|
Letter Frequency Effect
The letter frequency effect is an effect of letter frequency, according to which the frequency with which the letter is encountered influences the recognition time of a letter. Letters of high frequency show a significant advantage over letters of low frequency in letter naming, same-different matching, and visual search. Letters of high frequency are recognized faster than letters of low frequency. Appelman and Mayzner (1981) in their re-analysis of the studies concerning letter frequency effect have found that in 3 out of 6 studies using reaction times (RTs) as a dependent variable A variable is considered dependent if it depends on (or is hypothesized to depend on) an independent variable. Dependent variables are studied under the supposition or demand that they depend, by some law or rule (e.g., by a mathematical functio ... the letter frequency correlated significantly with RTs.Appelman, I. B., & Mayzner , M. S. (1981). The letter-frequency effect and the generality of famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letter Frequency
Letter frequency is the number of times letters of the alphabet appear on average in written language. Letter frequency analysis dates back to the Arab mathematician Al-Kindi (c. AD 801–873), who formally developed the method to break ciphers. Letter frequency analysis gained importance in Europe with the development of movable type in AD 1450, wherein one must estimate the amount of type required for each letterform. Linguists use letter frequency analysis as a rudimentary technique for language identification, where it is particularly effective as an indication of whether an unknown writing system is alphabetic, syllabic, or ideographic. The use of letter frequencies and frequency analysis plays a fundamental role in cryptograms and several word puzzle games, including hangman, ''Scrabble'', '' Wordle'' and the television game show '' Wheel of Fortune''. One of the earliest descriptions in classical literature of applying the knowledge of English letter frequency to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
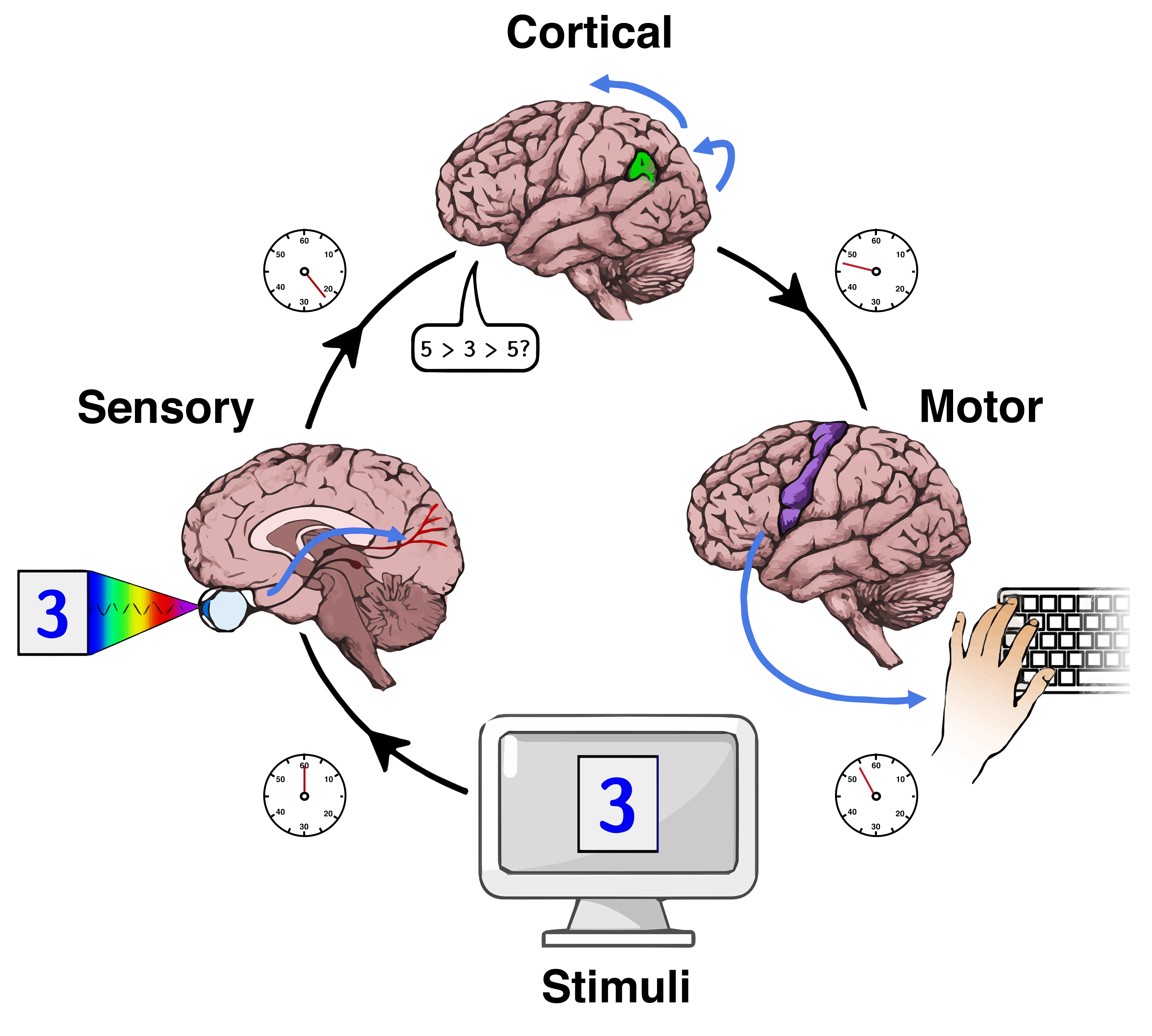
Mental Chronometry
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; also referred to as "response time") is measured by the elapsed time between stimulus onset and an individual's response on elementary cognitive tasks (ECTs), which are relatively simple perceptual-motor tasks typically administered in a laboratory setting. Mental chronometry is one of the core methodological paradigms of human experimental, cognitive, and differential psychology, but is also commonly analyzed in psychophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, and behavioral neuroscience to help elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying perception, attention, and decision-making in humans and other species. Mental chronometry uses measurements of elapsed time between sensory stimulus onsets and subsequent behavioral responses to study the time course of information processing in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent Variable
A variable is considered dependent if it depends on (or is hypothesized to depend on) an independent variable. Dependent variables are studied under the supposition or demand that they depend, by some law or rule (e.g., by a mathematical function), on the values of other variables. Independent variables, on the other hand, are not seen as depending on any other variable in the scope of the experiment in question. Rather, they are controlled by the experimenter. In pure mathematics In mathematics, a function is a rule for taking an input (in the simplest case, a number or set of numbers)Carlson, Robert. A concrete introduction to real analysis. CRC Press, 2006. p.183 and providing an output (which may also be a number). A symbol that stands for an arbitrary input is called an independent variable, while a symbol that stands for an arbitrary output is called a dependent variable. The most common symbol for the input is , and the most common symbol for the output is ; the functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics or psychology of language is the study of the interrelation between linguistic factors and psychological aspects. The discipline is mainly concerned with the mechanisms by which language is processed and represented in the mind and brain; that is, the psychology, psychological and neurobiology, neurobiological factors that enable humans to acquire, use, comprehend, and produce language. Psycholinguistics is concerned with the cognitive faculties and processes that are necessary to produce the grammatical constructions of language. It is also concerned with the perception of these constructions by a listener. Initial forays into psycholinguistics were in the philosophical and educational fields, mainly due to their location in departments other than applied sciences (e.g., cohesive data on how the human brain functioned). Modern research makes use of biology, neuroscience, cognitive science, linguistics, and information science to study how the mind-brain process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |