" is often used instead to contrast with "object", such that basic word order is often spoken of in terms such as Agent-Object-Verb (AOV) instead of Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). Topic-prominent la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |