|
Lavidaviridae
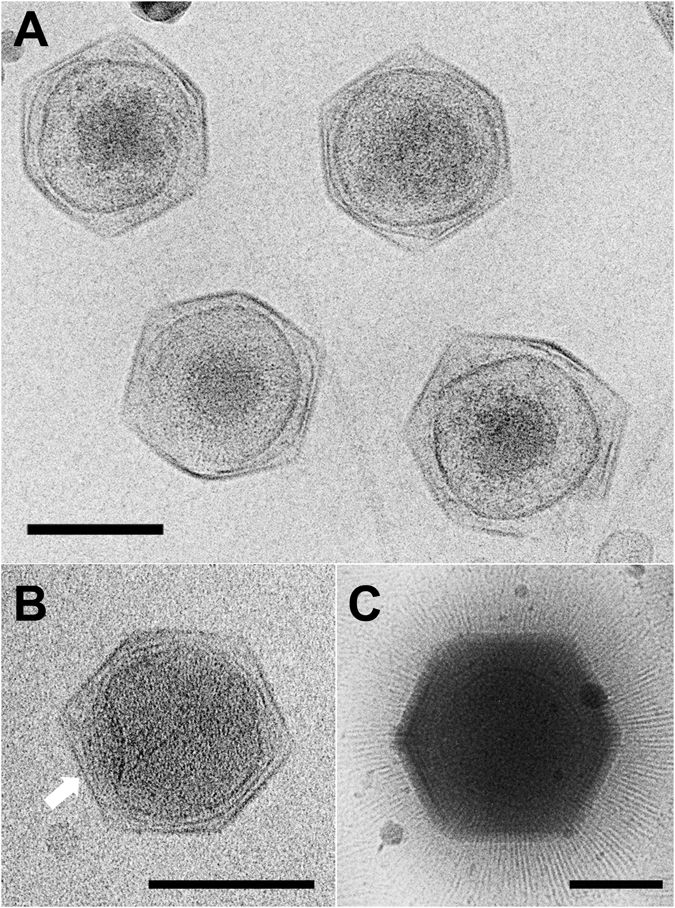
''Mavirus'' is a genus of double stranded DNA virus that can infect the marine phagotrophic flagellate ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'', but only in the presence of the giant ''CroV'' virus (''Cafeteria roenbergensis''). The genus contains only one species: ''Mavirus cafeteriae''. ''Mavirus'' can integrate into the genome of cells of ''C. roenbergensis'', and thereby confer immunity to the population The name is derived from Maverick virus. The virophage was discovered by Matthias G. Fischer of the University of British Columbia while he was working on Cafeteria roenbergensis virus as part of his PhD. __TOC__ Virology The genome is 19,063 bases long and encodes 20 predicted coding sequences. Seven have homology to the Maverick/Polinton family of transposons. The genome encodes a retroviral integrase, an adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase), a cysteine protease and a protein primed DNA polymerase A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virophage
Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for their own replication. One of the characteristics of virophages is that they have a parasitic relationship with the co-infecting virus. Their dependence upon the giant virus for replication often results in the deactivation of the giant viruses. The virophage may improve the recovery and survival of the host organism. Virophages constitute the class ''Virophaviricetes''. Discovery The first virophage was discovered in a cooling tower in Paris in 2008. It was discovered with its co-infecting giant virus, ''Acanthamoeba castellanii'' mamavirus (ACMV). The virophage was named Sputnik and its replication relied entirely on the co-infection of ACMV and its cytoplasmic replication machinery. Sputnik was also discovered to have an inhibitory e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virophages
Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the Coinfection, co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for their own replication. One of the characteristics of virophages is that they have a Parasitism, parasitic relationship with the co-infecting virus. Their dependence upon the giant virus for replication often results in the deactivation of the giant viruses. The virophage may improve the recovery and survival of the host organism. Virophages constitute the Class (biology), class ''Virophaviricetes''. Discovery The first virophage was discovered in a cooling tower in Paris in 2008. It was discovered with its co-infecting giant virus, ''Acanthamoeba castellanii'' mamavirus (ACMV). The virophage was named Sputnik virophage, Sputnik and its replication relied entirely on the co-infection of ACMV and its cytoplasmic replication mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Stranded DNA Virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom '' Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagotrophic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phagocytosis represents the scientific esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cafeteria Roenbergensis
''Cafeteria roenbergensis'' is a small bacterivorous marine flagellate. It was discovered by Danish marine ecologist Tom Fenchel and named by him and taxonomist David J. Patterson in 1988. It is in one of three genera of bicosoecids, and the first discovered of two known ''Cafeteria'' species. Bicosoecids belong to a broad group, the stramenopiles, also known as heterokonts (Heterokonta) that includes photosynthetic groups such as diatoms, brown, and golden algae, and non-photosynthetic groups such as opalinids, actinophryid "heliozoans", and oomycetes. The species is found primarily in coastal waters where there are high concentrations of bacteria on which it grazes. Its voracious appetite plays a significant role in regulating bacteria populations. Physiology ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'' is a slightly flattened, kidney-shaped bicosoecid. Its cell typically measures between 3 and 10 μm and it has a volume of around 20 μm3. It is colorless and has two unequally size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
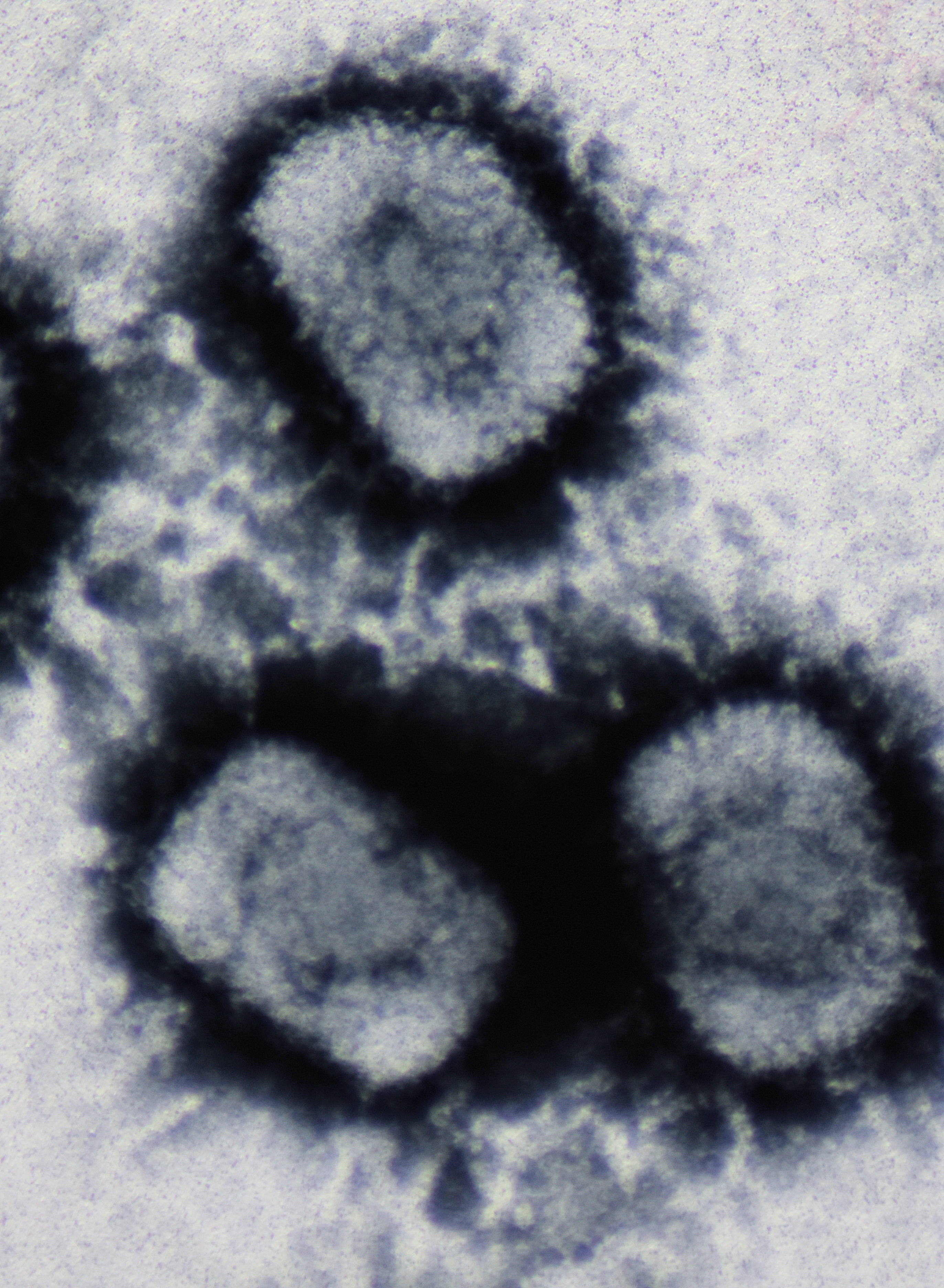
CroV
''Cafeteria roenbergensis'' virus (CroV), scientific name ''Rheavirus sinusmexicani'', is a giant virus that infects the marine bicosoecid flagellate ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'', a member of the microzooplankton community. History The virus was isolated from seawater samples collected from the Gulf of Mexico during 1989 to 1991, on a flagellate host that was misidentified as belonging to the genus ''Bodo (excavate), Bodo''; hence the original designation of the virus as BV-PW1. The virus was shown to be about 300 nm in diameter and have a complex internal structure, as well as evidence of a putative tail-like structure. Further work on the virus indicated that the host was an isolate of the genus ''Cafeteria'' and that the genome had a G+C content of ~34%. Further analysis suggested that the helicase of the virus was phylogenetically related to those found in the family ''Asfarviridae'', and that the virus shared properties with members of the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of Genus, genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias G
Matthias is a name derived from the Greek Ματθαίος, in origin similar to Matthew. Notable people Notable people named Matthias include the following: Religion * Saint Matthias, chosen as an apostle in Acts 1:21–26 to replace Judas Iscariot * Matthias of Trakai (–1453), Lithuanian clergyman, bishop of Samogitia and of Vilnius * Matthias Flacius, Lutheran reformer * Matthias the Prophet, see Robert Matthews (religious impostor) Claimed to be the reincarnation of the original Matthias during the Second Great Awakening * Matthias F. Cowley, Latter-day Saint apostle Arts * Matthias Bamert (born 1942), Swiss composer * Matthias Barr (1831-1911), Scottish poet * Matthias Grünewald, highly regarded painter from the German Renaissance * Matthias Jabs, German guitarist and songwriter * Matthías Jochumsson, Icelandic poet * Matthias Lechner, German film art director * Matthias Menck, German audio engineer, electronic music producer and DJ * Matthias Paul (actor), German act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC-BY Icon
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by Creative Commons, a U.S. non-profit corporation founded in 2001. There have also been five versions of the suite of licenses, numbered 1.0 through 4.0. Released in November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
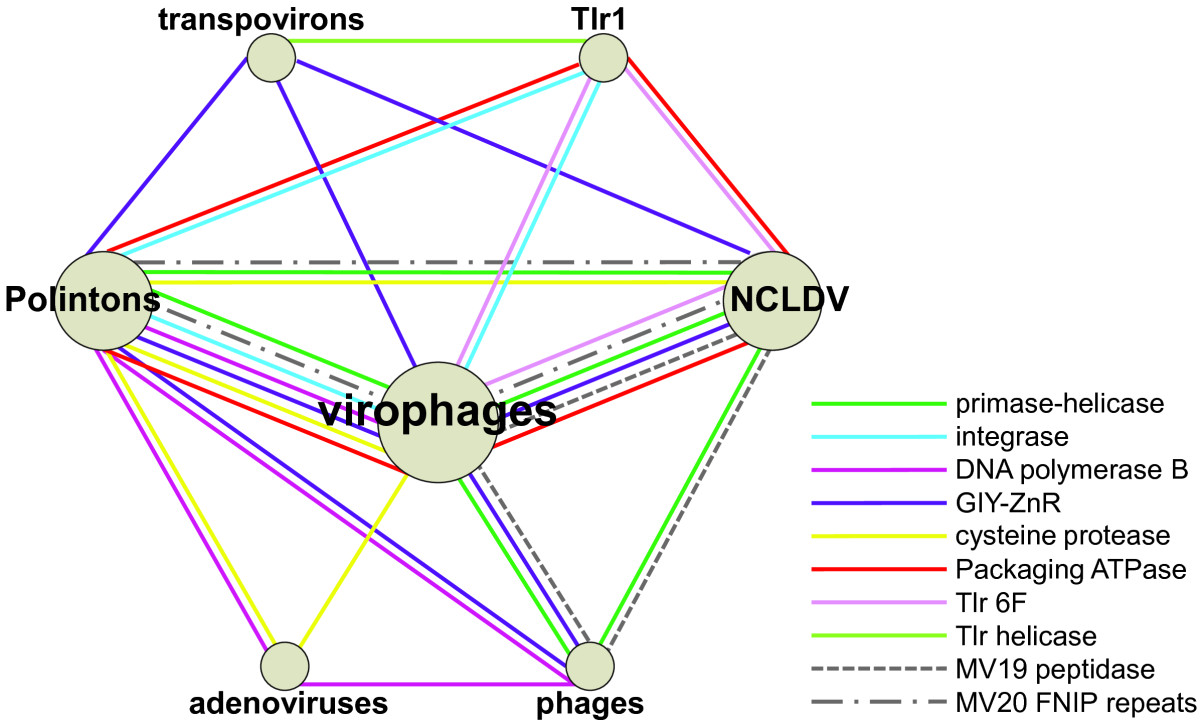
Polinton
Polintons (also called Mavericks) are large DNA transposons which contain genes with homology (biology), homology to virus, viral proteins and which are often found in eukaryotic genomes. They were first discovered in the mid-2000s and are the largest and most complex known DNA transposons. Polintons encode up to 10 individual proteins and derive their name from two key proteins, a DNA polymerase, DNA polymerase and a retroviral-like integrase, integrase. Properties A typical polinton is around 15–20 kilobase pairs in size, though examples have been described up to 40kb. Polintons encode up to 10 proteins, the key elements being the protein-primed type B DNA polymerase and the retroviral-like integrase from which they derive their name. Polintons are sometimes referred to as "self-synthesizing" transposons, because they encode the proteins necessary to replicate themselves. Most polintons also encode an adenoviral-like cysteine protease, an FtsK-like ATPase, and proteins with homol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transposon
A transposable element (TE), also transposon, or jumping gene, is a type of mobile genetic element, a nucleic acid sequence in DNA that can change its position within a genome. The discovery of mobile genetic elements earned Barbara McClintock a Nobel Prize in 1983. There are at least two classes of TEs: Class I TEs or retrotransposons generally function via reverse transcription, while Class II TEs or DNA transposons encode the protein transposase, which they require for insertion and excision, and some of these TEs also encode other proteins. Discovery by Barbara McClintock Barbara McClintock discovered the first TEs in maize (''Zea mays'') at the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory in New York. McClintock was experimenting with maize plants that had broken chromosomes. In the winter of 1944–1945, McClintock planted corn kernels that were self-pollinated, meaning that the silk (style) of the flower received pollen from its own anther. These kernels came from a long lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ... produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates (forms covalent links between) its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage integrases ( recombinases) used in biotechnology, such as λ phage integrase, as discussed in site-specific recombination. The macromolecular complex of an IN macromolecule bound to the ends of the viral DNA ends has been referred to as the '' intasome''; IN is a key component in this and the retroviral pre-integration complex. Structure All retroviral IN proteins contain three canonical domains, connected by flexible linkers: * an N-terminal HH-CC zinc-binding domain (a three-heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |