|
Leopold McClintock
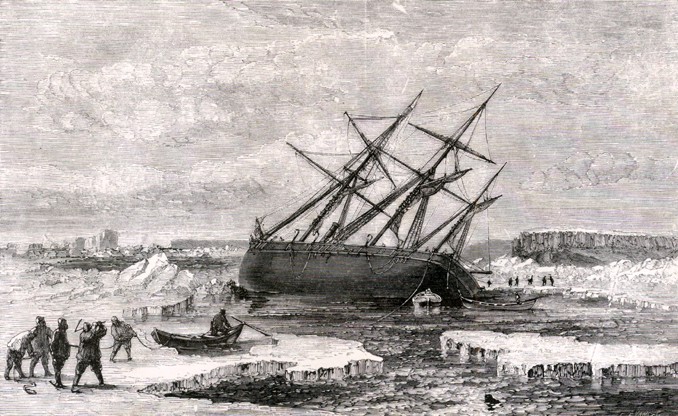
Sir Francis Leopold McClintock (8 July 1819 – 17 November 1907) was an Irish explorer in the British Royal Navy, known for his discoveries in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. He confirmed explorer John Rae (explorer), John Rae's controversial report gathered from Inuit sources on the fate of Franklin's lost expedition, the ill-fated Royal Navy undertaking commanded by Sir John Franklin in 1845 attempting to be the first to traverse the Northwest Passage. McClintock's report was received more favorably than that of Rae, who was shunned and denied recognition for having discovered the lost expedition's fate. Rae's report ultimately guided McClintock to the correct area to conduct a search. McClintock also stirred controversy with his claim that Franklin, before his death, had essentially discovered the Northwest Passage, while in reality he had not. Rae, with his discovery of Rae Strait, had discovered the real ice-free passage through North America's Arctic archipelago. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America And West Indies Station
The North America and West Indies Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed in North American waters from 1745 to 1956, with main bases at the Imperial fortresses of Bermuda and Halifax, Nova Scotia. The North American Station absorbed the separate Newfoundland Station in 1825 (becoming the North America and Newfoundland Station), and the Jamaica Station in 1830, to form the North America and West Indies Station. It was briefly abolished in 1907 before being restored in 1915. It was renamed the America and West Indies Station in 1926, absorbing what had been the South East Coast of America Station and the Pacific Station. It was commanded by Commanders-in-Chief whose titles changed with the changing of the formation's name, eventually by the Commander-in-Chief, America and West Indies Station. History The squadron was formed in 1745 to counter French forces in North America, with the headquarters at the Halifax Naval Yard in Nova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, which is, by itself, much larger than the combined area of the archipelago) and Iceland (an independent country). Situated in the northern extremity of North America and covering about , this group of 36,563 islands, surrounded by the Arctic Ocean, comprises much of Northern Canada, predominately Nunavut and the Northwest Territories. The archipelago is showing some effects of climate change, with some computer estimates determining that melting there will contribute to the rise in sea levels by 2100. History Around 2500 BCE, the first humans, the Paleo-Eskimos, arrived in the archipelago from the Canadian mainland. Between 1000 and 1500 CE, they were replaced by the Thule people, who are the ancestors of today's Inuit. British claims on the islands, the British A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is the point in the Southern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True South Pole to distinguish from the south magnetic pole. The South Pole is by definition the southernmost point on the Earth, lying antipode (geography), antipodally to the North Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° South, as well as the direction of true south. At the South Pole all directions point North; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the South Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, clockwise is east and counterclockwise is west. The South Pole is at the center of the Southern Hemisphere. Situated on the continent of Antarctica, it is the site of the United States Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station, which was established in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Falcon Scott
Captain Robert Falcon Scott (6 June 1868 – ) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer who led two expeditions to the Antarctic regions: the Discovery Expedition, ''Discovery'' expedition of 1901–04 and the Terra Nova Expedition, ''Terra Nova'' expedition of 1910–13. On the first expedition, he set a new southern record by marching to latitude 82°S and discovered the Antarctic Plateau, on which the South Pole is located. On the second venture, Scott led a party of five which reached the South Pole on 17 January 1912, less than five weeks after Amundsen's South Pole expedition. On the return journey from the Pole, a planned meeting with supporting dog teams from the base camp failed, despite Scott's written instructions, and at a distance of from their base camp at Hut Point and approximately from the next depot, Scott and his companions died. When Scott and his party's bodies were discovered, they had in their possession the first Antarctic fossils discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhauling
Manhauling or man-hauling is the pulling forward of sledges, trucks or other load-carrying vehicles by human power unaided by animals (e.g. huskies) or machines. The term is used primarily in connection with travel over snow and ice, and was common during Arctic and Antarctic expeditions before the days of modern motorised traction. In the years following the end of the Napoleonic wars the British Royal Navy took up polar/cold climate exploration as its chief peacetime activity. Due to its simplicity, manhauling was adopted by the early British naval expeditions, where it quickly became the preferred or even the 'traditional' technique. In time it would be hailed as inherently more noble than the sole use of dogs as practised by the native Arctic-dwelling peoples. The technique's chief advocate was Sir Clements Markham, President of the Royal Geographical Society during the latter part of the 19th century. A figure of considerable influence, he brought his prejudices to bear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Leopold McClintock's Sledge Flag (1850–1851)
Francis may refer to: People and characters *Pope Francis, head of the Catholic Church (2013–2025) *Francis (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters *Francis (surname) * Francis, a character played by YouTuber Boogie2988 Places * Rural Municipality of Francis No. 127, Saskatchewan, Canada * Francis, Saskatchewan, Canada ** Francis (electoral district) * Francis, Nebraska, USA * Francis Township, Holt County, Nebraska, USA * Francis, Oklahoma, USA *Francis, Utah, USA Arts, entertainment, media * ''Francis'' (film), the first of a series of comedies featuring Francis the Talking Mule, voiced by Chill Wills *''Francis'', a 1983 play by Julian Mitchell * Francis (band), a Sweden-based folk band *Francis (TV series), a Indian Bengali-language animated television series Other uses *FRANCIS, a bibliographic database * ''Francis'' (1793), a colonial schooner in Australia *Francis turbine, a type of water turbine See also *Saint Francis (other) * Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montevideo
Montevideo (, ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2023 census, the city proper has a population of 1,302,954 (about 37.2% of the country's total population) in an area of . Montevideo is situated on the southern coast of the country, on the northeastern bank of the Río de la Plata. A Portuguese garrison was established in the place where today is the city of Montevideo in November 1723. The Portuguese garrison was expelled in February 1724 by a Spanish soldier, Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, as a strategic move amidst the Spanish people, Spanish-Portuguese people, Portuguese dispute over the Río de la Plata Basin, platine region. There is no official document establishing the foundation of the city, but the "Diario" of Bruno Mauricio de Zabala officially mentions the date of 24 December 1726 as the foundation, corroborated by presential witnesses. The complete independence from Buenos Aires as a real city was not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drumcar House
Drumcar House (later: St. Mary's Hospital; currently: Saint John of God Residence) is a manor house in the historical parish of Drumcar in the barony of Ardee, northeast of Dunleer, County Louth, Leinster, Ireland. The house was built in 1777. It was home to the McClintock family from then to the 1940s, stemming from Alexander McClintock (1692–1775). One of its best known owners was John McClintock (1770–1855), John McClintock (1770–1855), a magistrate for County Louth, and formerly Serjeant at Arms in the Irish House of Commons, who was known to be occupying the estate in 1805 and until his death. The house was sold in about 1903 by The 2nd Baron Rathdonnell to his cousin, Frank McClintock (1853–1924), Rector of Drumcar and Dean of Armagh. In 1948, it became St. Mary's Hospital, a colony for the mentally ill. Still later, it was converted to Saint John of God Residence, a hospital/infirmary. The building is now registered with the National Inventory of Architectural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John McClintock (1770–1855)
John McClintock (14 August 1770 – 12 July 1855) was an Irish magistrate for County Louth, and formerly Serjeant at Arms in the Irish House of Commons. Early years He was the eldest son of John 'Bumper Jack' McClintock, MP for Enniskillen and Belturbet in the Irish House of Commons who commissioned the building of this mansion at Drumcar House near Drumcar, northeast of Dunleer in 1777. His mother was Patience, daughter of William Foster, esq. M.P. for the Co. Louth, and first-cousin to John Foster, 1st Baron Oriel. His paternal grandfather was Alexander McClintock (died May 1775). In 1787, John McClintock enrolled at Trinity College Dublin, studying for three and a half years before attaining his degree of Bachelor of Arts. Career Though he had intended becoming a lawyer, McClintock was granted the office of Serjeant at Arms to the Irish House of Commons in 1794, aged 21, in conjunction with his younger brother, William Foster McClintock (died 1839). McClintock wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rae Strait
Rae Strait is a small strait in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located between King William Island and the Boothia Peninsula on the mainland to the east. It is named after Scottish Arctic explorer John Rae (explorer), John Rae who, in 1854, was the first European to visit the area while mapping the northern coast of North America. At the time, King William Island was called King William Land, since it was thought to be adjoined to Boothia. On May 6, 1854, Rae and his two travelling companions reached a promontory on the western coast of Boothia which allowed them to look far west, at which point they realized King William Island was separated from the mainland. Said island protects the strait from the excessive flow of Drift ice, pack ice from the north, making its waters navigable for 19th-century ships. This proved to be of vital importance for the eventual completion of the Northwest Passage by Roald Amundsen in 1903–06, since the Norwegian sailed through Rae S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters. For centuries, European explorers, beginning with Christopher Columbus in 1492, sought a navigable passage as a possible trade route to Asia, but were blocked by North, Central, and South America; by ice, or by rough waters (e.g. Tierra del Fuego). An ice-bound northern route was discovered in 1850 by the Irish explorer Robert McClure, whose expedition completed the passage by hauling sledges. Scotsman John Rae (explorer), John Rae explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Franklin
Sir John Franklin (16 April 1786 – 11 June 1847) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer and colonial administrator. After serving in the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812, he led two expeditions into the Northern Canada, Canadian Arctic and through the islands of the Arctic Archipelago, during the Coppermine expedition of 1819 and the Mackenzie River expedition of 1825, and served as Governor of Tasmania, Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen's Land from 1837 to 1843. During Franklin's lost expedition, his third and final expedition, an attempt to traverse the Northwest Passage in 1845, Franklin's ships became icebound off King William Island in what is now Nunavut, where he died in June 1847. The icebound ships were abandoned ten months later, and the entire crew died from causes such as starvation, hypothermia, and scurvy. Biography Early life Franklin was born in Spilsby, Lincolnshire, on , the ninth of twelve children born to Hannah Weekes and Willingham Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |