|
Leontios
Leontius (; died 15 February 706) was Byzantine emperor from 695 to 698. Little is known of his early life, other than that he was born in Isauria in Asia Minor. He was given the title of ''patrikios'', and made ''strategos'' of the Anatolic Theme under Emperor Constantine IV. He led forces against the Umayyads during the early years of Justinian II's reign, securing victory and forcing the Umayyad caliph, Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, to sue for peace. In 692, Justinian declared war upon the Umayyads again, and sent Leontius to campaign against them. However, he was defeated decisively at the Battle of Sebastopolis, and imprisoned by Justinian for his failure. He was released in 695, and given the title of ''strategos'' of the Theme of Hellas in Southern Greece. After being released, he led a rebellion against Justinian, and seized power, becoming emperor in the same year. He ruled until 698, when he was overthrown by Apsimarus, a '' droungarios'' who had taken part in a fail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolic Theme
The Anatolic Theme (, ''Anatolikon hema'), more properly known as the Theme of the Anatolics (Greek: , ''thema Anatolikōn''), was a Byzantine theme (a military-civilian province) in central Asia Minor (modern Turkey). From its establishment, it was the largest and senior-most of the themes, and its military governors ('' stratēgoi'') were powerful individuals, several of them rising to the imperial throne or launching failed rebellions to capture it. The theme and its army played an important role in the Arab–Byzantine wars of the 7th–10th centuries, after which it enjoyed a period of relative peace that lasted until its conquest by the Seljuk Turks in the late 1070s. Geography and administration In its "classical" form during the 8th and 9th centuries, the theme stretched over the ancient regions of Lycaonia, Pisidia, Isauria, as well as most of Phrygia and parts of Galatia Salutaris.. Initially, the Anatolic Theme included the western and southern shores of Asia Minor as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sebastopolis
The Battle of Sebastopolis was fought at Sebastopolis (mostly identified with Elaiussa Sebaste in Cilicia but also with modern Sulusaray) in 692 CE between the Byzantine Empire and the Umayyad Caliphate under Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The battle ended the peace that had existed between the two powers since 680. The Umayyad army was led by Muhammad ibn Marwan. The Byzantines were led by Leontios and included a "special army" of 30,000 Anatolian Slavs under their leader, Neboulos. The Umayyads, incensed at the breaking of the treaty, used copies of its texts in the place of a flag. Though the battle seemed to be tilting to the Byzantine advantage, the defection of upwards of 20,000 Slavs ensured a Byzantine defeat.Ostrogorsky, George, ''History of the Byzantine state'',(Rutgers University Press, 1969), 131.Hendy, Michael F., ''Studies in the Byzantine Monetary Economy C. 300-1450'', (Cambridge University Press, 2008), 631.Haldon, John F., ''Byzantium in the seventh century'', (Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellas (theme)
The Theme of Hellas (, ''Thema Hellados'') was a Byzantine military-civilian province (''thema'', theme) located in southern Greece. The theme encompassed parts of Central Greece, Thessaly and, until , the Peloponnese peninsula. It was established in the late 7th century, and was broken up into smaller districts in the late 11th/early 12th century. The theme fell to the Crusader army led by Boniface of Montferrat in 1205. History 7th–8th centuries The ancient term "Hellas" was already in use in the 6th century to designate southern Greece in an administrative context, being employed in the '' Synekdemos'' as an alternative name for the Roman province of Achaea. During the late 6th and early 7th centuries, the collapse of the Byzantine Empire's Danube frontier allowed large-scale Slavic invasions and settlements to occur all over the Balkan peninsula. From 578, Slavic raids reached Thessaly and southern Greece. Aided by the Byzantine Empire's preoccupation with the long and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Al-Malik Ibn Marwan
Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan ibn al-Hakam (; July/August 644 or June/July 647 – 9 October 705) was the fifth Umayyad caliph, ruling from April 685 until his death in October 705. A member of the first generation of born Muslims, his early life in Medina was occupied with pious pursuits. He held administrative and military posts under Caliph Mu'awiya I (), founder of the Umayyad Caliphate, and his own father, Caliph Marwan I (). By the time of Abd al-Malik's accession, Umayyad authority had collapsed across the Caliphate as a result of the Second Fitna and had been reconstituted in Bilad al-Sham, Syria and Egypt in the Middle Ages, Egypt during his father's reign. Following a Battle of Khazir, failed invasion of Iraq in 686, Abd al-Malik focused on securing Syria before making further attempts to conquer the greater part of the Caliphate from his principal rival, the Mecca-based caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. To that end, he concluded an unfavorable truce with the reinvigorated Byz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droungarios
A ''droungarios'', also spelled ''drungarios'' (, ) and sometimes anglicized as Drungary, was a military rank of the late Roman and Byzantine empires, signifying the commander of a formation known as '' droungos''. Late Roman and Byzantine army Latin-speakers adopted the word ''drungus'' - first attested in the early 4th century - either from Gaulish or from a Germanic language. In the late 6th century, the Emperor Maurice (r. 582–602) in his '' Strategikon'' used ''droungos'' to refer to a specific tactical deployment, usually of cavalry, although still in the general sense of "grouping, division". The term ''droungarios'' (Greek: δρουγγάριος) is not documented before the early 7th century but might have been used as an informal or unofficial designation before that date. The office and the corresponding unit appear to have initially referred to ''ad hoc'' arrangements, but during the early 7th century these were formalized, like much of the Eastern Roman army's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
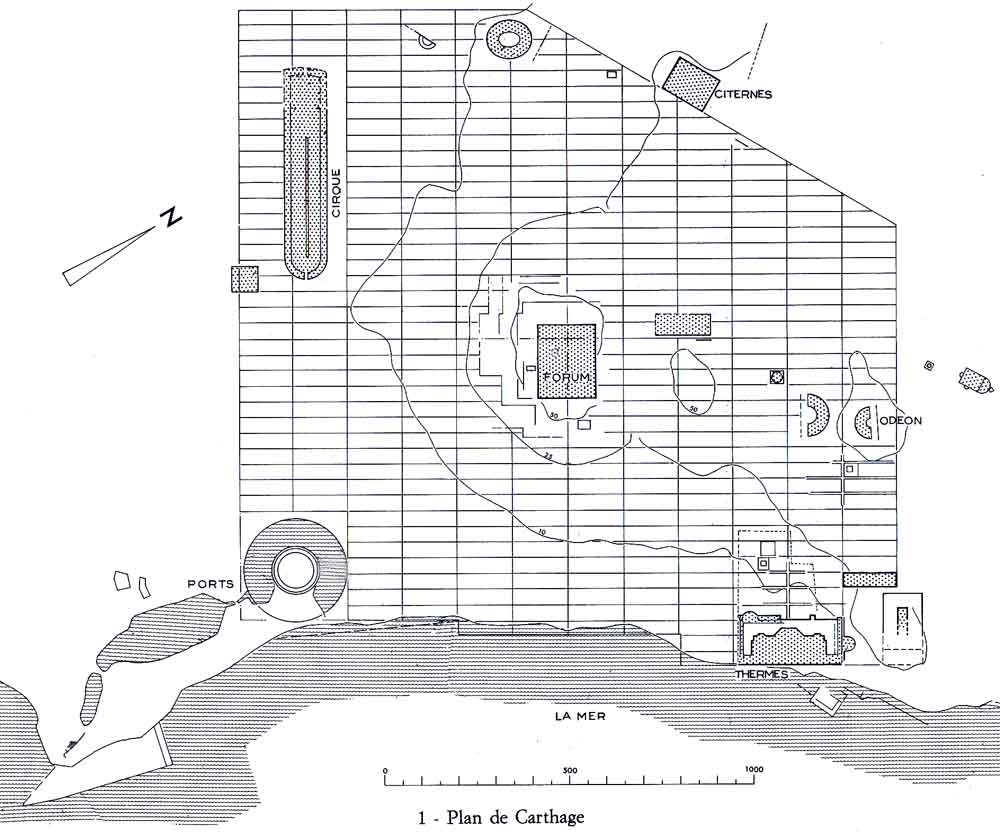
Roman Carthage
Roman Carthage was an important city in ancient Rome, located in modern-day Tunisia. Approximately 100 years after the destruction of Punic Carthage in 146 BC, a new city of the same name (Latin '' Carthāgō'') was built on the same land by the Romans in the period from 49 to 44 BC. By the 3rd century, Carthage had developed into one of the largest cities of the Roman Empire, with a population of several hundred thousand.Likely the fourth city in terms of population during the imperial period, following Rome, Alexandria and Antioch, in the 4th century also surpassed by Constantinople; also of comparable size were Ephesus, Smyrna and Pergamum. Stanley D. Brunn, Maureen Hays-Mitchell, Donald J. Zeigler (eds.), ''Cities of the World: World Regional Urban Development'', Rowman & Littlefield, 2012p. 27/ref> It was the center of the Roman province of Africa, which was a major breadbasket of the empire. Carthage briefly became the capital of a usurper, Domitius Alexander, in 308&nda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regnal Name
A regnal name, regnant name, or reign name is the name used by monarchs and popes during their reigns and subsequently, historically. Since ancient times, some monarchs have chosen to use a different name from their original name when they accede to the monarchy. The regnal name is usually followed by a regnal number, written as a Roman numeral, to differentiate that monarch from others who have used the same name while ruling the same realm. In some cases, the monarch has more than one regnal name, but the regnal number is based on only one of those names, for example Charles X Gustav of Sweden. If a monarch reigns in more than one realm, they may carry different ordinals in each one, as some realms may have had different numbers of rulers of the same regnal name. For example, the same person was both King James VI of Scotland and King James I of England. The ordinal is not normally used for the first ruler of the name, but is used in historical references once the name is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regnal Numbers
Regnal numbers are ordinal numbers—often written as Roman numerals—used to distinguish among persons with the same regnal name who held the same office, notably kings, queens regnant, popes, and rarely princes and princesses. It is common to start counting either since the beginning of the monarchy, or since the beginning of a particular line of state succession. For example, Boris III of Bulgaria and his son Simeon II were given their regnal numbers because the medieval rulers of the First and Second Bulgarian Empire were counted as well, although the recent dynasty dates only back to 1878 and is only distantly related to the monarchs of previous Bulgarian states. On the other hand, the kings of England and kings of Great Britain and the United Kingdom are counted starting with the Norman Conquest. That is why the son of Henry III of England is called Edward I, even though there were three English monarchs named Edward before the Conquest (they were distinguished by epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiquity to the Fourteenth Century''. Richard G. Hovannisian (ed.) New York: St. Martin's Press, 1997, pp. 1–17 Armenians constitute the main demographic group in Armenia and constituted the main population of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh until their Flight of Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians, subsequent flight due to the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh, 2023 Azerbaijani offensive. There is a large Armenian diaspora, diaspora of around five million people of Armenian ancestry living outside the Republic of Armenia. The largest Armenian populations exist in Armenians in Russia, Russia, the Armenian Americans, United States, Armenians in France, France, Armenians in Georgia, Georgia, Iranian Armenians, Iran, Armenians in Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinotomy
Rhinotomy is mutilation, usually amputation, of the Human nose, nose. It was a means of judicial punishment throughout the world, particularly for sexual transgressions, but in the case of adultery often applied only to women. Ancient usage The Code of Hammurabi contains references to amputation of bodily protrusions (such as lips, nose, breasts, etc.), as do the laws of History of ancient Egypt, ancient Egypt, and in Hindu medicine the writings of Charaka and the Sushruta Samhita. Ancient Egyptian pharaoh, Horemheb, authored a legal text, the Edict of Horemheb, which frequently stated rhinotomy as a criminal punishment. Rhinotomy as a punishment for adultery was customary in early India, and practised by the Ancient Greece, Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans, but only rarely; the practice was more prevalent in Byzantine Empire, Byzantium and among the Arabs, where the unfaithful woman was subjected to it while the man could get away with a flogging—and "often the husband whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle Of 1234
The ''Chronicle of 1234'' () is an anonymous West Syriac universal history from Creation until 1234. The unknown author was probably from Edessa. The ''Chronicle'' only survives in fragments, from which it is known to be divided into two parts: the first on ecclesiastical history, the second on secular. It was critically edited and translated by the French Orientalist Jean-Baptiste Chabot in 1920 (volume I covering ecclesiastical history) and by Albert Abouna in 1974 (volume II covering secular history). Unique among Syriac chronicles it depends in part on the ''Book of Jubilees''. The author also used the lost ''Ecclesiastical History'' of Dionysius of Tell Maḥrē for his coverage of the eighth through ninth centuries. He also uses Theophilus of Edessa (possibly through an Arabic translator) and al-Azdī, an Arabic author. Some of Theophilus's history now lost to us survives in the ''Chronicle of 1234'', such as his account of the Trojan War. The ''Chronicle'' also uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to the east, and Iran and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Nakhchivan to the south. Yerevan is the Capital city, capital, largest city and Economy of Armenia, financial center. The Armenian Highlands has been home to the Hayasa-Azzi, Shupria and Nairi. By at least 600 BC, an archaic form of Proto-Armenian language, Proto-Armenian, an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, had diffused into the Armenian Highlands.Robert Drews (2017). ''Militarism and the Indo-Europeanizing of Europe''. Routledge. . p. 228: "The vernacular of the Great Kingdom of Biainili was quite certainly Armenian. The Armenian language was obviously the region's vernacular in the fifth century BC, when Persian commanders and Greek writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |