|
Late Ancient History Of Christianity
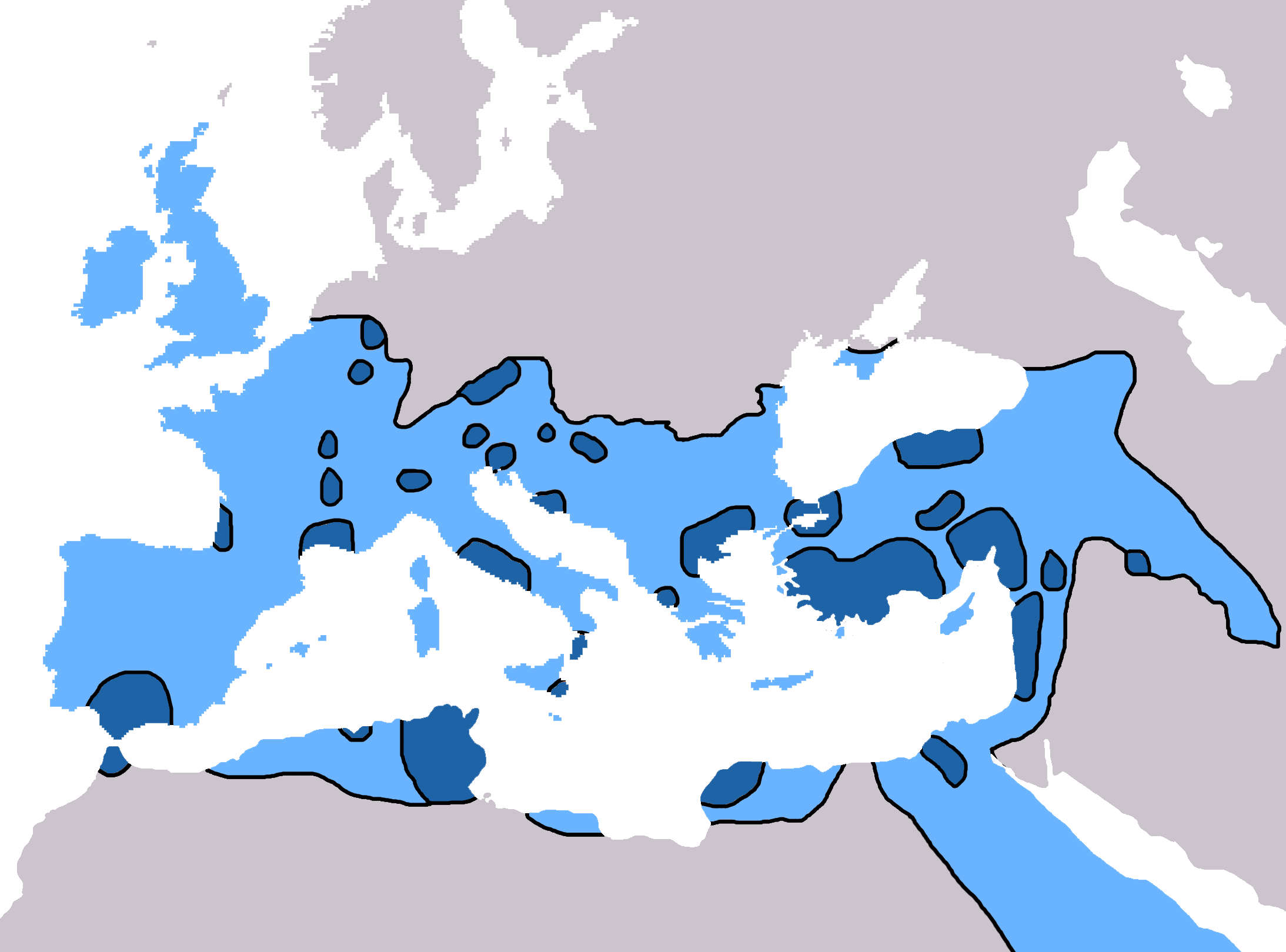
Christianity in late antiquity traces Christianity during the Christian Roman Empire — the period from the rise of Christianity under Emperor Constantine (c. 313), until the fall of the Western Roman Empire (c. 476). The end-date of this period varies because the transition to the sub-Roman period occurred gradually and at different times in different areas. One may generally date late ancient Christianity as lasting to the late 6th century and the re-conquests under Justinian (reigned 527–565) of the Byzantine Empire, though a more traditional end-date is 476, the year in which Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustus, traditionally considered the last western emperor. Christianity began to spread initially from Roman Judaea without state support or endorsement. It became the state religion of Armenia in either 301 or 314, of Ethiopia in 325, and of Georgia in 337. With the Edict of Thessalonica it became the state religion of the Roman Empire in 380. Persecution and legalisati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In The 4th Century
Christianity in the 4th century was dominated in its early stage by Constantine the Great and the First Council of Nicaea of 325, which was the beginning of the period of the First seven Ecumenical Councils (325–787), and in its late stage by the Edict of Thessalonica of 380, which made Nicene Christianity the state church of the Roman Empire. Christian persecutions : With Christianity the dominant faith in some urban centers, Christians accounted for approximately 10% of the Roman population by 300, according to some estimates. Roman Emperor Diocletian launched the bloodiest campaign against Christians that the empire had witnessed. The persecution ended in 311 with the death of Diocletian. The persecution ultimately had not turned the tide on the growth of the religion, and because of the rapid growth, Christians accounted for 56.5% of the Roman population by 350. Christians had already organized to the point of establishing hierarchies of bishops. In 301 the Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aksumite Empire
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging from the earlier Dʿmt civilization, the kingdom was founded in the first century. The city of Axum served as the kingdom's capital for many centuries until it relocated to Kubar in the ninth century due to declining trade connections and recurring invasions. The Kingdom of Aksum was considered one of the four great powers of the third century by the Persian prophet Mani, alongside Persia, Rome, and China. Aksum continued to expand under the reign of Gedara (), who was the first king to be involved in South Arabian affairs. His reign resulted in the control of much of western Yemen, such as the Tihama, Najran, al-Ma'afir, Zafar (until ), and parts of Hashid territory around Hamir in the northern highlands until a joint Himyarit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Musei Capitolini
Constantine most often refers to: * Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I * Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria Constantine may also refer to: People * Constantine (name), a masculine given name and surname Roman/Byzantine emperors * Constantine II (emperor) * Constantine III (Western Roman emperor) * Constantine III (Byzantine emperor) * Constantine IV * Constantine V * Constantine VI * Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus * Constantine VIII * Constantine IX Monomachos * Constantine X Doukas * Constantine XI Palaiologos Emperors not enumerated * Tiberius II, reigned officially as "Constantine" * Constans II, reigned officially as "Constantine" * Constantine (son of Leo V) * Constantine (son of Theophilos) * Constantine (son of Basil I) * Constantine Lekapenos * Constantine Doukas (co-emperor) * Constantine Laskaris (?) Other rulers * Constantine I, Prince of Armenia * Constantine II, Prince of Armenia * Constantine I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helena Of Constantinople
Flavia Julia Helena (; , ''Helénē''; – 330), also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an '' Augusta'' of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was born in the lower classes'' Anonymus Valesianus'1.2 "Origo Constantini Imperatoris". traditionally in the city of Drepanon, Bithynia, in Asia Minor, which was renamed Helenopolis. Helena ranks as an important figure in the history of Christianity. In her final years, she made a religious tour of Syria Palaestina and Jerusalem, during which ancient tradition claims that she discovered the True Cross. The Eastern Orthodox Church, Catholic Church, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Anglican Communion, and the Lutheran Church revere her as a saint. Early life Though Helena's birthplace is not known with certainty, Helenopolis, then Drepanon, in Bithynia, following Procopius, is the one supported by most secondary sources, and by far the most likely candidate f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I (emperor)
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Λικίνιος; c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign, he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan that granted official toleration to Christians in the Roman Empire. He was finally defeated at the Battle of Chrysopolis (AD 324), and was later executed on the orders of Constantine. Early reign Born to a Dacians, Dacian peasant family in Moesia Superior, Licinius accompanied his close childhood friend and future emperor Galerius, on the Persian expedition in 298. He was trusted enough by Galerius that in 307 he was sent as an envoy to Roman Italy, Italy, to attempt to reach some sort of agreement with the usurper Maxentius. When Galerius went to deal with Maxentius personally after the death of Severus II, he left the eastern provinces in Licinius' care. Upon his return to the east Galerius elevated Licinius to the rank of ''Augustus (tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edict Of Milan
The Edict of Milan (; , ''Diatagma tōn Mediolanōn'') was the February 313 agreement to treat Christians benevolently within the Roman Empire. Frend, W. H. C. (1965). ''The Early Church''. SPCK, p. 137. Western Roman Emperor Constantine I and Emperor Licinius, who controlled the Balkans, met in Mediolanum (modern-day Milan) and, among other things, agreed to change policies towards Christians following the edict of toleration issued by Emperor Galerius two years earlier in Serdica. The Edict of Milan gave Christianity legal status and a reprieve from persecution but did not make it the state church of the Roman Empire, ''The Cambridge History of Christianity''. Cambridge University PressQuote "Christianity did not become the official religion of the empire under Constantine, as is often mistakenly claimed..." which occurred in AD 380 with the Edict of Thessalonica,Encyclopedia Britannica"Christianity: The Alliance Between Church and Empire" Quote: "...Emperor Theodosius I (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galerius
Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; Greek: Γαλέριος; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. He participated in the system of government later known as the Tetrarchy, first acting as '' caesar'' under Emperor Diocletian. In this period Galerius obtained victory warring against the Persian Sassanian Empire, defeating Narseh at the battle of Satala in 298 and possibly sacking the Sassanian capital of Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across the Danube against the Carpi, defeating them in 297 and 300. Galerius was promoted to ''augustus'' upon the abdication of Diocletian in 305, but had to contend with multiple usurpers as the Tetrarchic system broke down. Although he was a staunch opponent of Christianity, he ended the Diocletianic Persecution by issuing the Edict of Serdica in 311. Early life Galerius was born in the Danube provinces, either near Serdica or at the place where he later built his palace named after his mother – Felix Romuliana ( Gamzigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edict Of Serdica
The Edict of Serdica, also called Edict of Toleration by Galerius, was issued in 311 in Serdica (now Sofia, Bulgaria) by Roman Emperor Galerius. It officially ended the Diocletianic Persecution of Christianity in the Eastern Roman Empire. The Edict implicitly granted Christianity the status of '' religio licita'', a worship that was recognized and accepted by the Roman Empire. It was the first edict legalizing Christianity and preceded the Edict of Milan by two years. History On 23 February 303, on the Terminalia feast, Emperor Diocletian, on the proposal of Galerius, issued a persecutory edict. The edict prescribed: * Destroying churches and burning their Holy Scriptures * Confiscation of church property * Banning Christians from undertaking collective legal action * Loss of privileges for Christians of high rank who refused to recant * Arresting some state officials. In 305, Diocletian abdicated and was replaced by Galerius, his successor, who continued persecution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |