|
Lepidosauromorph
Lepidosauromorpha (in PhyloCode known as Pan-Lepidosauria) is a group of reptiles comprising all diapsids closer to lizards than to archosaurs (which include crocodiles and birds). The only living sub-group is the Lepidosauria, which contains two subdivisions, Squamata, which contains lizards and snakes, and Rhynchocephalia, the only extant species of which is the tuatara. Lepidosauromorphs are distinguishable from archosauromorphs (reptiles closer to archosaurs) by their primitive sprawling gait (allowing for the same sinusoidal trunk and tail movement seen in fish), the sliding "joint" between the coracoids and the sternum (for a longer stride), and their pleurodont dentition. In contrast, Archosauromorphs possess a parasagittal gait, a reduction in their dermal girdle, a reduction and/or loss of the sternum, and a more thecodont dentition. Living lepidosauromorphs have retained an ectothermic (" cold blooded") metabolism, unlike the ancestral condition in archosauromorphs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
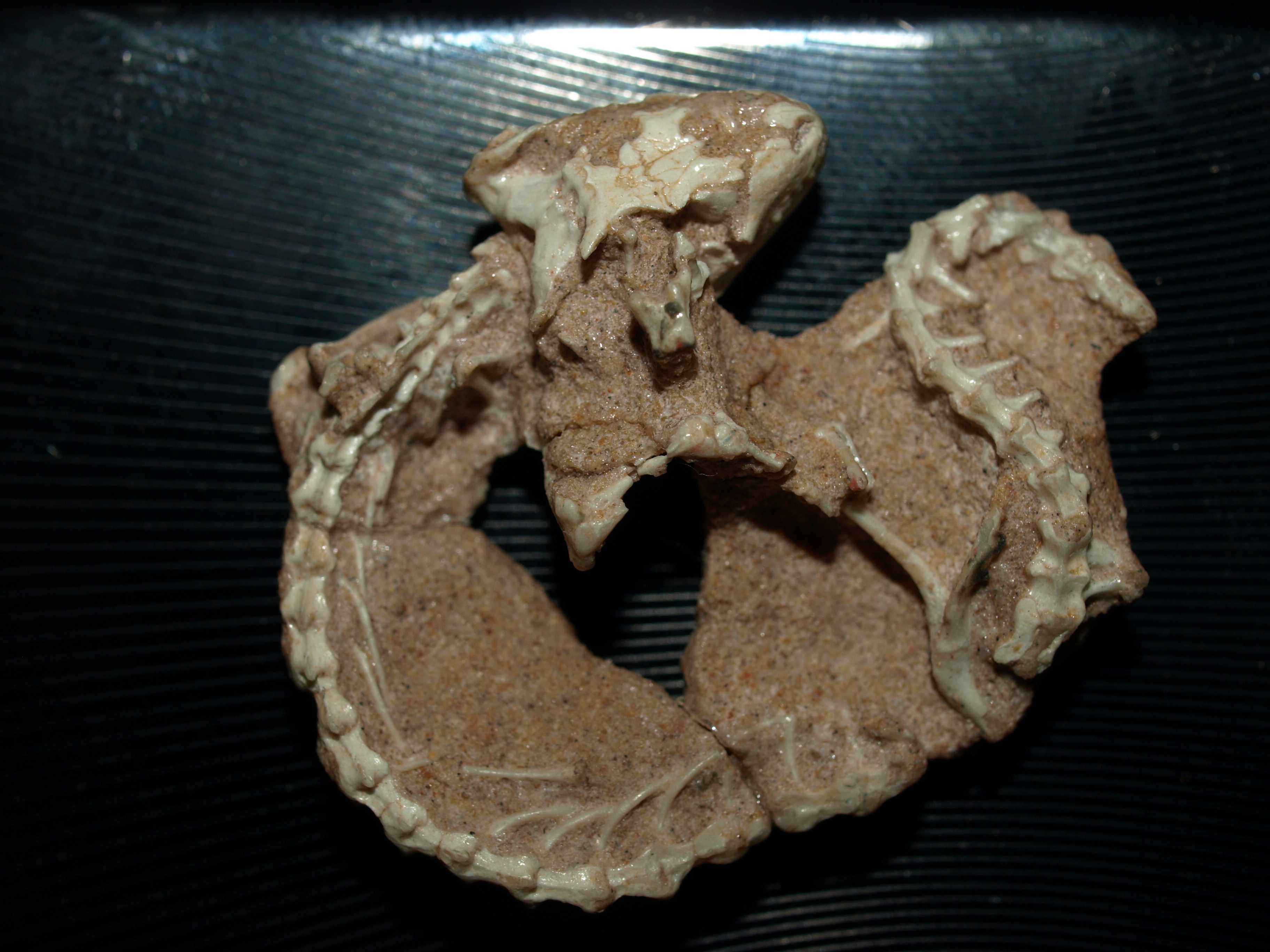
Sophineta Cracoviensis
''Sophineta'' is an extinct genus of basal lepidosauromorph reptile known from the Early Triassic (late Olenekian age) of Małopolska Province, southern Poland. It contains a single species, ''Sophineta cracoviensis''. Discovery ''Sophineta'' was first described and named by Susan E. Evans and Magdalena Borsuk−Białynicka in 2009, and the type species is ''Sophineta cracoviensis''. It is known from holotype ZPAL RV/175, a nearly complete right maxilla. Many isolated or associated skull and postcranial fragments are referred to the species, representing frontals, parietals, prefrontal, postfrontals, postorbitals, jugals, squamosals, pterygoids, quadrates, maxillae, premaxilla, dentaries, vertebrae and ilia. ''Sophineta'' fossils were discovered ''in situ'' and collected in 1982 by a team (Paszkowski and Wieczorek) from the Institute of Geological Sciences of Jagiellonian University in Kraków. They were collected from the Czatkowice 1 locality, a single exposure near K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidosauria
The Lepidosauria (, from Greek meaning ''scaled lizards'') is a Order (biology), superorder or Class (biology), subclass of reptiles, containing the orders Squamata and Rhynchocephalia. Squamata also includes Lizard, lizards and Snake, snakes. Squamata contains over 9,000 species, making it by far the most species-rich and diverse order of non-avian reptiles in the present day. Rhynchocephalia was a formerly widespread and diverse group of reptiles in the Mesozoic era, Mesozoic Era. However, it is represented by only one living species: the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus),'' a superficially lizard-like reptile native to New Zealand. Lepidosauria is a monophyletic group (i.e. a clade), containing all descendants of the Most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor of squamates and rhynchocephalians. Lepidosaurs can be distinguished from other reptiles via several traits, such as large Keratin, keratinous Scale (anatomy), scales which may overlap one another. Purely in the conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchocephalia
Rhynchocephalia (; ) is an order of lizard-like reptiles that includes only one living species, the tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') of New Zealand. Despite its current lack of diversity, during the Mesozoic rhynchocephalians were a speciose group with high morphological and ecological diversity. The oldest record of the group is dated to the Middle Triassic around 238 to 240 million years ago, and they had achieved global distribution by the Early Jurassic. Most rhynchocephalians belong to the group Sphenodontia ('wedge-teeth'). Their closest living relatives are lizards and snakes in the order Squamata, with the two orders being grouped together in the superorder Lepidosauria. Rhynchocephalians are distinguished from squamates by a number of traits, including the retention of rib-like gastralia bones in the belly, as well as most rhynchocephalians having acrodont teeth that are fused to the crests of the jaws (the latter also found among a small number of modern lizard grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha ( Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including '' Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and '' Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Trias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest Order (biology), order of reptiles; most members of which are commonly known as Lizard, lizards, with the group also including Snake, snakes. With over 11,991 species, it is also the second-largest order of Neontology, extant (living) vertebrates, after the Perciformes, perciform fish. Squamates are distinguished by their skins, which bear horny scale (zoology), scales or shields, and must periodically engage in molting. They also possess movable quadrate bones, making possible movement of the Maxilla, upper jaw relative to the neurocranium. This is particularly visible in snakes, which are able to open their mouths very widely to accommodate comparatively large prey. Squamates are the most variably sized living reptiles, ranging from the Sphaerodactylus ariasae, dwarf gecko (''Sphaerodactylus ariasae'') to the reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus''). The now-Extinction, extinct mosasaurs reached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lizards
Lizard is the common name used for all squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The grouping is paraphyletic as some lizards are more closely related to snakes than they are to other lizards. Lizards range in size from chameleons and geckos a few centimeters long to the 3-meter-long Komodo dragon. Most lizards are quadrupedal, running with a strong side-to-side motion. Some lineages (known as "legless lizards") have secondarily lost their legs, and have long snake-like bodies. Some lizards, such as the forest-dwelling '' Draco'', are able to glide. They are often territorial, the males fighting off other males and signalling, often with bright colours, to attract mates and to intimidate rivals. Lizards are mainly carnivorous, often being sit-and-wait predators; many smaller species eat insects, while the Komodo eats ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads ( cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Locomotion
Terrestrial locomotion has evolution, evolved as animals adapted from ecoregion#Marine, aquatic to ecoregion#Terrestrial, terrestrial environments. Animal locomotion, Locomotion on land raises different problems than that in water, with reduced friction being replaced by the increased effects of gravity. As viewed from evolutionary taxonomy, there are three basic forms of animal locomotion in the terrestrial environment: *#Legged locomotion, legged – moving by using appendages *#Limbless locomotion, limbless locomotion – moving without legs, primarily using the body itself as a propulsive structure. *#Rolling, rolling – rotating the body over the substrate Some terrains and land cover, terrestrial surfaces permit or demand alternative locomotive styles. A sliding component to locomotion becomes possible on slippery surfaces (such as ice and snow), where locomotion is aided by potential energy, or on loose surfaces (such as sand or scree), where friction is low but purchase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuatara
The tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') is a species of reptile endemic to New Zealand. Despite its close resemblance to lizards, it is actually the only extant member of a distinct lineage, the previously highly diverse order Rhynchocephalia. The name is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order, which was highly diverse during the Mesozoic era. Rhynchocephalians first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic, around 240 million years ago, and reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic, when they represented the world's dominant group of small reptiles. Rhynchocephalians declined during the Cretaceous, with their youngest records outside New Zealand dating to the Paleocene. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). Tuatara are of interest for studying the evolution of reptiles. Tuatara are greenish brown an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
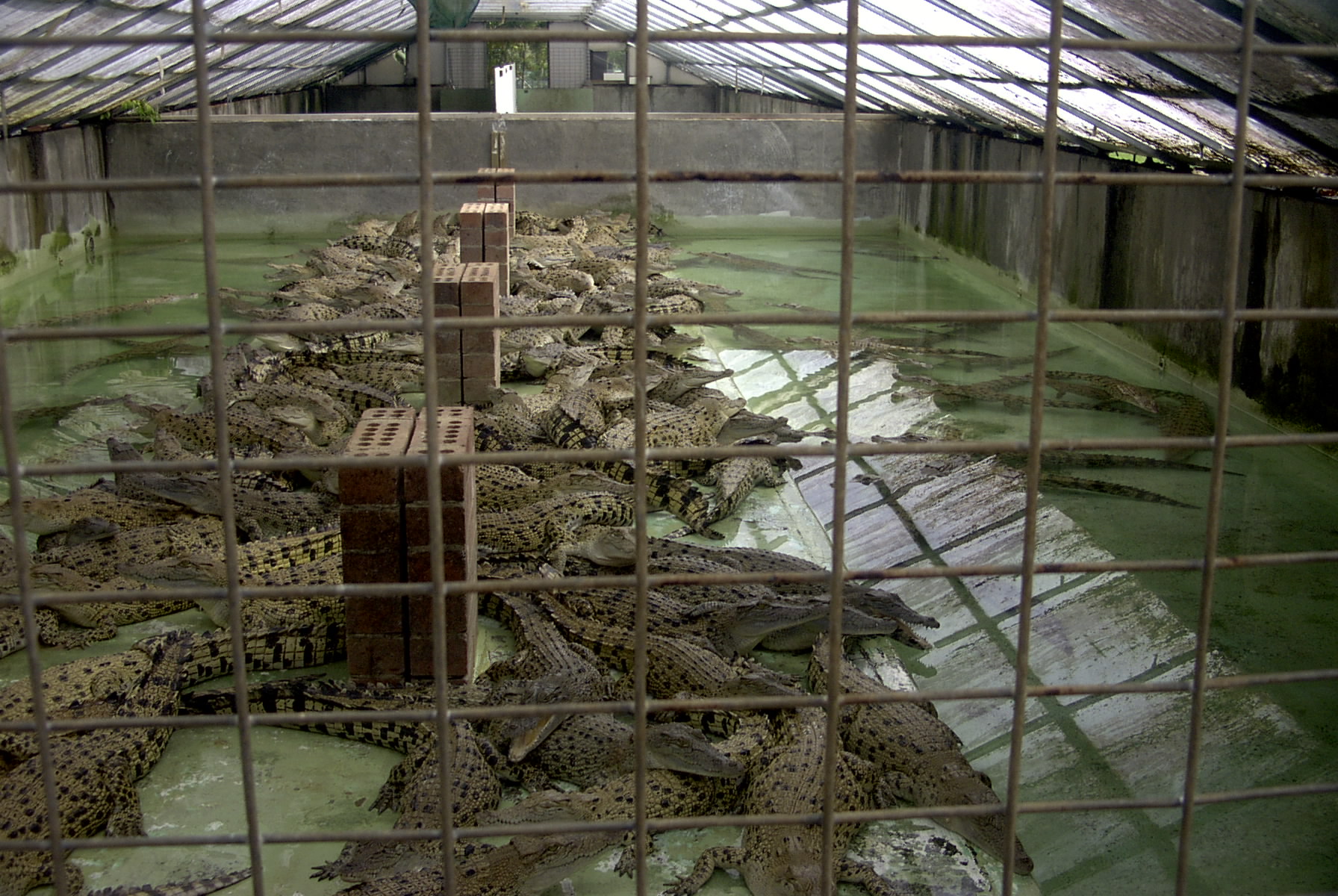
Crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include all extant taxon, extant members of the order (biology), order Crocodilia, which includes the alligators and caimans (both members of the family Alligatoridae), the gharial and false gharial (both members of the family Gavialidae) as well as other extinct Taxon, taxa. Crocodile Measurement, size, Morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour and ecology differ among species. However, they have many similarities in these areas as well. All crocodiles are semiaquatic and tend to congregate in freshwater habitats such as rivers, lakes, wetlands and sometimes in brackish water and Seawater, saltwater. They are carnivorous animals, feeding mostly on vertebrates such as fish, reptiles, birds and mammals, and sometimes on invertebrates such as mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |