|
Lev Semyonovich Berg
Lev Semyonovich Berg, also known as Leo S. Berg (; 14 March 1876 – 24 December 1950) was a leading Russian geographer, biologist and ichthyologist who served as President of the Soviet Geographical Society between 1940 and 1950. He is known for his own evolutionary theory, nomogenesis (a form of orthogenesis incorporating mutationism) as opposed to the theories of Darwin and Lamarck. Life Lev Berg was born in Bessarabia in a Jewish family, the son of Simon Gregoryevich Berg, a notary, and Klara Lvovna Bernstein-Kogan. He graduated from the Second Kishinev Gymnasium in 1894. Like some of his relatives, Berg converted to Christianity in order to pursue his studies at Moscow State University. At Moscow University, Berg studied hydrobiology and geography. He later studied ichthyology and in 1928 was awarded he was also a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Lev Berg graduated from the Moscow State University in 1898. Between 1903 and 1914, he worked in the Museum of Zoolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bender, Moldova
Bender (, ) or Bendery (, ; ), also known as Tighina ( mo-Cyrl, Тигина, links=no), is a city within the internationally recognized borders of Moldova under ''de facto'' control of the unrecognized Transnistria, Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (Transnistria) (PMR) since 1992. It is located on the western bank of the river Dniester in the historical region of Bessarabia. Together with its suburb Proteagailovca, the city forms a municipality, which is separate from Administrative-Territorial Units of the Left Bank of the Dniester, Transnistria (as an administrative unit of Moldova) according to Moldovan law. Bender is located in the buffer zone established at the end of the 1992 War of Transnistria. While the Joint Control Commission has overriding powers in the city, Transnistria has ''de facto'' administrative control. The Tighina Fortress, fortress of Tighina was one of the important historic fortresses of the Principality of Moldova until 1812. Name First mentioned in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few Academy name changes, ending as The Imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transnistrian Republican Bank
The Transnistrian Republican Bank (; or , ; ) or Pridnestrovian Republican Bank is the central bank of Transnistria. It issues its own currency, the Transnistrian ruble, and also a series of memorial gold and silver coins, among them '' The Outstanding People of Pridnestrovie''. History The Transnistrian Republican Bank has largely been held afloat by economic intervention from Russia who is the only state that has provided financial assistance to Transnistria, however, since 2014, Russian aid has steadily declined forcing the Transnistrian Republican Bank to rely further on domestic and Moldovan financial institutions, investments and credit. In October 2006, the bank inaugurated a new headquarters of a size of in Tiraspol. As part of the |
Volkovo Cemetery
The Volkovo Cemetery (also Volkovskoe) ( or Во́лково кла́дбище) is one of the largest and oldest non- Orthodox cemeteries in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Until the early 20th century it was one of the main burial grounds for Lutheran Germans in Russia. It is estimated that over 100,000 people have been buried at this cemetery since 1773. Origins 1770–1773 Between late 1771 and 1772, Catherine the Great, empress of the Russian Empire, issued an edict which decreed that, from that point on, any person who died (regardless of social standing or class origins) no longer had the right to be buried within church crypts or adjacent churchyards. New cemeteries had to be built across the entire Russian Empire and from then on they all had to be located outside city limits. One of the main motivations behind these measures was overcrowding in church crypts and graveyards. However, the true deciding factor which led to the new laws being enforced on such a mass scale across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komarovo, Saint Petersburg
Komarovo ( rus, Комаро́во, p=kəmɐˈrovə; ) is a administrative divisions of Saint Petersburg, municipal settlement in Kurortny District of the federal cities of Russia, federal city of Saint Petersburg, St. Petersburg, Russia, located in the Karelian Isthmus on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, and a station of the Saint Petersburg-Vyborg railroad. It is about northwest of central Saint Petersburg. Population: Komarovo is renowned for being the residence of numerous Russian intellectuals and prominent figures in science and culture. Among some of its most notable residents were, for example, three Nobel Prize laureates: Ivan Pavlov, Joseph Brodsky, and Zhores Alferov. The list also includes renowned individuals such as jeweller Peter Carl Fabergé, composer Dmitri Shostakovich, poet Anna Akhmatova, dissident Dmitry Likhachev, ballet dancers Mathilde Kschessinska and Galina Ulanova, film actor Innokenty Smoktunovsky, as well as science-fiction authors Arkady a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (''Salmo'') and North Pacific (''Oncorhynchus'') basins. ''Salmon'' is a colloquial or common name used for fish in this group, but is not a scientific name. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen, all coldwater fish of the subarctic and cooler temperate regions with some sporadic endorheic populations in Central Asia. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the shallow gravel stream bed, beds of freshwater headstreams and spend their juvenile fish, juvenile years in rivers, lakes and freshwater wetlands, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. The common name "lamprey" is probably derived from Latin , which may mean "stone licker" ( "to lick" + "stone"), though the etymology is uncertain. "Lamprey" is sometimes seen for the plural form. About 38 extant species of lampreys are known, with around seven known extinct species. They are classified in three families—two small families in the Southern Hemisphere (Geotriidae, Mordaciidae) and one large family in the Northern Hemisphere (Petromyzontidae). Genetic evidence suggests that lampreys are more closely related to hagfish, the only other living group of jawless fish, than they are to jawed vertebrates, forming the superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossils of stem-group lampreys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR State Prize
The USSR State Prize () was one of the Soviet Union’s highest civilian honours, awarded from its establishment in September 1966 until the dissolution of the USSR in 1991. It recognised outstanding contributions in the fields of science, mathematics, literature, the arts, and architecture. History State Stalin Prize (1941–1956) The award traces its origins to the State Stalin Prize (), commonly known as the Stalin Prize, which was established in 1941. It honoured achievements in science, technology, literature, and the arts deemed vital to the Soviet war effort and postwar reconstruction.Volkov, Solomon; Bouis, Antonina W., trans. 2004. ''Shostakovich and Stalin: The Extraordinary Relationship Between the Great Composer and the Brutal Dictator''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-375-41082-1. Ceremonies were suspended during 1944–45 and then held twice in 1946 (January for works from 1943–44; June for 1945 works). USSR State Prize (1966–1991) By 1966, the Stalin Prize h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyology
Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish, including bony fish (Osteichthyes), cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes), and jawless fish (Agnatha). According to FishBase, 35,800 species of fish had been described as of March 2025, with approximately 250 new species described each year. Etymology The word is derived from the Ancient Greek words ἰχθύς, ''ikhthus'', meaning "fish"; and λόγος, ''logos'', meaning "study". History The study of fish dates from the Upper Paleolithic Revolution (with the advent of "high culture"). The science of ichthyology was developed in several interconnecting epochs, each with various significant advancements. The study of fish receives its origins from humans' desire to feed, clothe, and equip themselves with useful implements. According to Michael Barton, a prominent ichthyologist and professor at Centre College, "the earliest ichthyologists were hunters and gatherers who had learned how to obtain the most use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "slope"; and , '' -logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. Climate concerns the atmospheric condition during an extended to indefinite period of time; weather is the condition of the atmosphere during a relative brief period of time. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. This topic of study is regarded as part of the atmospheric sciences and a subdivision of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology includes some aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry. The main methods employed by climatologists are the analysis of observations and modelling of the physical processes that determine climate. Short term weather forecasting can be interpreted in terms of knowledge of longer-term phenomena of climate, for insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily Dokuchaev
Vasily Vasilyevich Dokuchaev (; 1 March 1846 – 8 November 1903) was a Russian geologist and geographer who is credited with laying the foundations of soil science. The Ukrainian city of Dokuchaievsk is named after him. Overview Vasily Vasilevich Dokuchaev is commonly regarded as the father of soil science, the study of soils in their natural setting. He developed soil science in Russia and was perhaps the first to conduct broad geographical investigations of different soil types. His contribution to science figuratively "put soils on the map". He introduced the idea that other variables could explain the geographical variations in soil type besides geological factors (parent material), such as climatic and topographic factors, and by the duration of pedogenesis (soil formation). He developed the very first soil classification, using these ideas as a starting point. His ideas were taken up by many soil scientists, including Hans Jenny. Dokuchaev's work on soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
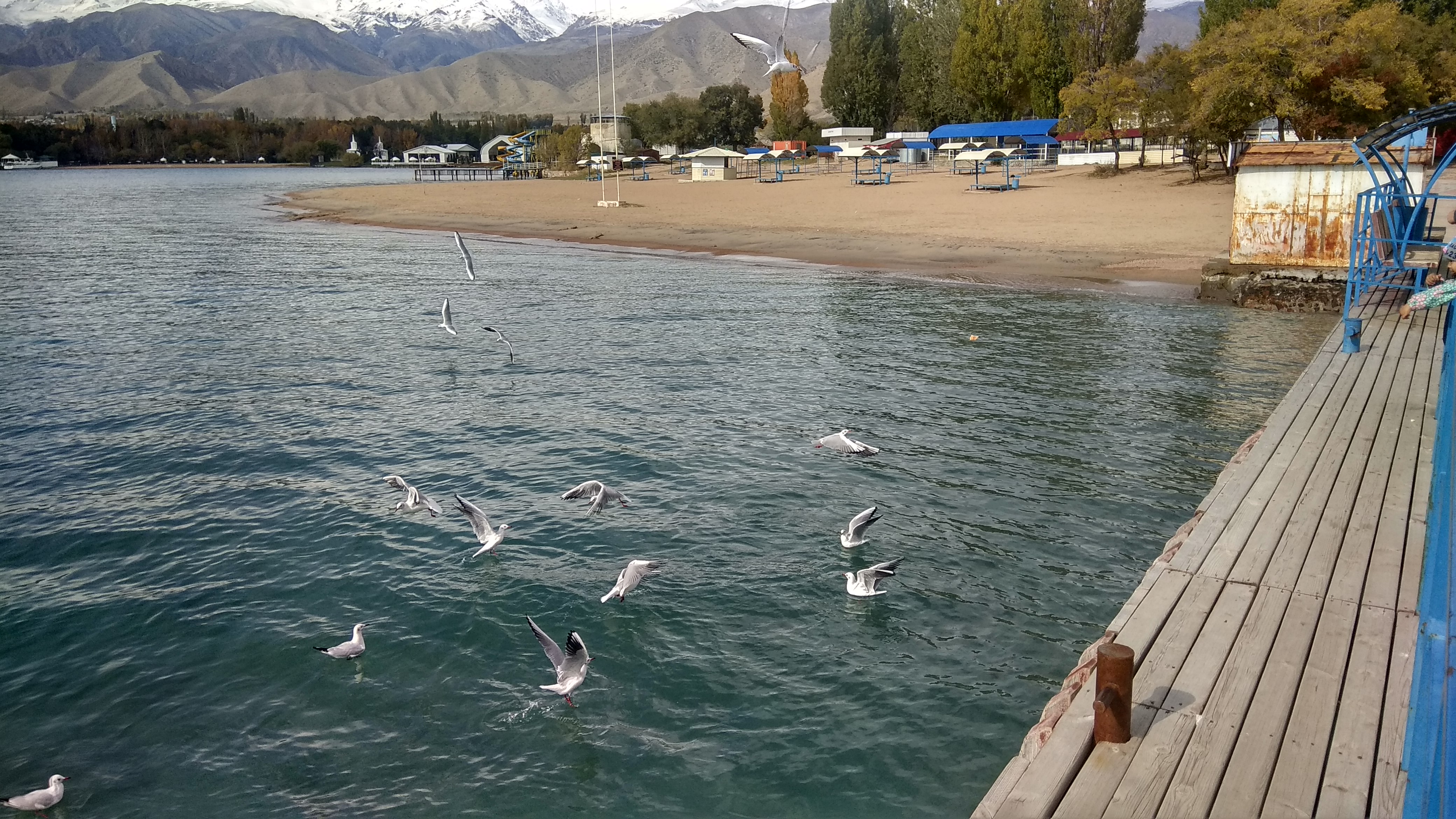
Issyk-Kul
Issyk-Kul () or Ysyk-Köl (, ; ) is an endorheic saline lake in the western Tianshan Mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan, just south of a dividing range separating Kyrgyzstan from Kazakhstan. It is the eighth-deepest lake in the world, the eleventh-largest lake in the world by volume (though not in surface area), the deepest lake whose deepest point is above sea level (939 meters or 3,080 feet), and the third-largest saline lake. Although it is located at a lofty elevation of and subject to severe cold during winter, it rarely freezes over due to high salinity, hence its name, which in the Kyrgyz language means "warm lake". The lake is a Ramsar site of globally significant biodiversity and forms part of the Issyk-Kul Biosphere Reserve. Geography Issyk-Kul Lake is long, up to wide and its surface area is . It is the second-largest mountain lake in the world behind Lake Titicaca in South America. It is at an altitude of and reaches in depth. About 118 rivers and streams f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |