|
Leslie R. Groves
Leslie Richard Groves Jr. (17 August 1896 – 13 July 1970) was a United States Army Corps of Engineers officer who oversaw the construction of the Pentagon and directed the Manhattan Project, a top secret research project that developed the atomic bomb during World War II. The son of a U.S. Army chaplain, Groves lived at various Army posts during his childhood. In 1918, he graduated fourth in his class at the United States Military Academy at West Point and was commissioned into the United States Army Corps of Engineers. In 1929, he went to Nicaragua as part of an expedition to conduct a survey for the Inter-Oceanic Nicaragua Canal. Following the 1931 Nicaraguan earthquake, Groves took over Managua's water supply system, for which he was awarded the Nicaraguan Presidential Medal of Merit. He attended the Command and General Staff School at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, in 1935 and 1936, and the Army War College in 1938 and 1939, after which he was posted to the War Departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albany, New York
Albany ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It is located on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River. Albany is the oldest city in New York, and the county seat of and most populous city in Albany County, New York, Albany County. Albany's population was 99,224 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census and estimated at 101,228 in 2023. The city is the economic and cultural core of New York State's Capital District (New York), Capital District, a metropolitan area including the nearby cities and suburbs of Colonie, New York, Colonie, Troy, New York, Troy, Schenectady, New York, Schenectady, and Saratoga Springs, New York, Saratoga Springs. With a population of 1.23 million in 2020, the Capital District is the third-most populous metropolitan region in the state. The Hudson River area was originally inhabited by Algonquian languages, Algonquian-speaking Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, B.S., B.Sc., SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree that is awarded for programs that generally last three to five years. The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of London in 1860. In the United States, the Lawrence Scientific School first conferred the degree in 1851, followed by the University of Michigan in 1855. Nathaniel Shaler, who was Harvard's Dean of Sciences, wrote in a private letter that "the degree of Bachelor of Science came to be introduced into our system through the influence of Louis Agassiz, who had much to do in shaping the plans of this School." Whether Bachelor of Science or Bachelor of Arts degrees are awarded in particular subjects varies between universities. For example, an economics student may graduate as a Bachelor of Arts in one university but as a Bachelor of Science in another, and occasionally, both options are offered. Some universities follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of War
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, also bearing responsibility for naval affairs until the establishment of the United States Department of the Navy, Navy Department in 1798, and for most land-based air forces until the creation of the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force on September 18, 1947. The United States Secretary of War, secretary of war, a civilian with such responsibilities as finance and purchases and a minor role in directing military affairs, headed the War Department throughout its existence. The War Department existed for 158 years, from August 7, 1789, to September 18, 1947, when it split into the United States Department of the Army, Department of the Army and the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army War College
The United States Army War College (USAWC) is a U.S. Army staff college in Carlisle Barracks, Pennsylvania, with a Carlisle postal address, on the 500-acre (2 km2) campus of the historic Carlisle Barracks. It provides graduate-level instruction to senior military officers, government officials, and civilians to prepare them for senior leadership assignments and responsibilities. Each year, a number of Army colonels and lieutenant colonels are considered by a board for admission. Approximately 800 students attend at any one time, half in a two-year-long distance learning program, and the other half in an on-campus, full-time resident program lasting ten months. Upon completion, the college grants its graduates a master's degree in Strategic Studies. The Army War College is a split-functional institution. Emphasis is placed on research and students are also instructed in leadership, strategy, and joint-service/international operations. It is one of the senior service colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., and the oldest permanent settlement in Kansas. Fort Leavenworth has been historically known as the "Intellectual Center of the Army." During the country's Territorial evolution of the United States, westward expansion, Fort Leavenworth was a forward destination for thousands of soldiers, surveyors, immigrants, Native Americans in the United States, American Indians, preachers and settlers who passed through. Today, the garrison supports the United States Army Training and Doctrine Command, US Army Training and Doctrine Command (TRADOC) by managing and maintaining the home of the United States Army Combined Arms Center, US Army Combined Arms Center (CAC). CAC's mission involves leader development, collective training, and Army doctrine and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command And General Staff School
The United States Army Command and General Staff College (CGSC or, obsolete, USACGSC) at Fort Leavenworth, Kansas, is a graduate school for United States Army and sister service officers, interagency representatives, and international military officers. The college was established in 1881 by William Tecumseh Sherman as the School of Application for Infantry and Cavalry (later simply the Infantry and Cavalry School), a training school for infantry and cavalry officers. In 1907 it changed its title to the School of the Line. The curriculum expanded throughout World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War and continues to adapt to include lessons learned from current conflicts. In addition to the main campus at Fort Leavenworth, the college has satellite campuses at Fort Belvoir, Virginia; Fort Gregg-Adams (Virginia), Fort Gregg-Adams, Virginia; Fort Eisenhower, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia; and Redstone Arsenal, Alabama. The college also maintains a distance-lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Managua
Managua () is the capital city, capital and largest city of Nicaragua, and one of the List of largest cities in Central America, largest cities in Central America. Located on the shores of Lake Managua, the city had an estimated population of 1,055,247 as of 2020, and a population of 1,401,687 in its metropolitan area. The city also serves as the seat of Managua Department. Founded in 1819, Managua became the national capital in 1852. The city underwent a rapid expansion and urbanization between 1842 and 1930, leading it to become one of the most developed cities in Central America. Several earthquakes have affected the city's growth, especially the 1931 Nicaragua earthquake, 1931 earthquake and the 1972 Nicaragua earthquake, 1972 earthquake, but the city has been rebuilt several times. Today, the city is a major economic hub for both the country and Central America. Etymology There are two possible origins for the name "Managua". It may have originated from the term ''Mana-ahua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1931 Nicaragua Earthquake
The 1931 Nicaragua earthquake devastated Nicaragua's capital city of Managua on 31 March 1931. It had a moment magnitude of 6.1 and a maximum MSK intensity of VI (''Strong''). Between 1,000 and 2,450 people were killed. A major fire started and destroyed thousands of structures, burning into the next day. At least 45,000 were left homeless and losses of $35 million were recorded. Earthquake and aftermath The earthquake hit Managua at 10:10 or 10:19 AM on 31 March, and caused cracks to spread throughout the western side of the city. East Managua was largely untouched. The main quake's duration was around 5 to 6 seconds. The quake was largely centered in Managua. Granada, Nicaragua, was unaffected. The earthquake caused a large fire, which burned for five days, destroying 33 blocks in "the richest and most important area of the city". Around of the city were seriously damaged and a further saw "minor damage". All major government buildings in the city except for the National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
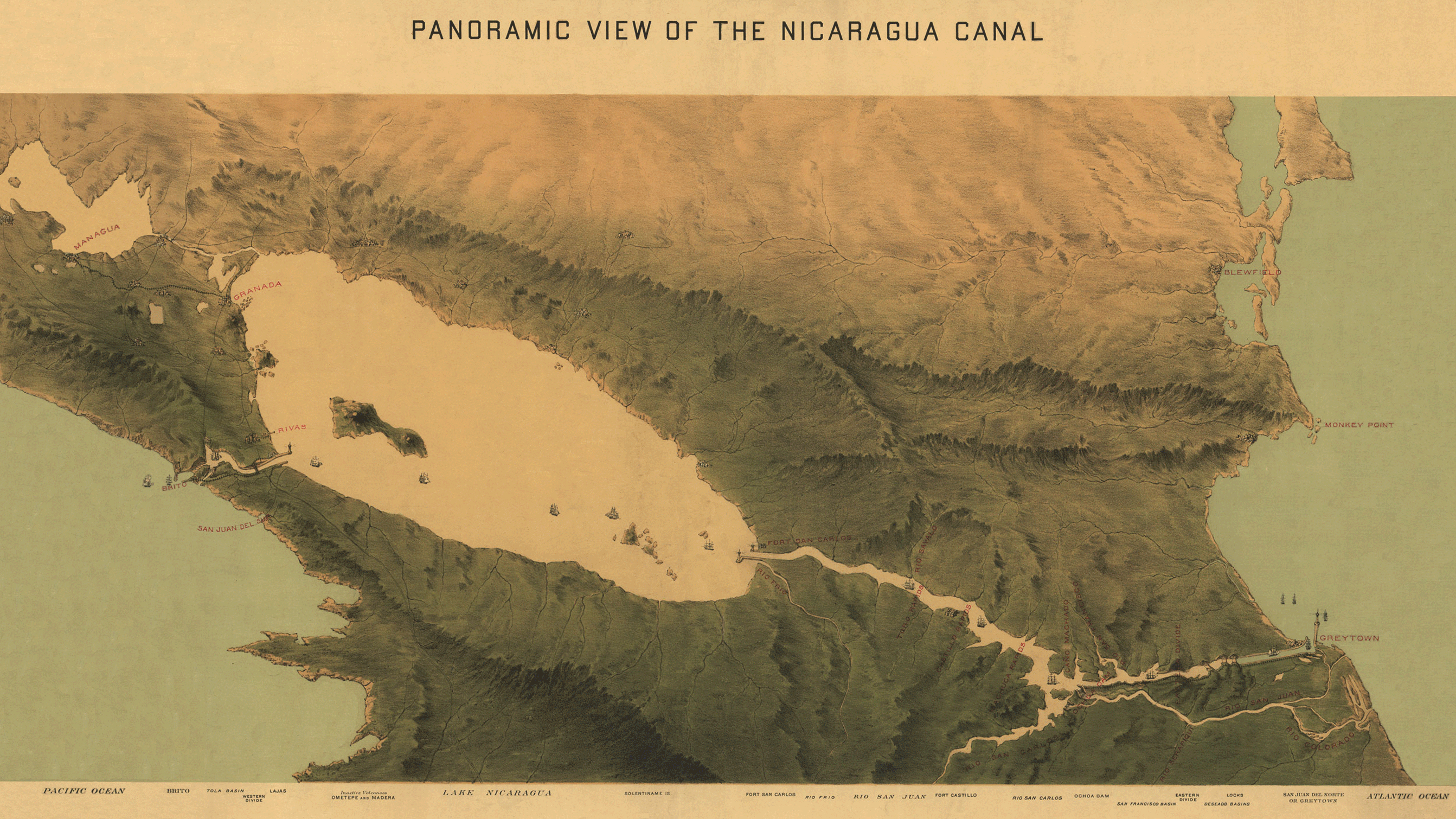
Inter-Oceanic Nicaragua Canal
Attempts to build a canal across Nicaragua to connect the Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ... with the Pacific Ocean stretch back to the early colonial era. Construction of such a shipping route—using the San Juan River (Nicaragua), San Juan River as an access route to Lake Nicaragua—was first proposed then. Napoleon III wrote an article about its feasibility in the middle of the 19th century. The History of the United States (1865–1918), United States abandoned plans to construct a waterway in Nicaragua in the early 20th century after it purchased the French interests in the Panama Canal, which has served as the main connecting route across Central America since its completion. Because the steady increase in world shipping may make it an econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America after Guatemala and Honduras. Nicaragua is bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean and shares maritime borders with El Salvador to the west and Colombia to the east. The country's largest city and national capital is Managua, the List of largest cities in Central America#Largest cities proper, fourth-largest city in Central America, with a population of 1,055,247 as of 2020. Nicaragua is known as "the breadbasket of Central America" due to having the most fertile soil and arable land in all of Central America. Nicaragua's multiethnic population includes people of mestizo, indigenous, European, and African heritage. The country's most spoken language is Spanish language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Point, New York
West Point is the oldest continuously occupied military post in the United States. Located on the Hudson River in New York (state), New York, General George Washington stationed his headquarters in West Point in the summer and fall of 1779 during the American Revolutionary War, and later called it "the most important Post in America" in 1781 following the war's end. West Point also was the site of General Benedict Arnold's failed attempt at treason during the Revolutionary War. West Point was first occupied by the United States Armed Forces in January 1778 by Brigadier General Samuel Holden Parsons. Since, West Point has been occupied by the United States Army. It comprises land and water including the campus of the United States Military Academy, which is commonly referred to as "West Point". West Point is a census-designated place (CDP) located in the town of Highlands, New York, Highlands in Orange County, New York, Orange County, located on the western bank of the Hudson Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaplain Corps (United States Army)
The United States Army Chaplain Corps (USACC) consists of ordained clergy of multiple faiths who are commissioned officer, commissioned Army officers serving as military chaplains as well as Enlisted rank, enlisted soldiers who serve as assistants. Their purpose is to offer religious church services, counseling, and moral support to the armed forces, whether in peacetime or at war. U.S. Army Institute for Religious Leadership See footnotes The U.S. Army Institute for Religious Leadership (USAIRL) is part of the Armed Forces Chaplaincy Center (AFCC), which also includes the Air Force Chaplain Service Institute (AFCSI) and the United States Navy Chaplain Corps#Naval Chaplaincy School and Center, U.S. Naval Chaplaincy School and Center (NCSC). The three schools are co-located at Fort Jackson (South Carolina), Fort Jackson, in Columbia, S.C. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |