|
Latin Spanish
The different dialects of the Spanish language spoken in the Americas are distinct from each other, as well as from those varieties spoken in the Iberian Peninsula and the Spanish Mediterranean islands—collectively known as Peninsular Spanish—and Spanish spoken elsewhere, such as in Equatorial Guinea, Western Sahara, or in the Philippines. There is great diversity among the various Hispanic American vernaculars, as there are no common traits shared by all of them which are not also in existence in one or more of the variants of Iberian Spanish. A general Hispanic American "standard" does, however, vary from the Castilian "standard" register used in television, music and, notably, in the dubbing industry. Of the more than 498 million people who speak Spanish as their native language, more than 455 million are in Latin America, the United States and Canada, as of 2022. The total amount of native and non-native speakers of Spanish as of October 2022 well-exceeds 595 million. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardized varieties, such as those used in developing countries or isolated areas. The non-standard dialects of a language with a writing system will operate at different degrees of distance from the standardized written form. Standard and nonstandard dialects A ''standard dialect'', also known as a "standardized language", is supported by institutions. Such institutional support may include any or all of the following: government recognition or designation; formal presentation in schooling as the "correct" form of a language; informal monitoring of everyday Usage (language), usage; published grammars, dictionaries, and textbooks that set forth a normative spoken and written form; and an extensive formal literature (be it prose, poetry, non-ficti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiom
An idiom is a phrase or expression that largely or exclusively carries a Literal and figurative language, figurative or non-literal meaning (linguistic), meaning, rather than making any literal sense. Categorized as formulaic speech, formulaic language, an idiomatic expression's meaning is different from the Literal and figurative language, literal meanings of each word inside it. Idioms occur frequently in all languages. In English language, English alone there are an estimated twenty-five thousand idiomatic expressions. Some well known idioms in English are "spill the beans" (meaning "reveal secret information"), "it's raining cats and dogs" (meaning "it's raining intensely"), and "break a leg" (meaning "good luck"). Derivations Many idiomatic expressions were meant literally in their original use, but occasionally the attribution of the literal meaning changed and the phrase itself grew away from its original roots—typically leading to a folk etymology. For instance, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leísmo
''Leísmo'' ("using ''le''") is a dialectal variation in the Spanish language that occurs largely in Spain. It involves using the indirect object pronouns ''le'' and ''les'' in place of the (generally standard) direct object pronouns ''lo'', ''la'', ''los'', and ''las'', especially when the direct object refers to a male person or people. ''Leísmo'' with animate objects is both common and prescriptively accepted in many dialects spoken in Spain, but uncommon in most others. It thus typically correlates with the use of the preposition ''a'' for animate direct objects (for this "personal a", see Spanish prepositions). ''Leísmo'' is always rejected in linguistic prescription when the direct object to which it refers is not an animate object. For example: :' ("I see the boy") → ''Lo veo'' (standard Spanish, with ''lo'') :' ("I see the boy") → ''Le veo'' (''leísmo'', common in Spain; other regions prefer ''lo veo'') :' ("I see the tree") → ''Le veo'' (not accepted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Personal Pronouns
Spanish personal pronouns have distinct forms according to whether they stand for the subject ( nominative) or object, and third-person pronouns make an additional distinction for direct object ( accusative) or indirect object ( dative), and for reflexivity as well. Several pronouns also have special forms used after prepositions. Spanish is a pro-drop language with respect to subject pronouns, and, like many European languages, Spanish makes a T-V distinction in second person pronouns that has no equivalent in modern English. Object pronouns can be both clitic and non-clitic, with non-clitic forms carrying greater emphasis. With clitic pronouns, proclitic forms are much more common, but enclitic forms are mandatory in certain situations. There is significant regional variation in the use of personal pronouns, especially second-person pronouns. Table of personal pronouns All the personal pronouns used in Spanish are outlined in the table below. Ladino, historically spok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Alveolar Retracted Sibilant
The voiceless alveolar fricatives are a type of fricative consonant pronounced with the tip or blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge (gum line) just behind the teeth. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are at least six types with significant perceptual differences: *The voiceless alveolar sibilant (the standard symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet or IPA) has a strong hissing sound, as the ''s'' in English ''sink''. It is one of the most common sounds in the world. *The voiceless denti-alveolar sibilant (an ''ad hoc'' notation using IPA conventions), also called apico-dental, has a weaker lisping sound like English ''th'' in ''thin''. It occurs in Spanish dialects in southern Spain (eastern Andalusia). *The voiceless alveolar retracted sibilant ">Voiceless alveolar fricative#Voiceless alveolar retracted sibilant"> and the subform apico-alveolar , or called grave, has a weak hushing sound reminiscent of fricatives. It is used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
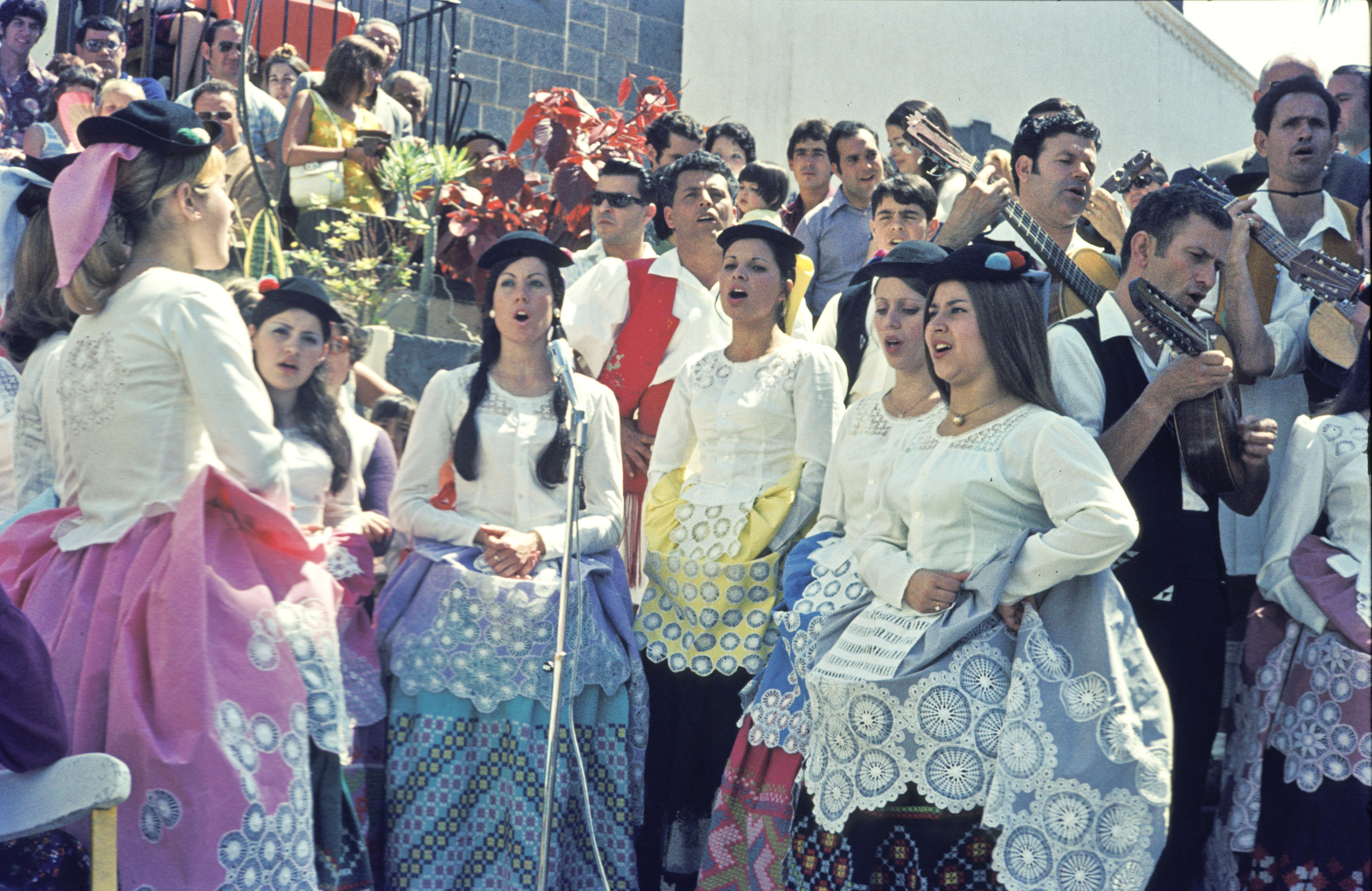
Canarian People
Canary Islanders, or Canarians (), are the people of the Canary Islands, an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain near the coast of Maghreb, Northwest Africa. The distinctive variety of the Spanish language spoken in the region is known as ''habla canaria'' (Canary speech) or the (''dialecto'')'' canario'' (Canarian Spanish, Canarian dialect). The Canarians, and their descendants, played a major role during the conquest, colonization, and eventual independence movements of various countries in Latin America. Their ethnic and cultural presence is most palpable in the countries of Uruguay, Venezuela, Cuba and the Dominican Republic as well as the Territories of the United States, US territory of Puerto Rico. History The original inhabitants of the Canary Islands are commonly known as Guanches (although this term in its strict sense only refers to the original inhabitants of Tenerife). They are most probably descendants of the Berbers of North Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andalusian People
The Andalusians () are the people of Andalusia, an Autonomous Community, autonomous community in southern Spain. Statute of Autonomy of Andalusia, Andalusia's statute of autonomy defines Andalusians as the Spanish citizens who reside in any of the municipalities of Andalusia, as well as those Spaniards who reside abroad and had their last Spanish residence in Andalusia, and their descendants. Since reform in 2007, the Andalusian statute of autonomy identifies the territory as a ''historic nationality'' in the preamble. The Royal Spanish Academy, Spanish Language Academy recognizes Andalusian Spanish as a set of diverse dialect, dialects. Andalusian nationalism is the belief that Andalusians are a nation separate from other ethnicities within Spain. History and culture In Antiquity, Andalusian people used to trade with Phoenicia, Phoenicians and Jews some thousand years before Christ, and they were called as Tarshish or Tartessos in the Old Testament and Greek texts. The gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
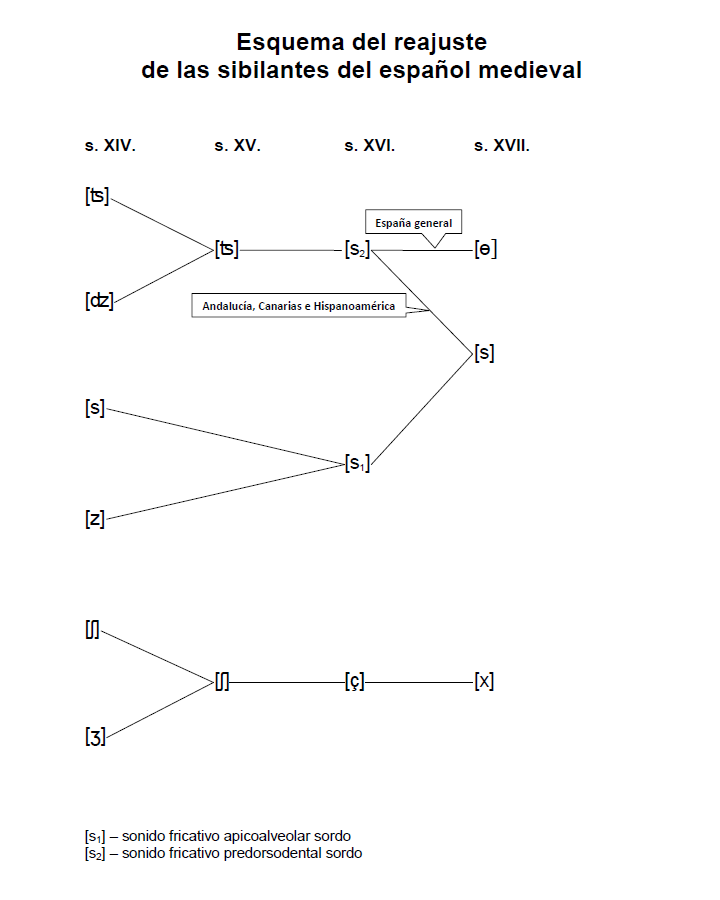
Seseo
In Spanish dialectology, the realization of coronal fricatives is one of the most prominent features distinguishing various dialect regions. The main three realizations are the phonemic distinction between and ('), the presence of only alveolar ('), or, less commonly, the presence of only a denti-alveolar that is similar to ('). While an urban legend attributes the presence of the dental fricative to a Spanish king with a lisp, the various realizations of these coronal fricatives are actually a result of historical processes that date to the 15th century. Origins Castilian 'lisp' A persistent urban legend claims that the prevalence of the sound in Spanish can be traced to a Spanish king who spoke with a lisp, whose pronunciation spread via prestige borrowing to the rest of the population. This myth has been discredited by scholars. traces the origins of the legend to a chronicle of Pero López de Ayala which says that Peter of Castile "lisped a little" (). However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distinción
In Spanish dialectology, the realization of coronal fricatives is one of the most prominent features distinguishing various dialect regions. The main three realizations are the phonemic distinction between and ('), the presence of only alveolar ('), or, less commonly, the presence of only a denti-alveolar that is similar to ('). While an urban legend attributes the presence of the dental fricative to a Spanish king with a lisp, the various realizations of these coronal fricatives are actually a result of historical processes that date to the 15th century. Origins Castilian 'lisp' A persistent urban legend claims that the prevalence of the sound in Spanish can be traced to a Spanish king who spoke with a lisp, whose pronunciation spread via prestige borrowing to the rest of the population. This myth has been discredited by scholars. traces the origins of the legend to a chronicle of Pero López de Ayala which says that Peter of Castile "lisped a little" (). However, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canarian Spanish
Canarian Spanish or Canary Island Spanish (Spanish terms in descending order of frequency: , , , or ) is a variant of standard Spanish spoken in the Canary Islands by the Canary Islanders. Canarian Spanish heavily influenced the development of Caribbean Spanish and other American Spanish vernaculars because Spanish America was originally largely settled by colonists from the Canary Islands and Andalusia; those dialects, including the standard language, were already quite close to Canarian and Andalusian speech. In the Caribbean, Canarian speech patterns were never regarded as either foreign or very different from the local accent. The incorporation of the Canary Islands into the Crown of Castile began with Henry III (1402) and was completed under the Catholic Monarchs. The expeditions for their conquest started off mainly from ports of Andalusia, which is why the Andalusians predominated in the Canaries. There was also an important colonising contingent from Portugal in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken language in the United States and, since 2025, the official language of the United States. It is also an official language in 32 of the 50 U.S. states and the ''de facto'' common language used in government, education, and commerce in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and in all territories except Puerto Rico. Since the late 20th century, American English has become the most influential form of English worldwide. Varieties of American English include many patterns of pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, and particularly spelling that are unified nationwide but distinct from other forms of English around the world. Any North American English, American or Canadian accent perceived as lacking noticeably local, ethnic, or cultural markedness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispanic America
Hispanic America ( or ), historically known as Spanish America () or Castile (historical region), Castilian America (), is the Spanish-speaking countries and territories of the Americas. In all of these countries, Spanish language, Spanish is the main language - sometimes sharing Official language, official status with one or more Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous languages (such as Guaraní language, Guaraní, Quechua language, Quechua, Aymara language, Aymara, or Mayan languages, Mayan) or English (in Puerto Rico), and Latin Catholicism is the predominant religion. Hispanic America is sometimes grouped together with Brazil under the term Ibero-America, meaning those countries in the Americas with cultural roots in the Iberian Peninsula. Hispanic America also contrasts with Latin America, which includes not only Hispanic America, but also Brazil (the former Portuguese America) and, by few definitions, the former French colonization of the Americas, French colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |