|
Larotrectinib
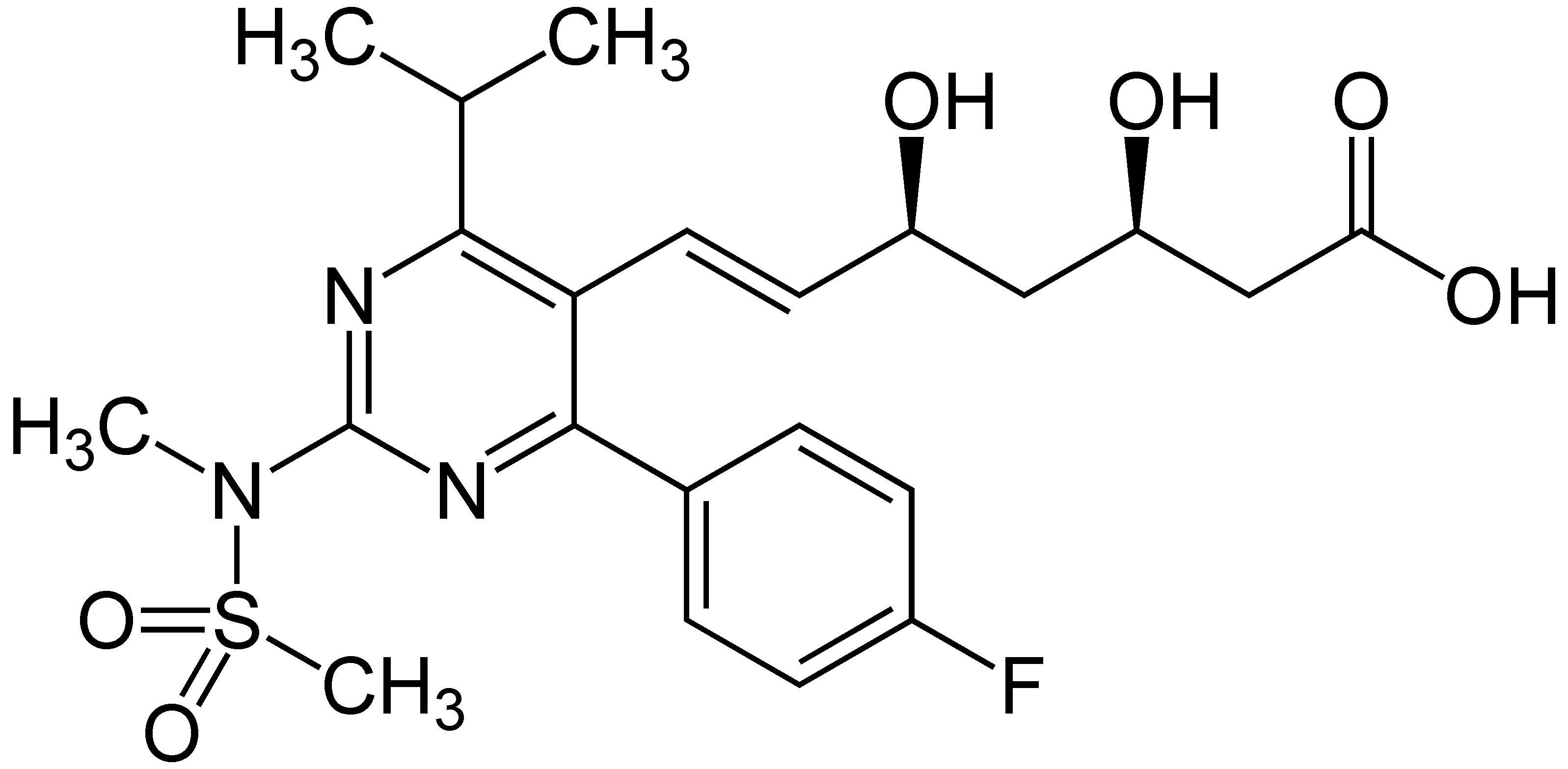
Larotrectinib, sold under the brand name Vitrakvi, is a medication for the treatment of cancer. It is an inhibitor of tropomyosin kinase receptors TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC. It was discovered by Array BioPharma and licensed to Loxo Oncology in 2013. Larotrectinib was initially awarded orphan drug status in 2015, for soft tissue sarcoma, and breakthrough therapy designation in 2016 for the treatment of metastatic solid tumors with NTRK fusion. Some clinical trial results were announced in 2017. On 26 November 2018, Larotrectinib was approved by the FDA. Larotrectinib was the first drug to be specifically developed and approved to treat ''any'' cancer containing certain mutations, as opposed to cancers of specific tissues (i.e., the approval is " tissue agnostic"). Several earlier drugs, including pembrolizumab, were eventually approved by the FDA for treatment of specific mutations independent of the type of cancer, but those drugs had been initially developed for specific cancer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue-agnostic Drug
Tissue-agnostic cancer drugs are antineoplastic drugs that treat cancers based on the mutations that they display, instead of the tissue type in which they appear. Tissue-agnostic drugs that have been approved for medical use include Pembrolizumab, Larotrectinib, Selpercatinib, Entrectinib, and Pralsetinib. History Pembrolizumab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in May 2017. Larotrectinib was approved by the FDA in November, 2018. Selpercatinib (LOXO-292) received priority review in September 2018 and was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2020. Entrectinib was approved for medical use in the United States in August 2019, in Australia in May 2020, and in the European Union in July 2020. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. Pralsetinib was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2020. Tissue-agnostic cancer drugs that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TrkA
Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA), also known as high affinity nerve growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 1, or TRK1-transforming tyrosine kinase protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTRK1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor (NTKR) family. This kinase is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself ( autophosphorylation) and members of the MAPK pathway. The presence of this kinase leads to cell differentiation and may play a role in specifying sensory neuron subtypes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis, self-mutilating behaviors, intellectual disability and/or cognitive impairment and certain cancers. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been found, but only three have been characterized to date. Function and Interaction with NGF TrkA is the high affinity catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TrkC
Tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC), also known as NT-3 growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 3, or TrkC tyrosine kinase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NTRK3'' gene. TrkC is the high affinity catalytic receptor for the neurotrophin NT-3 (neurotrophin-3). As such, TrkC mediates the multiple effects of this neurotrophic factor, which includes neuronal differentiation and survival. The TrkC receptor is part of the large family of receptor tyrosine kinases. A "tyrosine kinase" is an enzyme which is capable of adding a phosphate group to the certain tyrosines on target proteins, or "substrates". A receptor tyrosine kinase is a "tyrosine kinase" which is located at the cellular membrane, and is activated by binding of a ligand via its extracellular domain. Other example of tyrosine kinase receptors include the insulin receptor, the IGF-1 receptor, the MuSK protein receptor, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor, etc. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Brands
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceuticals; consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer and dyer Friedrich Weskott. As was common in this era, the company was established as a dyestuffs producer. The versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand their business into other areas, and in 1899 Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. In 1904 Bayer received a trademark for the "Bayer Cross" logo, which was subsequently stamped onto each aspirin tablet, creating an iconic product that is still sold by Bayer. Other commonly known pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Agnostic Antineoplastic Agents
Tissue may refer to: Biology * Tissue (biology), an ensemble of similar (or dissimilar in structure but same in origin) cells that together carry out a specific function * ''Triphosa haesitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue moth") found in North America * ''Triphosa dubitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue") found in Afro-Eurasia Paper products * Tissue paper, a type of thin, gauzy translucent paper used for wrapping and cushioning items ** Facial tissue, tissue paper used for cleaning the face ** Japanese tissue, tissue paper from Japan made of vegetable fibers ** Toilet paper, tissue paper used for cleaning the anus ** Wrapping tissue, tissue paper used for wrapping and cushioning items Other * Aerial tissue, an acrobatic art form and one of the circus arts * "The Tissue (Tomaranai Seishun) is the third single by the Japanese girl idol group Shiritsu Ebisu Chugaku (or fourth counting one cover single), released in Japan on April 27, 2011 on the indie label S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-in-class Medication
A first-in-class medication is a pharmaceutical that uses a "new and unique mechanism of action" to treat a particular medical condition. While the Food and Drug Administration's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research tracks first-in-class medications and reports on them annually, first-in-class is not considered a regulatory category. Although many first-in-class medications qualify as breakthrough therapies, Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapies and/or orphan drugs, first-in-class status itself has no regulatory effect. Examples Controversy Safety By definition, a first-in-class drug does not have the safety evidence from analogous products that not-first-in-class drugs would have. However, a study investigating recalls and warnings in relation to first-in-class drugs approved between 1997 and 2012 by Health Canada has found that first-in-class drugs actually have a more favourable benefit-to-harm ratio. Economics First-in-class drugs are often seen as commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, animal foods & feed and veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not directly related to food or drugs, but involves such things as regulating lasers, cellular phones, and condoms, as well as control of disease in contexts v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembrolizumab
Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast cancer. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Common side effects include fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, itchy skin (pruritus), diarrhea, nausea, rash, fever (pyrexia), cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea), constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. It is an IgG4 isotype antibody that blocks a protective mechanism of cancer cells and thereby, allows the immune system to destroy them. It targets the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) receptor of lymphocytes. It works by targeting the cellular pathway of proteins found on the body's immune cells and some cancer cells, known as PD-1/PD-L1. Pembrolizumab was approved for medical use in the United States in 2014. In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphan Drug Status
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy in many countries and has yielded medical breakthroughs that might not otherwise have been achieved, due to the economics of drug research and development. In the U.S. and the EU, it is easier to gain marketing approval for an orphan drug. There may be other financial incentives, such as an extended period of exclusivity, during which the producer has sole rights to market the drug. All are intended to encourage development of drugs which would otherwise lack sufficient profit motive to attract corporate research budgets and personnel. Definition According to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an orphan drug is defined as one "intended fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakthrough Therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "breakthrough therapy" designation is not intended to imply that a drug is actually a "breakthrough" or that there is high-quality evidence of treatment efficacy for a particular condition; rather, it allows the FDA to grant priority review to drug candidates if preliminary clinical trials indicate that the therapy may offer substantial treatment advantages over existing options for patients with serious or life-threatening diseases. The FDA has other mechanisms for expediting the review and approval process for promising drugs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, and priority review. Requirements A breakthrough therapy designation can be assigned to a drug if "it is a drug which is intended alone or in combinatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)