|
Leopardus Narinensis
''Leopardus narinensis'', also called the red tigrina, Nariño cat, and Galeras cat by the scientists who discovered it, is a putative species of small wild Felidae, cat in the genus ''Leopardus''. It was described in 2023, based on a single skin collected in 1989. Etymology The specific epithet ''narinensis'' refers to the Nariño Department in southern Colombia, where the skin was collected. The proposed common names "Nariño cat" and "Galeras cat" also refer to where it was found (the Galeras volcano in the Nariño Department), while "red tigrina" refers to its markedly reddish coloring. Taxonomy and phylogeny The skin was first collected in 1989 and donated to a Colombian national institute, which later transferred its biological collections to the Alexander von Humboldt Biological Resources Research Institute, where it remained classified as an ocelot skin until 2001, when Manuel Ruiz-García noticed it while searching for jaguar and puma specimens. He recognized it as being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany and mycology, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, generally pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same genetic individual. A holotype is not necessarily "ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
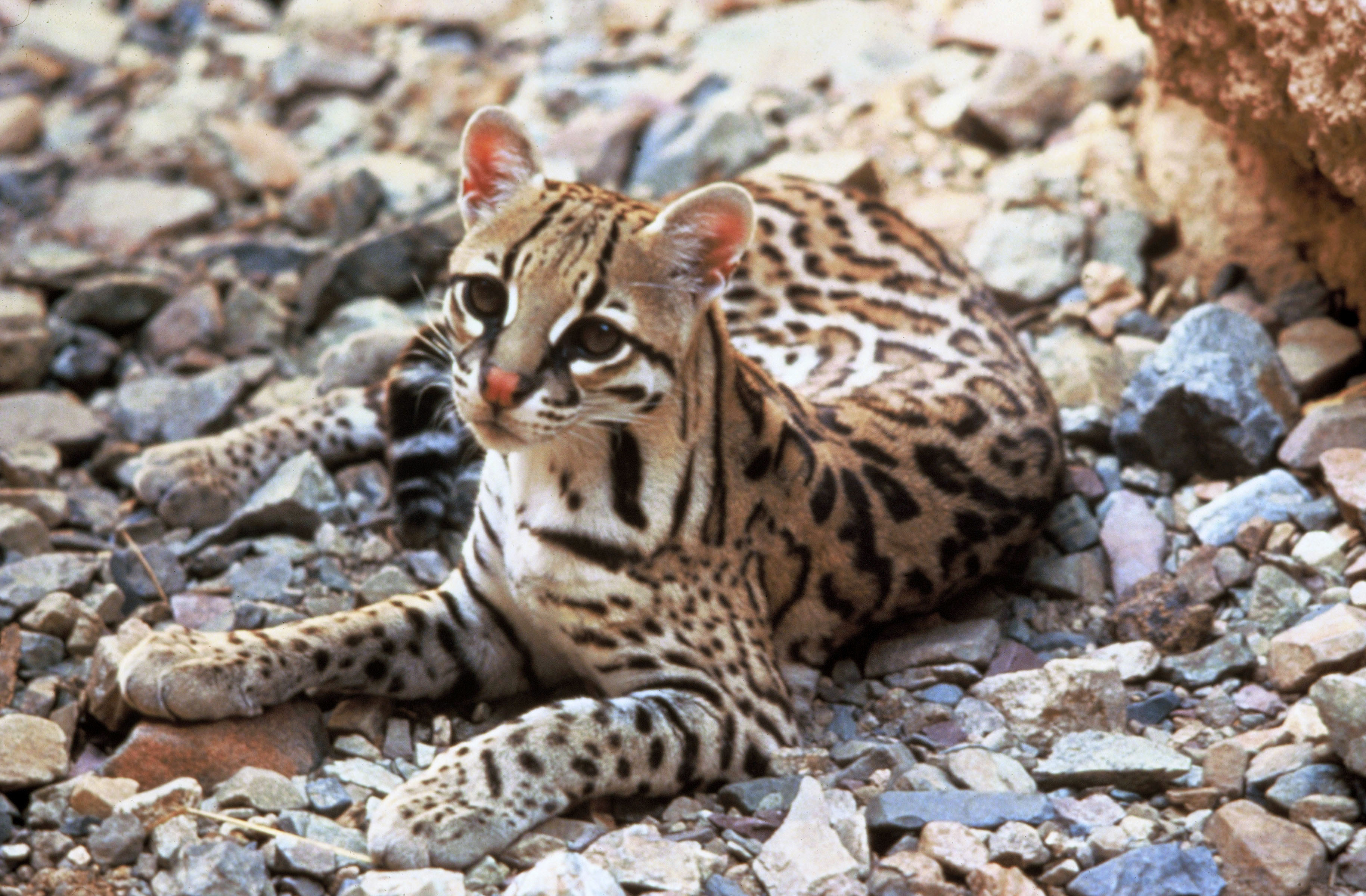
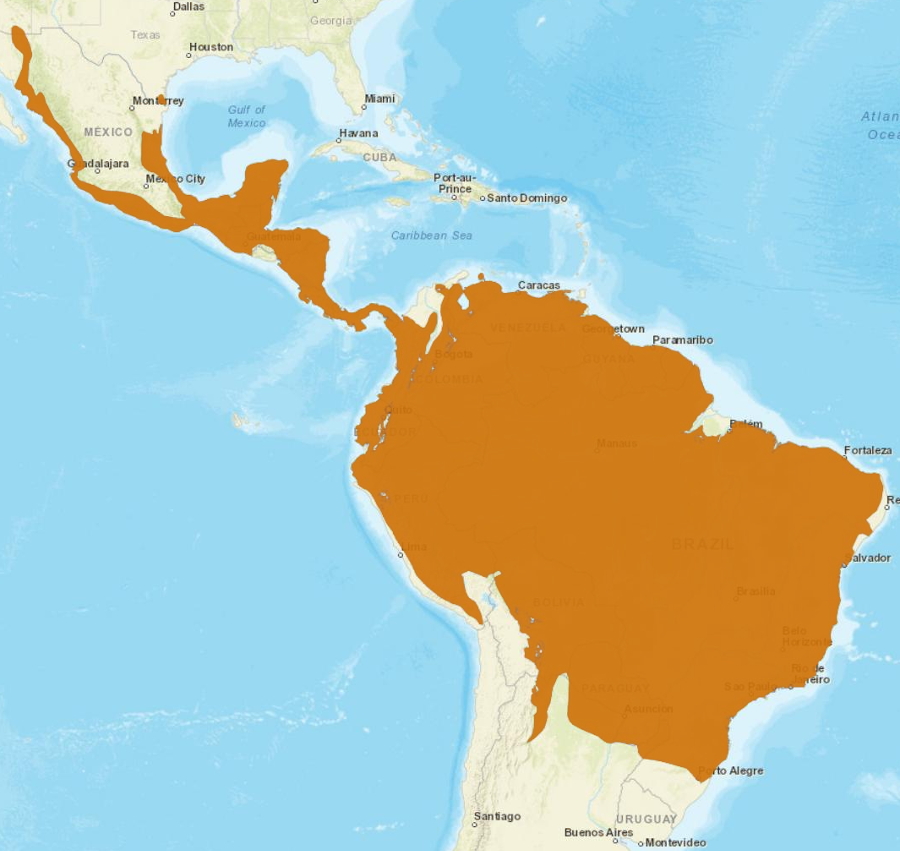
Leopardus Pardalis
The ocelot (''Leopardus pardalis'') is a medium-sized spotted Felidae, wild cat that reaches at the shoulders and weighs between on average. It is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, Central America, Central and South America, and the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Margarita Island, Margarita. Carl Linnaeus scientific description, scientifically described it in 1758. Two subspecies are recognized. The ocelot is efficient at climbing, leaping and swimming. It prefers areas close to water sources with dense vegetation cover and high prey availability. It preys on small terrestrial mammals, such as armadillos, opossums, and lagomorphs. It is typically active during twilight and at night and tends to be solitary and Territory (animal), territorial. Both sexes become sexual maturity, sexually mature at around two years of age and can breed throughout the year; peak mating season varies geographically. After a gestation period of two to three months, the female giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felids Of South America
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ). The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the greatest diversity in fur patterns of all terrestrial carnivores. Cats have retractile claws, slender muscular bodies and strong flexible forelimbs. Their teeth and facial muscles allow for a powerful bite. They are all obligate carnivores, and most are solitary predators ambushing or stalking their prey. Wild cats occur in Africa, Europe, Asia and the Americas. Some wild cat species are adapted to forest and savanna habitats, some to arid environments, and a few also to wetlands and mountainous terrain. Their activity patterns range from nocturnal and crepuscular to Diurnality, diurnal, depending on their preferred prey species. Reginald Innes Pocock divided the extant Felidae into three subfamilies: the Pantherinae, the Felinae and the Acin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold Glacial period, glacial periods and warmer Interglacial, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Páramo
Páramo () may refer to a variety of alpine tundra ecosystems located in the Andes Mountain Range, South America. Some ecologists describe the páramo broadly as "all high, tropical, montane vegetation above the continuous timberline". A narrower term classifies the páramo according to its regional placement in the northern Andes of South America and adjacent southern Central America. The páramo is the ecosystem of the regions above the continuous forest line, yet below the permanent snowline. It is a "Neotropical high mountain biome with a vegetation composed mainly of giant rosette plants, shrubs and grasses". According to scientists, páramos may be "evolution, evolutionary hot spots", meaning that they are among the fastest evolving regions on Earth. Location The Northern Andean Páramo global ecoregion includes the Cordillera Central páramo (Ecuador, Peru), Santa Marta páramo (Colombia), Cordillera de Merida páramo (Venezuela) and Northern Andean páramo (Colombia, Ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigrina (other) in science fiction fandom
{{Disambiguation ...
Tigrina may refer to: * several felines: ** '' Leopardus guttulus'', the southern tigrina ** '' Leopardus tigrinus'', the tigrina or oncilla ** ''Leopardus narinensis'', the red tigrina * "Tigrina", a pseudonym used by pioneering lesbian publisher Lisa Ben Edythe D. Eyde (November 7, 1921 – December 22, 2015) better known by her pen name Lisa Ben, was an American editor, author, active fantasy-fiction fan and fanzine contributor (often using the name Tigrina in these activities), and songwrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopardus Geoffroyi
''Leopardus'' is a genus comprising eight species of small cats native to the Americas. This genus is considered the oldest branch of a genetic lineage of small cats in the Americas whose common ancestor crossed the Bering land bridge from Asia to North America in the late Miocene. Characteristics ''Leopardus'' species have spotted fur, with ground colors ranging from pale buff, ochre, fulvous and tawny to light gray. Their small ears are rounded and white-spotted; their rhinarium is prominent and naked above, and their nostrils are widely separated. They have 36 chromosomes, whereas other felids have 38. Taxonomy The generic name ''Leopardus'' was proposed by John Edward Gray in 1842, when he described two spotted cat skins from Central America and two from India in the collection of the Natural History Museum, London. Several genera were proposed in the 19th and early 20th centuries for small spotted cats in the Americas, including: *''Dendrailurus'', ''Lynchailurus'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopardus Guigna
The kodkod (''Leopardus guigna''), also called güiña, is the smallest felid species native to the Americas. It lives primarily in central and southern Chile, as well as marginally in adjoining areas of Argentina. Since 2002, it has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List as the total population may be fewer than 10,000 mature individuals; it is threatened by persecution, and habitat loss and prey base. Characteristics The kodkod's fur color ranges from brownish-yellow to grey-brown. It has dark spots, a pale underside and a ringed tail. The ears are black with a white spot, while the dark spots on the shoulders and neck almost merge to form a series of dotted streaks. Melanistic kodkods with spotted black coats are quite common. It has a small head, large feet, and a thick tail. Adult kodkods are in head to body length with a short tail and a shoulder height of about . Weight ranges between . Melanistic phenotype The melanistic phenotype is caused by the deletion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopardus Jacobita
The Andean mountain cat (''Leopardus jacobita'') is a small wild cat native to the high Andes that has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List because fewer than 1,500 individuals are thought to exist in the wild. It is traditionally considered a sacred animal by indigenous Aymara and Quechua people. The Andean mountain cat was first described by Emilio Cornalia, who named it in honor of Jacobita Mantegazza. It is a monotypic species. Characteristics The Andean mountain cat has ashy-gray fur, a grey head, and rounded ears. The nose and lips are black, and the areas around them are white; two dark brown lines run from the corners of the eyes across the cheeks. There are black spots on the forelegs, yellowish-brown blotches on the flanks, and up to two narrow, dark rings on the hind limbs. The long, bushy tail has six to nine rings, which are dark brown to black. The markings of juveniles are darker and smaller than those of adults. The skulls of adult specimens range in le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopardus Tigrinus
The oncilla (''Leopardus tigrinus''), also known as the northern tiger cat, little spotted cat, and tigrillo, is a small spotted cat ranging from Central America to central Brazil. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, and the population is threatened by deforestation and conversion of habitat to agricultural land. In 2013, it was proposed to assign the oncilla populations in southern Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina to a new species: the southern tiger cat (''L. guttulus''), after it was found that it does not interbreed with the oncilla population in northeastern Brazil. Characteristics The oncilla resembles the margay (''L. wiedii'') and the ocelot (''L. pardalis''), but it is smaller, with a slender build and narrower muzzle. Oncillas are one of the smallest wild cats in South America, reaching a body length of with a long tail. While this is somewhat longer than the average domestic cat, the oncilla is generally lighter, weighing . The fur is thick and soft, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopardus Wiedii
The margay (''Leopardus wiedii'') is a small wild cat native to Mexico, Central and South America. A solitary and nocturnal felid, it lives mainly in primary evergreen and deciduous forest. Until the 1990s, margays were hunted for the wildlife trade, at which point the killing of the species was outlawed in most countries; however, years of persecution resulted in a notable population decrease. Since 2008, the margay has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, as the population is thought to be declining due to loss of habitat and deforestation. The scientific name ''Felis wiedii'' was used by Heinrich Rudolf Schinz in 1821 in his first scientific description of the margay, named in honour of Prince Maximilian of Wied-Neuwied, who collected specimens in Brazil. Characteristics The margay is very similar to the larger ocelot (''Leopardus pardalis'') in appearance, although the head is a little shorter, the eyes larger, and the tail and legs longer. It weighs from , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |