|
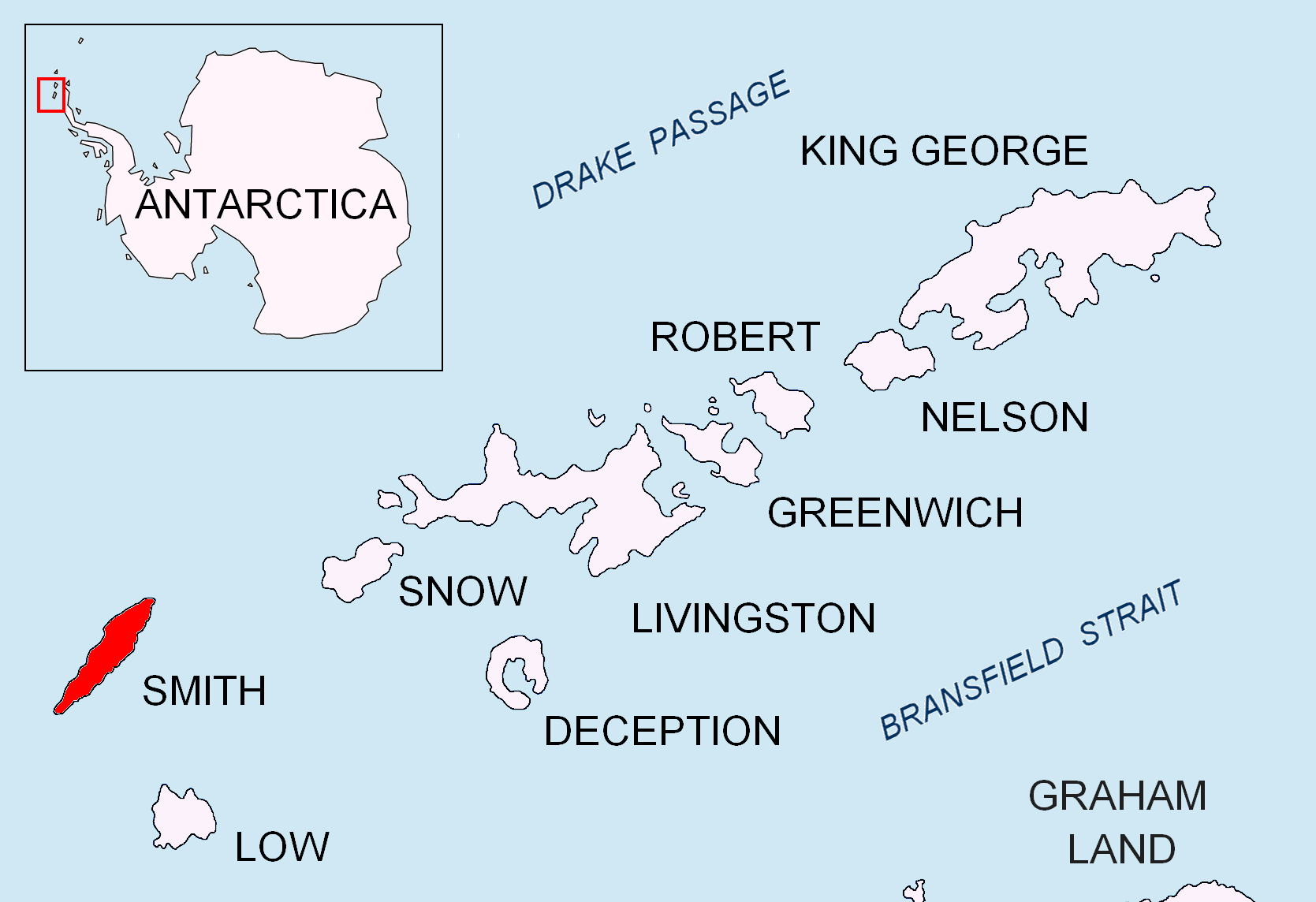
Lenoir Rock
Lenoir Rock (, ) is the rock off the NW coast of Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica 230 m long in southwest-northeast direction and 85 m wide with a surface area of 1.29 ha. The vicinity was visited by early 19th century sealers.L. IvanovGeneral Geography and History of Livingston Island.In: ''Bulgarian Antarctic Research: A Synthesis''. Eds. C. Pimpirev and N. Chipev. Sofia: St. Kliment Ohridski University Press, 2015. pp. 17–28 The feature is named after Étienne Lenoir (1744-1832), a Belgian-French scientific instrument maker and inventor of the repeating circle; in association with other names in the area deriving from the early development or use of geodetic instruments and methods. Location Lenoir Rock is located at ,Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer. Antarctic Place-names Commission which is 380 m southwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
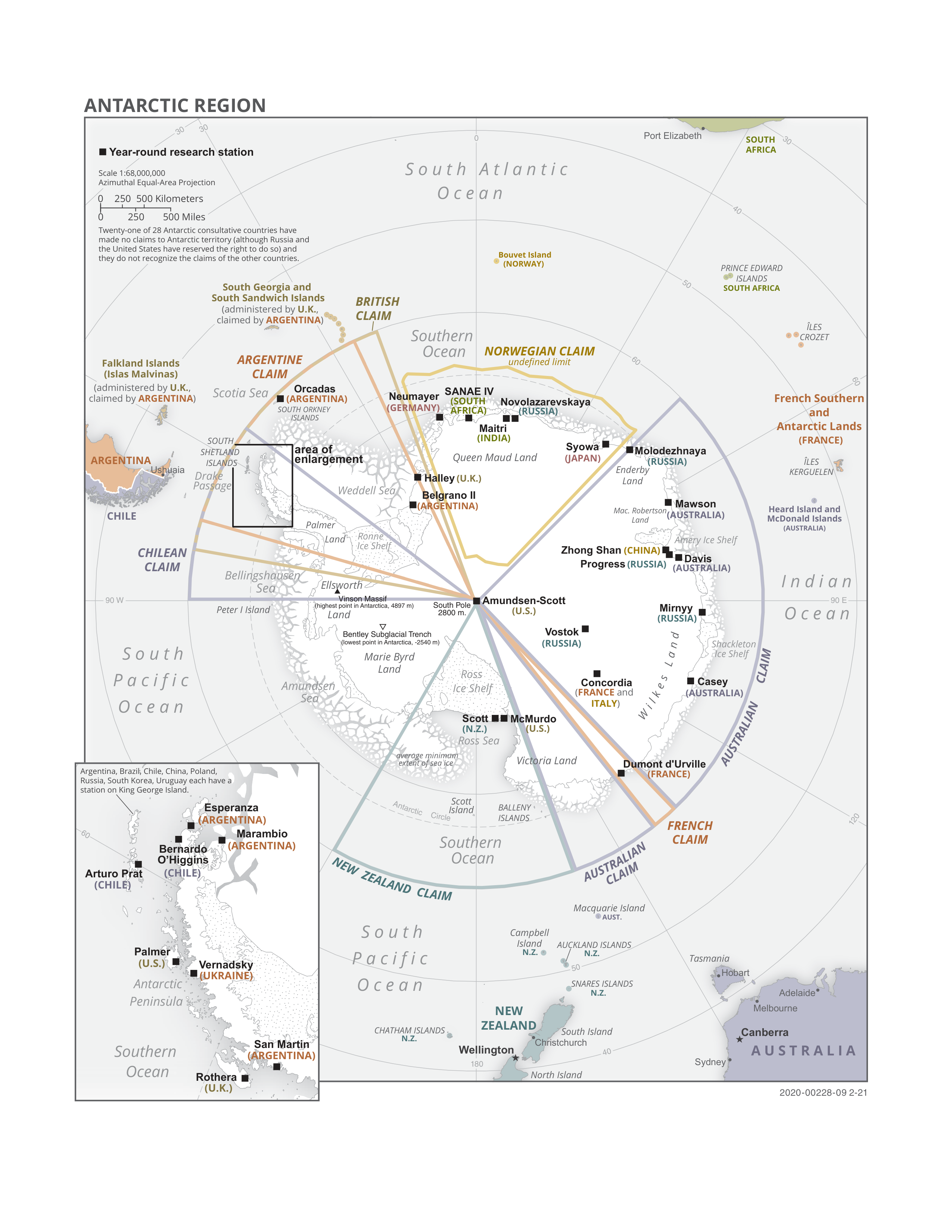
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Shetland Islands
The South Shetland Islands are a group of List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands, Antarctic islands located in the Drake Passage with a total area of . They lie about north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories. According to British government language on the topic, "the whole of Antarctica is protected in the interests of peace and science." The islands have been claimed by three countries, beginning with the United Kingdom since 1908 (since 1962 as part of the equally unrecognized British Antarctic Territory). The islands are also claimed by the governments of Chile (since 1940, as part of the Antártica Chilena province), and by Argentina (since 1943, as part of Argentine Antarctica, Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina, Tierra del Fuego Province). Several countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War, designating the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning Military activity in the Antarctic, military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelf, ice shelves south of 60th parallel south, 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina. The main treaty was opened for signature on 1 December 1959, and officially coming into force, entered into force on 23 June 1961. The original signatories were the 12 countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith Island (South Shetland Islands)
__NOTOC__ Smith Island is long and wide, lying west of Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands of the British Antarctic Territory. It is separated from Snow Island by the -wide Boyd Strait, and from Low Island by the -wide Osmar Strait. Surface area is .L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2010. (First edition 2009. ) The discovery of the South Shetland Islands was first reported in 1819 by Capt. William Smith, after whom the island is named. This island was known to both American and British sealers as early as 1820, and the name Smith has been well established in international usage for over 100 years, although in Russian literature it is often referred to as Borodino Island, sometimes marked as Borodino (Smith) Island. The island hosts no research stations or camps, and is seldom visited by scientists or mountaineers. Its interior is entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Hunting
Seal hunting, or sealing, is the personal or commercial hunting of Pinniped, seals. Seal hunting is currently practiced in nine countries: Canada, Denmark (in self-governing Greenland only), Russia, the United States (above the Arctic Circle in Alaska), Namibia, Estonia, Norway, Finland and Sweden. Most of the world's seal hunting takes place in Canada and Greenland. The Canadian Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Department of Fisheries and Oceans (DFO) regulates the seal hunt in Canada. It sets quotas (total allowable catch – TAC), monitors the hunt, studies the seal population, works with the Canadian Sealers' Association to train sealers on new regulations, and promotes sealing through its website and spokespeople. The DFO set harvest quotas of over 90,000 seals in 2007; 275,000 in 2008; 280,000 in 2009; and 330,000 in 2010. The actual kills in recent years have been less than the quotas: 82,800 in 2007; 217,800 in 2008; 72,400 in 2009; and 67,000 in 2010. In 2007, Norway repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Étienne Lenoir (instrument Maker)
Étienne Lenoir (1744–1832) was a French scientific instrument maker and inventor of the repeating circle.Chronologie scientifique, technologique et économique de la France - Page 137 Danièle et Jean-Claude Clermontel - 2009 "POIDS ET MESURES : le 9 juin 1795, Étienne Lenoir fabrique le premier mètre étalon, sur la base de la mesure du méridien, effectuée en 1754 par l'abbé de La Caille (soit : 5 129 070 toises de Paris, du pôle à l'équateur)." When hired by Jean-Charles de Borda around 1772 to work on the reflecting circle, he was about thirty years old and nearly illiterate. However, his intelligence and mechanical genius allowed him to perform work that few others could perform. He played a significant role in the improvements to the reflecting circle and later used this experience in inventing the repeating circle. As a result of this work, he became known as the pre-eminent maker of instruments for astronomy, navigation and surveying in France. In 1787, the king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeating Circle
The repeating circle is an instrument for geodetic surveying, developed from the Reflecting instrument#reflecting circle, reflecting circle by Étienne Lenoir (instrument maker), Étienne Lenoir in 1784. He invented it while an assistant of Jean-Charles de Borda, who later improved the instrument. It was notable as being the equal of the Ramsden surveying instruments#great theodolite, great theodolite created by the renowned instrument maker, Jesse Ramsden. It was used to arc measurement, measure the meridian arc from Dunkirk to Barcelona by Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, Jean Baptiste Delambre and Pierre Méchain (see: meridian arc of Delambre and Méchain). Construction and operation The repeating circle is made of two telescopes mounted on a shared axis with scales to measure the angle between the two. The instrument combines multiple measurements to increase accuracy with the following procedure: At this stage, the angle on the instrument is double the angle of interest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional space, 3D. It is called planetary geodesy when studying other astronomical body, astronomical bodies, such as planets or Natural satellite, circumplanetary systems. Geodynamics, Geodynamical phenomena, including crust (geology), crustal motion, tides, and polar motion, can be studied by designing global and national Geodetic control network, control networks, applying space geodesy and terrestrial geodetic techniques, and relying on Geodetic datum, datums and coordinate systems. Geodetic job titles include geodesist and geodetic surveyor. History Geodesy began in pre-scientific Classical antiquity, antiquity, so the very word geodesy comes from the Ancient Greek word or ''geodaisia'' (literally, "division of Earth"). Early ideas about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jireček Point
Jireček Point (, ) is the point on the northwest coast of Smith Island (South Shetland Islands), Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica forming the south side of the entrance to Cabut Cove and the northeast side of the entrance to Bourchier Cove. Situated 1.1 km south-southeast of Markeli Point and 2.35 km north-northeast of Villagra Point. The point is named after the settlements of Irechek (village), Irechek in northeastern and Irechekovo in southeastern Bulgaria, in connection with the Czechs, Czech historian and Bulgarian educator Konstantin Jireček (1854–1918). Location Jireček Point is located at . Bulgarian mapping in 2009. MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. * L.L. Ivanov. :commons:File:Livingston-Island-Map-2010.jpg, Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villagra Point
Villagra Point is the point on the northwest coast of Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica forming the south side of the entrance to Bourchier Cove. The feature's name is given by Argentina. Location Villagra Point is located at which is 3.07 km south by west of Markeli Point, 2.35 km south-southwest of Jireček Point Jireček Point (, ) is the point on the northwest coast of Smith Island (South Shetland Islands), Smith Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica forming the south side of the entrance to Cabut Cove and the northeast side of the entrance t ... and 3.06 km north-northeast of Garmen Point (Bulgarian mapping in 2009). MapsChart of South Shetland including Coronation Island, &c.from the exploration of the sloop Dove in the years 1821 and 1822 by George Powell Commander of the same. Scale ca. 1:200000. London: Laurie, 1822. * L.L. Ivanov. Antarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands. Scale 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Antarctic And Subantarctic Islands
This is a list of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands. * Antarctic islands are, in the strict sense, the islands around mainland Antarctica, situated on the Antarctic Plate, and south of the Antarctic Convergence. According to the terms of the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, claims to sovereignty over lands south of 60th parallel south, 60° S are not asserted.Antarctic Treaty, Article VI Dec. 1, 1959 12 UST 794; 402 UNTS 71; 19 ILM 860 (1980) * Sub-Antarctic islands are the islands situated closer to another continental mainland or on another list of tectonic plates, tectonic plate, but are biogeography, biogeographically linked to the Antarctic or being parts of the Antarctic realm, roughly north of and adjacent to the Antarctic Convergence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |