|
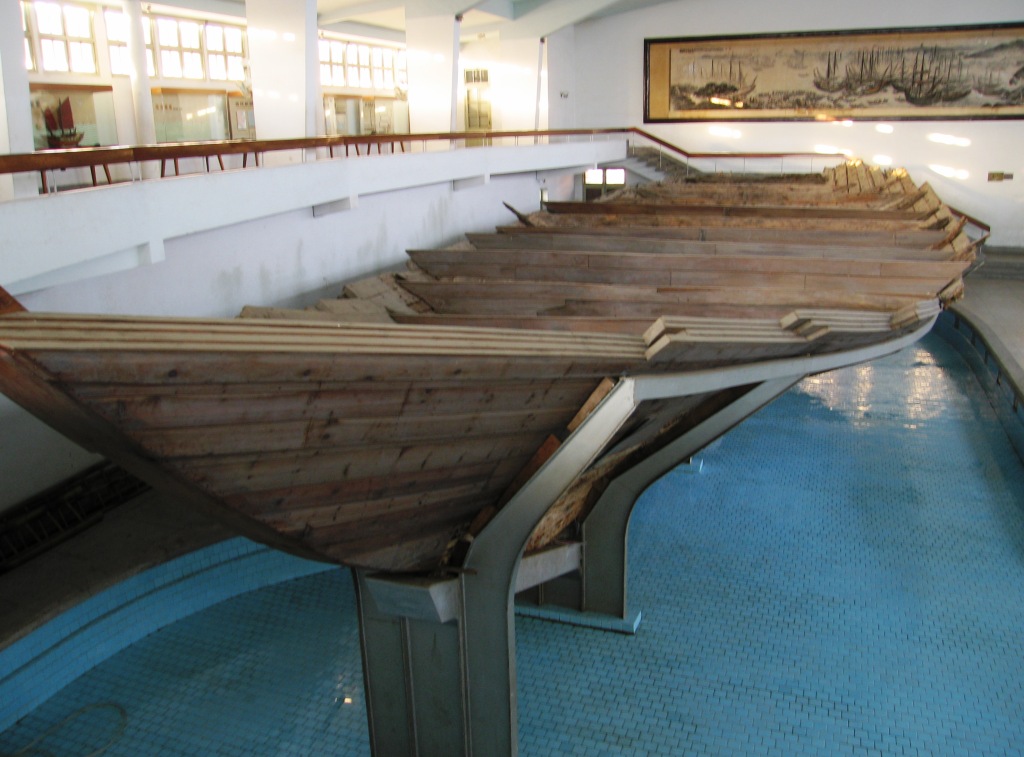
Letov Š-16
The Letov Š-16 was a single-engined twin-seat biplane aircraft used in the bomber and aerial observation roles. It was designed by Alois Šmolík and produced by the Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak aircraft manufacturer Letov Kbely. It was a broadly conventional aircraft, being largely composed of duralumin and steel while using straightforward and economic construction techniques. Its wing structure was somewhat unorthodox, having a lengthy portion of the spar (aeronautics), spar that was largely unsupported, save for a form of strut bracing (aeronautics), bracing typically reserved for torpedo bombers. Separate models were developed for bomber and observation duties; however, there was little difference in their manufacture beyond their equipment fitout. The Š-16 performed its maiden flight in 1926 in aviation, 1926.Taylor and Alexander 1969, pp. 62–63. would be procured not only by the Czechoslovak Air Force but also by several export customers. The aircraft was produced in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letov Kbely
Letov is an aircraft company located in Letňany district of Prague, Czech Republic. It is the oldest aircraft company in the region. History Letov was founded in 1918 by the Czechoslovak Ministry of Defense to repair World War I trophy planes. The first indigenous aircraft, the Letov Š-1, was designed and built in 1920, and some 50 aircraft types were built by 1939. During World War II the factory served as repair shop for the German Luftwaffe. Production lines were also set up during World War II for combat versions of the Junkers Ju 290, Ju 290 aircraft, commencing with the Ju 290 A-2, which carried a search radar for its patrol role. Since the 1950s, the plant has manufactured parts for the MiG-15, MiG-19 and MiG-21. Over 4,000 wings and empennages for Aero L-29 Delfín, L-29 Delfín, a jet engine, jet trainer aircraft that became the standard jet trainer for the air forces Warsaw Pact nations in the 1960s, were built by Letov. The company has also built wings and empennag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to the southeast, and shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of , with a population of 1.9million. The country has a Temperate climate, temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city is Riga. Latvians, who are the titular nation and comprise 65.5% of the country's population, belong to the ethnolinguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian language, Latvian. Russians in Latvia, Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population; 37.7% of the population speak Russian language, Russian as their native tongue. After centuries of State of the Teutonic Order, Teutonic, Swedish Livonia, Swedish, Inflanty Voi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skoda L
Škoda means "pity" in the Czech and Slovak languages. It may also refer to: Czech brands and enterprises * Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav ** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Škoda Auto responsible for motorsport activities * Škoda Transportation, engineering company that manufactures rail vehicles, based in Plzeň * Škoda Works, engineering company, predecessor of Škoda Transportation * Škoda-Kauba, aircraft manufacturing subsidiary of the Škoda Works in occupied Czechoslovakia in World War II * Doosan Škoda Power, subsidiary of the Doosan Group, based in Plzeň People * Škoda (surname) * Skoda (Portuguese footballer) (born 1960) Art * ''Škoda lásky'', the original Czech title of the "Beer Barrel Polka" Other * British Rail Class 90, an electric locomotive nicknamed Skoda * ''Skoda'' (barquentine), sailing vessel built in Kingsport, Nova Scotia, in 1893 * Skoda Xanthi F.C., former name of the Greek football club Xan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, the chord is an imaginary straight line segment joining the leading edge and trailing edge of an aerofoil cross section parallel to the direction of the airflow. The chord length is the distance between the trailing edge and the leading edge. L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 5.2, Pitman Publishing Limited, London. The point on the leading edge used to define the main chord may be the surface point of minimum radius. p.18 For a turbine aerofoil, the chord may be defined by the line between points where the front and rear of a 2-dimensional blade section would touch a flat surface when laid convex-side up. The wing, horizontal stabilizer, vertical stabilizer and propeller/rotor blades of an aircraft are all based on aerofoil sections, and the term ''chord'' or ''chord length'' is also used to describe their width. The chord of a wing, stabilizer and propeller is determined by measuring the distance between leading and trailing edges in the direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Arms
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions). The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes containing gunpowder and pellet projectiles were mounted on spears to make the portable fire lance, operable by a single person, which was later used effectively as a shock weapon in the siege of De'an in 1132. In the 13th century, fire lance barrels were replaced with metal tubes and transformed into the metal-barreled hand cannon. The technology gradually spread throughout Eurasia during the 14th century. Older firearms typically used black powder as a propellant, but modern firearms use smokeless powder or other explosive propellants. Most modern firearms (with the notable exception of smoothbore shotguns) have rifled barrels to impart spin to the projectile for improved flight stabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the Hevea brasiliensis, Pará rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". Manufacturers refine this latex into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination with other materials. In most of its useful forms, it has a large stretch ratio and high resilience and also is buoyant and water-proof. Industrial demand for rubber-like materials began to out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firewall (engine)
In automotive engineering, the firewall (American English) or bulkhead (British English) is the part of the automobile body ( unibody or body-on-frame) that separates the engine compartment from the passenger compartment (driver and passengers). It is most commonly a separate component of the body or, in monocoque construction, a separate steel pressing, but may be continuous with the floorpan, or its edges may form part of the door pillars. The inner and outer surfaces of the firewall are often coated with noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) absorber to prevent most engine noise from reaching the passenger compartment. The name originates from steam-powered vehicles, where the firewall separated the driver from the fire heating the boiler. In competition, firewalls are found in specially prepared cars for compartmentalisation. For example, a typical conversion of a production car for rallying will include a metal firewall which seals the fuel tank off from the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulkhead (partition)
A bulkhead is an upright wall within the hull (watercraft), hull of a ship, within the fuselage of an airplane, or a car. Other kinds of partition elements within a ship are deck (ship), decks and deckheads. Etymology The word ''bulki'' meant "cargo" in Old Norse. During the 15th century sailors and builders in Europe realized that walls within a vessel would prevent cargo from shifting during passage. In shipbuilding, any vertical panel was called a head. So walls installed abeam (side-to-side) in a vessel's hull were called "bulkheads". Now, the term bulkhead applies to every vertical panel aboard a ship, except for the hull itself. History Bulkheads were known to the ancient Greeks, who employed bulkheads in triremes to support the back of rams. By the Athenian trireme era (500 BC), the hull was strengthened by enclosing the bow behind the ram, forming a bulkhead compartment. Instead of using bulkheads to protect ships against rams, Greeks preferred to reinforce the hull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welding
Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Common alternative methods include solvent welding (of thermoplastics) using chemicals to melt materials being bonded without heat, and #Solid-state welding, solid-state welding processes which bond without melting, such as pressure, cold welding, and diffusion bonding. Metal welding is distinct from lower temperature bonding techniques such as brazing and soldering, which do not melt the base metal (parent metal) and instead require flowing a filler metal to solidify their bonds. In addition to melting the base metal in welding, a filler material is typically added to the joint to form a pool of molten material (the weld pool) that cools to form a joint that can be stronger than the base material. Welding also requires a form of shield to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
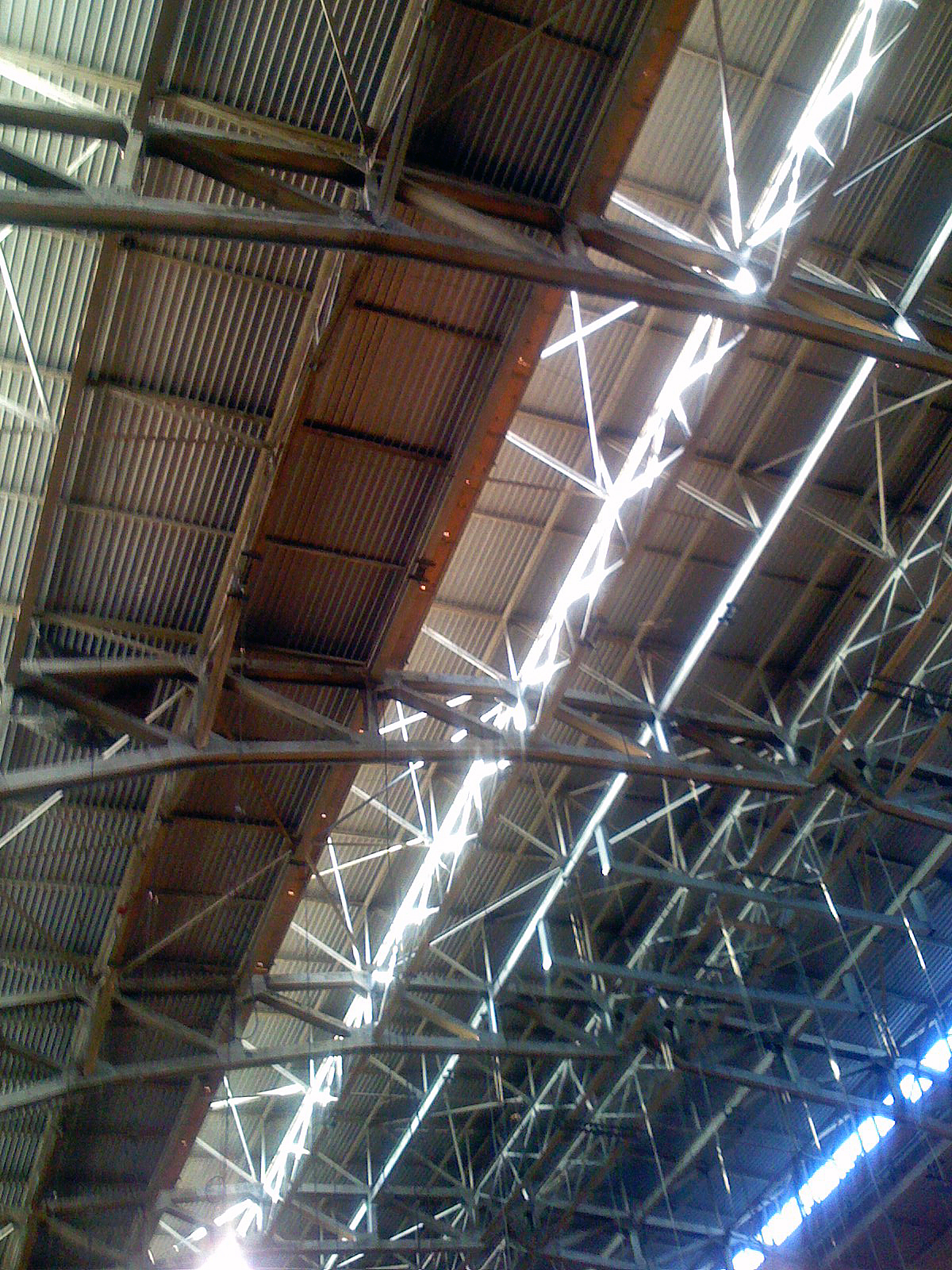
Longerons
In engineering, a longeron or stringer is a load-bearing component of a framework. The term is commonly used in connection with aircraft fuselages and automobile chassis. Longerons are used in conjunction with stringers to form structural frameworks. Aircraft In an aircraft fuselage, stringers are attached to formers (also called frames) and run in the longitudinal direction of the aircraft. They are primarily responsible for transferring the aerodynamic loads acting on the skin onto the frames and formers. In the wings or horizontal stabilizer, longerons run spanwise (from wing root to wing tip) and attach between the ribs. The primary function here also is to transfer the bending loads acting on the wings onto the ribs and spar. The terms "longeron" and "stringer" are sometimes used interchangeably. Historically, though, there is a subtle difference between the two terms. If the longitudinal members in a fuselage are few in number (usually 4 to 8) and run all along the fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girder
A girder () is a Beam (structure), beam used in construction. It is the main horizontal support of a structure which supports smaller beams. Girders often have an I-beam cross section composed of two load-bearing ''flanges'' separated by a stabilizing ''web'', but may also have a box girder, box shape, Z shape, or other forms. Girders are commonly used to build bridges. A girt is a vertically aligned girder placed to resist shear loads. Small steel girders are Rolling (metalworking), rolled into shape. Larger girders (1 m/3 feet deep or more) are made as plate girders, welded or bolted together from separate pieces of steel plate. The Warren truss, Warren type girder replaces the solid web with an open latticework truss between the flanges. This arrangement combines strength with economy of materials, minimizing weight and thereby reducing loads and expense. Patented in 1848 by its designers James Warren (engineer), James Warren and Willoughby Theobald Monzani, its st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
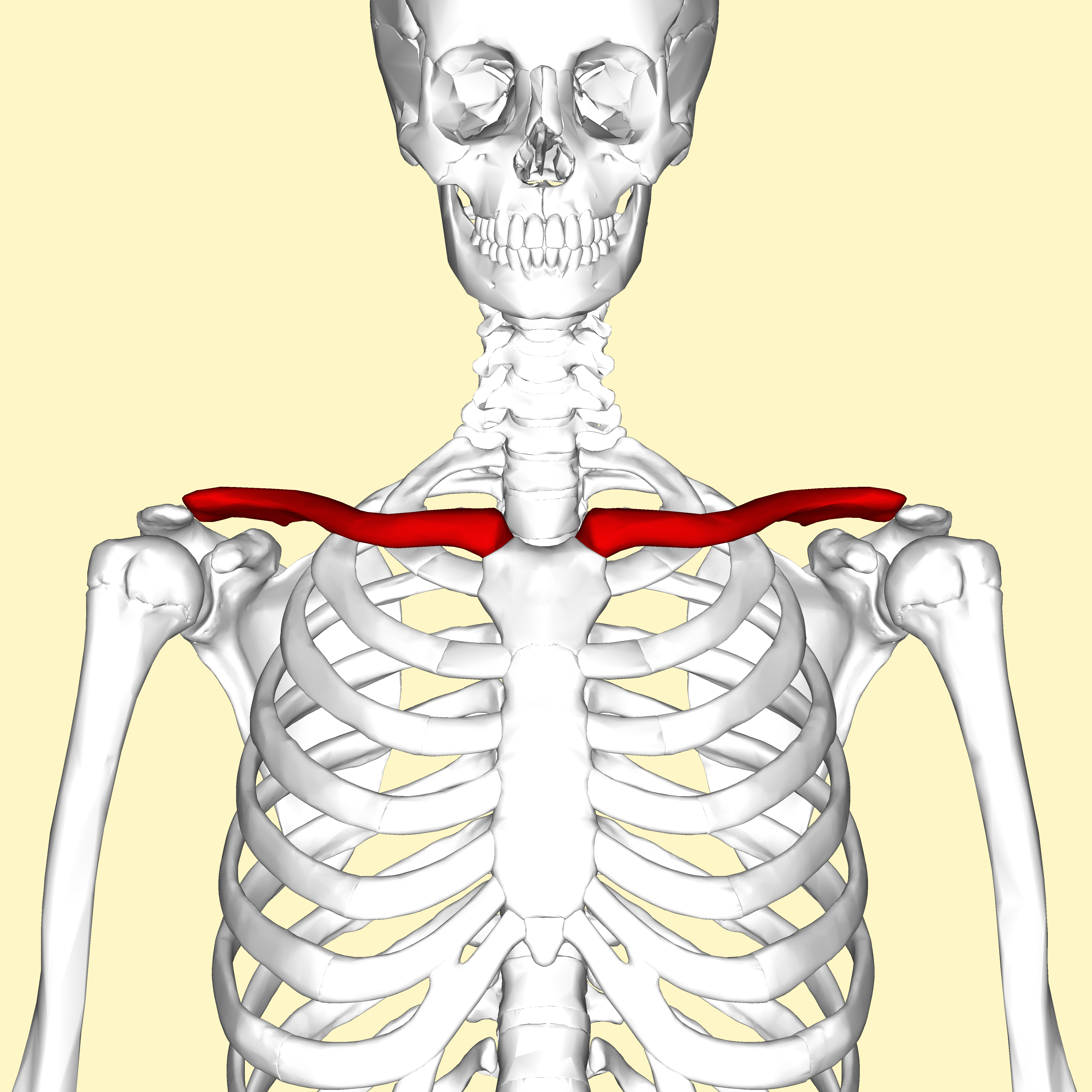
Strut
A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension. A stay is sometimes used as a synonym for strut, but some sources distinguish that struts are braces for holding compressive forces apart, while stays are braces for keeping stretching forces together. Human anatomy Part of the functionality of the clavicle is to serve as a strut between the scapula and sternum, resisting forces that would otherwise bring the upper limb close to the thorax. Keeping the upper limb away from the thorax is vital for its range of motion. Complete lack of clavicles may be seen in cleidocranial dysostosis, and the abnormal proximity of the shoulders to the median plane in cases of this genetic condition exemplifies the clavicle's importance as a strut. Architecture and construction Strut is a common name in timber framing for a support or brace of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |