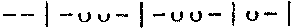|
Latin Poetry
The history of Latin poetry can be understood as the adaptation of Greek models. The verse comedies of Plautus, the earliest surviving examples of Latin literature, are estimated to have been composed around 205–184 BC. History Scholars conventionally date the start of Latin literature to the first performance of a play in verse by a Greek slave, Livius Andronicus, at Rome in 240 BC. Livius translated Greek New Comedy for Roman audiences, using meters that were basically those of Greek drama, modified to the needs of Latin. His successors Plautus ( 254 – 184 BC) and Terence ( 195/185 – 159? BC) further refined the borrowings from the Greek stage and the prosody of their verse is substantially the same as for classical Latin verse. Ennius (239 – 169 BC), virtually a contemporary of Livius, introduced the traditional meter of Greek epic, the dactylic hexameter, into Latin literature; he substituted it for the jerky Saturnian meter in which Livius had been composing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QS Maximus Memorial Stone
QS may refer to: Business * QS mark (for "quality and safety"), on Chinese products *Quacquarelli Symonds, an education and careers networking company **''QS World University Rankings'', an annual publication * Quality System (QS) Regulation, a business process *Quantity surveyor, a professional in the construction industry concerned with costs and contracts * Travel Service (IATA airline designator QS) *Quadraphonic sound, the Sansui QS Regular Matrix system Politics * Québec solidaire, a political party in Quebec, Canada * Quis separabit?, an Irish Loyalist motto Science, technology, and mathematics Biology and medicine * ATCvet code QS ''Sensory organs'', a section of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System for veterinary medicinal products *'' Quantum satis'', a Latin term meaning "the amount which is needed", used in food and drug regulation * Quinolinate synthase, an enzyme * Quorum sensing, a system of interaction in natural and synthetic populations Comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandrian Period
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting a lengthy military campaign throughout Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to northwestern India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he campaigned in the Balkans and reasserted control over Thrace and parts of Illyria before marching on the city of Thebes, which was subsequently destroyed in battle. Alexander then led the League of Corinth, and used his authority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcaeus Of Mytilene
Alcaeus of Mytilene (; , ''Alkaios ho Mutilēnaios''; – BC) was a lyric poet from the Greek island of Lesbos who is credited with inventing the Alcaic stanza. He was included in the canonical list of nine lyric poets by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria. He was a contemporary of Sappho, with whom he may have exchanged poems. He was born into the aristocratic governing class of Mytilene, the main city of Lesbos, where he was involved in political disputes and feuds. Biography The broad outlines of the poet's life are well known. He was born into the aristocratic, warrior class that dominated Mytilene, the strongest city-state on the island of Lesbos and, by the end of the seventh century BC, the most influential of all the North Aegean Greek cities, with a strong navy and colonies securing its trade-routes in the Hellespont. The city had long been ruled by kings born to the Penthilid clan but, during the poet's life, the Penthilids were a spent force and rival arist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 BC – 27 November 8 BC), Suetonius, Life of Horace commonly known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his '' Odes'' as the only Latin lyrics worth reading: "He can be lofty sometimes, yet he is also full of charm and grace, versatile in his figures, and felicitously daring in his choice of words."Quintilian 10.1.96. The only other lyrical poet Quintilian thought comparable with Horace was the now obscure poet/metrical theorist, Caesius Bassus (R. Tarrant, ''Ancient Receptions of Horace'', 280) Horace also crafted elegant hexameter verses ('' Satires'' and '' Epistles'') and caustic iambic poetry ('' Epodes''). The hexameters are amusing yet serious works, friendly in tone, leading the ancient satirist Persius to comment: "as his friend laughs, Horace slyly puts his finger on his every fault; once let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Ancient Greek comedy, comic playwright from Classical Athens, Athens. He wrote in total forty plays, of which eleven survive virtually complete today. The majority of his surviving plays belong to the genre of comic drama known as Old Comedy and are considered its most valuable examples. Aristophanes' plays were performed at the religious festivals of Athens, mostly the City Dionysia and the Lenaia, and several of them won the first prize in their respective competitions. Also known as "The Father of Comedy" and "the Prince of Ancient Comedy", Aristophanes wrote plays that often dealt with real-life figures, including Euripides and Alcibiades, and contemporary events, such as the Peloponnesian War. He has been said to recreate the life of ancient Athens more convincingly than any other author. His plays are characterized by preposterous premises, explicit language, wordplays, and political satire. His powers of ridicule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iambic Tetrameter
Iambic tetrameter is a meter (poetry), poetic meter in Ancient Greek poetry, ancient Greek and Latin poetry; as the name of ''a rhythm'', iambic tetrameter consists of four metra, each metron being of the form , x – u – , , consisting of a spondee and an Iamb (poetry), iamb, or two iambs. There usually is a break in the centre of the line, thus the whole line is: , x – u – , x – u – , , x – u – , , x – u – , ("x" is a syllable that can be long or short, "–" is a long syllable, and "u" is a short one.) In modern English poetry, it refers to a line consisting of four iamb (poetry), iambic foot (prosody), feet. The word "tetrameter" simply means that there are four feet in the line; ''iambic tetrameter'' is a line comprising four iambs, defined by accent. The scheme is thus: x / x / x / x / (In this case, "x" is an unstressed syllable while "/" is a stressed syllable.) Some poetic forms rely upon the iambic tetrameter, for example triole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choliamb
Choliambic verse (), also known as limping iambs or scazons or halting iambic,. is a form of meter (poetry), meter in poetry. It is found in both Ancient Greek literature, Greek and Latin literature, Latin poetry in the classical antiquity, classical period. Choliambic verse is sometimes called ''scazon'', or "lame iambic", because it brings the reader down on the wrong "foot" by reversing the stresses of the last few beats. It was originally pioneered by the Greek lyric poet Hipponax, who wrote "lame trochaics" as well as "lame iambics". The basic structure is much like iambic trimeter, except that the last cretic is made heavy by the insertion of a Long syllable, longum instead of a syllable weight, breve. Also, the third anceps of the iambic trimeter line must be short in limping iambs. In other words, the line scans as follows (where — is a long syllable, ⏑ is a short syllable, and × is an anceps): :× — ⏑ — , × — ⏑ — , ⏑ — — — As in all classica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asclepiad (poetry)
An Asclepiad (Latin: ''Asclepiadeus'') is a line of poetry following a particular metrical pattern. The form is attributed to Asclepiades of Samos and is one of the Aeolic verse, Aeolic metres. As with other Aeolic metrical lines, the asclepiad is built around a choriamb. The Asclepiad may be described as a glyconic that has been expanded with one (Lesser Asclepiad) or two (Greater Asclepiad) further choriambs. The pattern (using "–" for a long syllable, "u" for a short and "x" for an "anceps" or free syllable, which can be either – or u) is: x x - u u - , - u u - u - (Lesser Asclepiad / ''Asclepiadeus minor'') x x - u u - , - u u - , - u u - u - (Greater Asclepiad / ''Asclepiadeus maior'') In Horace's ''Odes'', there is almost always a caesura after the 6th syllable. Asclepiads are often found mixed with the pherecratean and glyconic, which have a similar rhythm: x x - u u - - (Pherecratean) x x - u u - u - (Glyconic) Martin Litchfield West, West (1982) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphic Stanza
The Sapphic stanza, named after the Ancient Greek poet Sappho, is an Aeolic verse form of Quatrain, four lines. Originally composed in quantitative verse and unrhymed, imitations of the form since the Middle Ages typically feature rhyme and accentual prosody. It is "the longest lived of the Classical lyric strophes in the West". Definitions In poetry, "Sapphic" may refer to three distinct but related Aeolic verse forms; for full discussion see Hendecasyllable. # The ''greater Sapphic'', a 15-syllable line, with the structure: – u – – – , u u – , – u u – u – – –=long syllable; u=short syllable; , =caesura # The ''lesser Sapphic'', an 11-syllable line, with the structure: – u – x – u u – u – – x=anceps (either long or short) # The ''Sapphic stanza'', typically conceptualized as comprising 3 ''lesser Sapphic'' lines followed by an adonic, with the structure: – u u – – Classical Latin poets duplicated the Sapphic stanza with subtle modificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hendecasyllabic Verse
In poetry, a hendecasyllable (as an adjective, hendecasyllabic) is a line of eleven syllables. The term may refer to several different poetic meters, the older of which are quantitative and used chiefly in classical (Ancient Greek and Latin) poetry, and the newer of which are syllabic or accentual-syllabic and used in medieval and modern poetry. Classical In classical poetry, "hendecasyllable" or "hendecasyllabic" may refer to any of three distinct 11-syllable Aeolic meters, used first in Ancient Greece and later, with little modification, by Roman poets. Aeolic meters are characterized by an Aeolic base × × followed by a choriamb – u u –; where – = a long syllable, u = a short syllable, and × = an anceps, that is, a syllable either long or short. The three Aeolic hendecasyllables (with base and choriamb in bold) are: Phalaecian hendecasyllable (): × × – u u – u – u – – This line is named after Phalaecus, a minor Hellenistic poet who used it in epig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |