|
Larrouy Island
Larrouy Island is an island long and wide which rises to , (the Peak Pilot) lying in Grandidier Channel off the northwest coast of Velingrad Peninsula north of Ferin Head, Antarctica. It was discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, who named it for Paul Augustin Jean Larrouy, at that time a French Minister Plenipotentiary An envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary, usually known as a minister, was a diplomatic head of mission who was ranked below ambassador. A diplomatic mission headed by an envoy was known as a legation rather than an embassy. Under th .... See also * List of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic islands References Islands of Graham Land Graham Coast {{GrahamCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
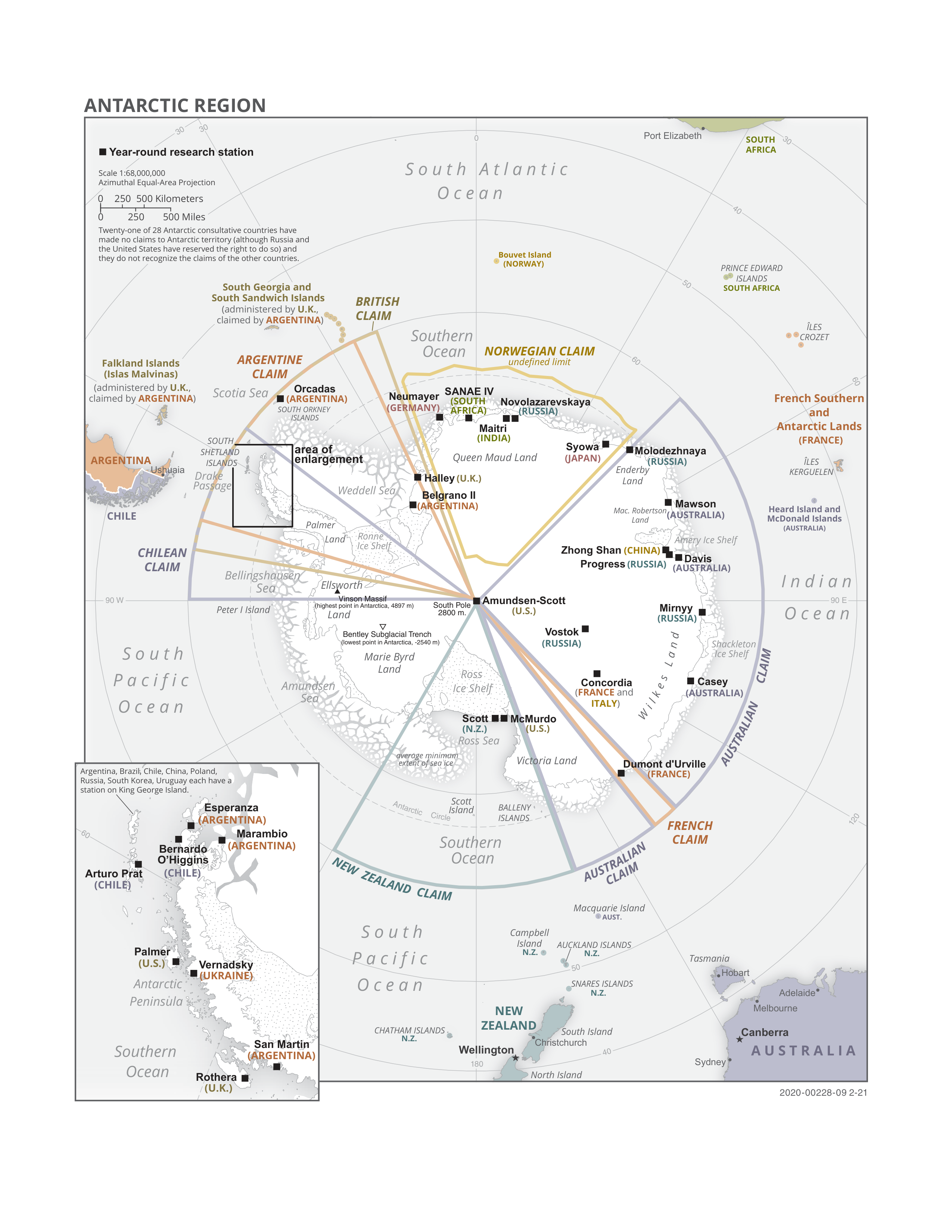
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandidier Channel
Grandidier Channel () is a navigable channel between the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica, and the north end of the Biscoe Islands, extending from Penola Strait southwestward to the vicinity of Larrouy Island. It was first charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, and named by Jean-Baptiste Charcot for Alfred Grandidier Alfred Grandidier (20 December 1836 – 13 September 1921) was a French naturalist and explorer. From a very wealthy family, at the age of 20, he and his brother, Ernest Grandidier (1833–1912), undertook a voyage around the world. At first ..., President of the Paris Geographical Society. Charcot applied the name to the entire body of water between the mainland and the Biscoe Islands but the name has since been restricted to the navigable portion described. File:GrandidierChannel01.JPG, Cruising Grandidier Channel in January 2014 File:GrandidierChannel05.JPG, Iceberg in Grandidier Channel File:GrandidierChannel07.JPG, Grandidier Chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velingrad Peninsula
Velingrad Peninsula ( bg, полуостров Велинград, poluostrov Velingrad, ) is the ice-covered peninsula projecting 22.5 km in northwest direction from Graham Coast on the west side of Antarctic Peninsula. Bounded by Barilari Bay to the northeast and Holtedahl Bay to the southwest, and separated from Biscoe Islands to the northwest by Grandidier Channel. Its base is surmounted by Chiren Heights. The UK station Prospect Point operated at the west extremity of the peninsula in 1957–59. The peninsula is named after the city of Velingrad in Southern Bulgaria. Location Velingrad Peninsula is centred at . British mapping in 1971 and 1976. Maps * British Antarctic Territory. Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Series, Sheet W 65 64. Directorate of Overseas Surveys, Tolworth, UK, 1971. * British Antarctic Territory. Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Series, Sheet W 66 64. Directorate of Overseas Surveys, Tolworth, UK, 1976.Antarctic Digital Databas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferin Head
Ferin Head () is a headland north of the entrance to Holtedahl Bay, in the northwest of Velingrad Peninsula on the Graham Coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, who from a distant position in Pendleton Strait charted this feature as an island, which Jean-Baptiste Charcot named for A. Ferin, French Vice-consul at Ponta Delgada in the Azores. The British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under John Rymill John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Seco ..., 1934–37, charted this coast and correlated their work with that of Charcot. Ferin Head, as here applied, is in accord with the BGLE interpretation. References SCAR Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica Headlands of Graham Land Graham Coast {{GrahamCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05
The French Antarctic Expedition is any of several French expeditions in Antarctica. First expedition In 1772, Yves-Joseph de Kerguelen-Trémarec and the naturalist Jean Guillaume Bruguière sailed to the Antarctic region in search of the fabled Terra Australis. Kerguelen-Trémarec took possession of various Antarctic territories for France, including what would later be called the Kerguelen Islands. In Kerguelen-Trémarec's report to King Louis XV, he greatly overestimated the value of the Kerguelen Islands. The King sent him on a second expedition to Kerguelen in late 1773. When it became clear that these islands were desolate, useless, and not the Terra Australis, he was sent to prison. Second expedition In 1837, during an 1837–1840 expedition across the deep southern hemisphere, Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville sailed his ship ''Astrolabe'' along a coastal area of Antarctica which he later named Adélie Land, in honor of his wife. During the Antarctic part of this exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Charcot
Jean-Baptiste-Étienne-Auguste Charcot (15 July 1867 – 16 September 1936), born in Neuilly-sur-Seine, was a French scientist, medical doctor and polar scientist. His father was the neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893). Life Jean-Baptiste Charcot was appointed leader of the French Antarctic Expedition with the ship ''Français'' exploring the west coast of Graham Land from 1904 until 1907. The expedition reached Adelaide Island in 1905 and took pictures of the Palmer Archipelago and Loubet Coast. From 1908 until 1910, another expedition followed with the ship '' Pourquoi Pas ?'', exploring the Bellingshausen Sea and the Amundsen Sea and discovering Loubet Land, Marguerite Bay, Mount Boland and Charcot Island, which was named after his father, Jean-Martin Charcot. anhere./ref> He named Hugo Island after Victor Hugo, the grandfather of his wife, Jeanne Hugo. Later on, Jean-Baptiste Charcot explored Rockall in 1921 and Eastern Greenland and Svalbard from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Augustin Jean Larrouy
Paul Augustin Jean Larrouy was a French diplomat born in Lagardelle-sur-Leze in France on 1 January 1857File for the title Officer of the French Legion d'Honneur on the database Leonore and who died in Buenos Aires on 10 August 1906. Notably, he has been Résident Général in second in Madagascar from March 1888 until 12 December 1889, and in his second term Résident Général in Madagascar from October 1892 until 1894. Action in Madagascar Paul Augustin Jean Larrouy's role during his second stay in Madagascar as General Resident was to maintain the French Authority without losing face in front of a non-abiding Malagasy power supported by England. The Malagasy government was confronted to a Menalamba revolt against the agreements signed with France in 1885 by the queen Ranavalona III. He leaves Tananarive at his request in 1894, and is succeeded by Charles Le Myre de Vilers. After the stay of the later, France decides a complete annexation of Madagascar in 1896 and call G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Plenipotentiary
An envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary, usually known as a minister, was a diplomatic head of mission who was ranked below ambassador. A diplomatic mission headed by an envoy was known as a legation rather than an embassy. Under the system of diplomatic ranks established by the Congress of Vienna (1815), an envoy was a diplomat of the second class who had plenipotentiary powers, i.e., full authority to represent the government. However, envoys did not serve as the personal representative of their country's head of state. Until the first decades of the 20th century, most diplomatic missions were legations headed by diplomats of the envoy rank. Ambassadors were only exchanged between great powers, close allies, and related monarchies. After World War II it was no longer considered acceptable to treat some nations as inferior to others, given the United Nations doctrine of equality of sovereign states. The rank of envoy gradually became obsolete as countries upgraded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Graham Land
An island or isle is a piece of subcontinental land completely surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges Delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental islands and oceanic islands. There are also artificial islands (man-made islands). There are about 900,000 official islands in the world. This number consists of all the officially-reported islands of each country. The total number of islands in the world is unknown. There may be hundreds of thousands of tiny islands that are unknown and uncounted. The number of sea islands in the world is estimated to be more than 200,000. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |