|
Laramidia
Laramidia was an island continent that existed during the Late Cretaceous period (99.6–66 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma), when the Western Interior Seaway split the continent of North America in two. In the Mesozoic era, Laramidia was an island land mass separated from Appalachia (landmass), Appalachia to the east by the Western Interior Seaway. It was home to many dinosaurs including Ankylosauria, ankylosaurs, Ceratopsia, ceratopsians, and Tyrannosauroidea, tyrannosaurs. The seaway eventually shrank, split across the Dakotas, and retreated toward the Gulf of Mexico and the Hudson Bay. The masses joined, forming the continent of North America. Laramidia is named after the Laramide orogeny. The name was coined by J. David Archibald in 1996. Geography Laramidia stretched from modern-day Alaska to Mexico. The area is rich in dinosaur fossils. Tyrannosauridae, Tyrannosaurs, Dromaeosauridae, dromaeosaurids, Troodontidae, troodontids, Hadrosaurid, hadrosaurs, ceratopsians (including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
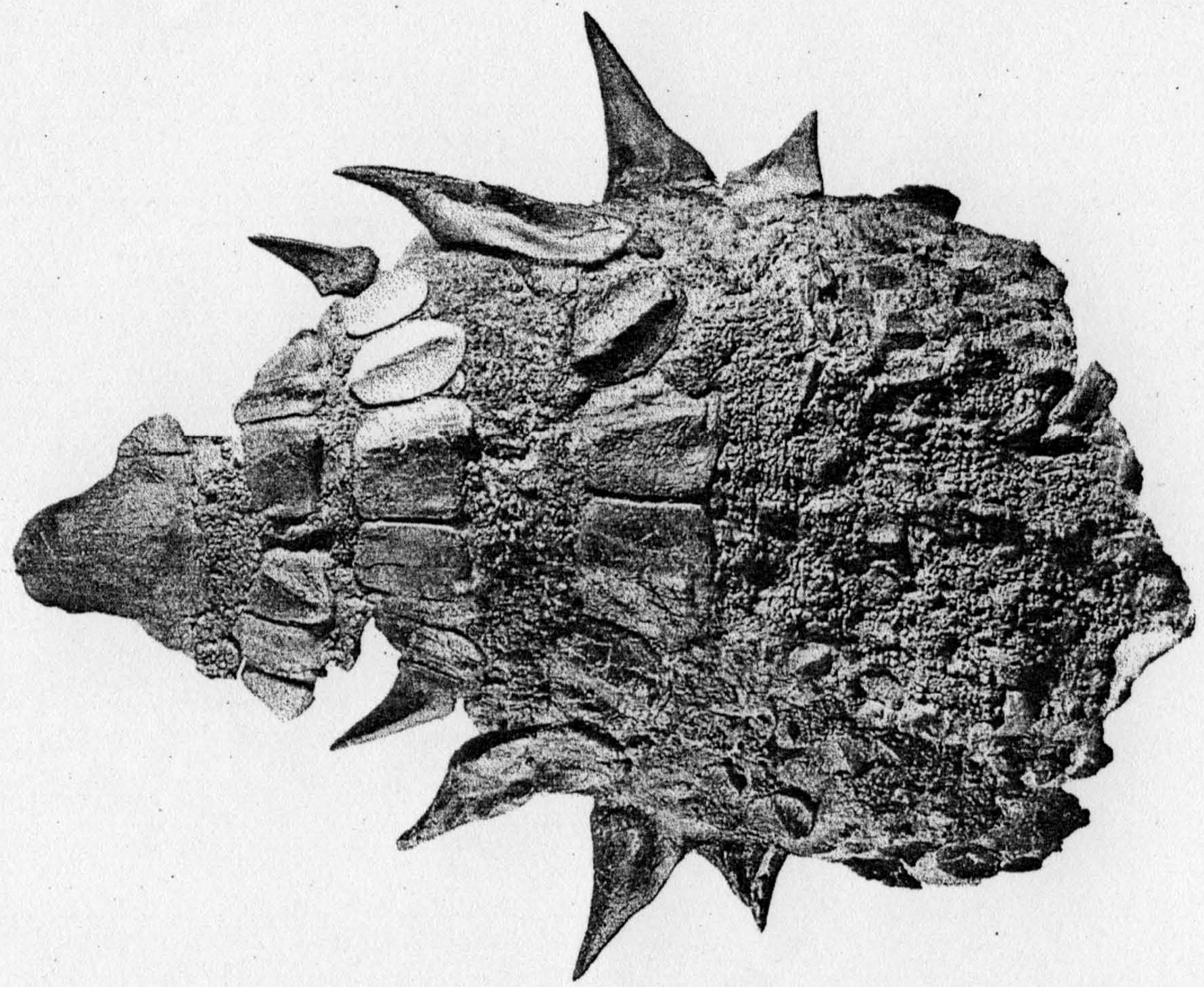
Kosmoceratops
''Kosmoceratops'' () is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur that lived in North America about 76–75.9 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period (geology), period. Specimens were discovered in Utah in the Kaiparowits Formation of the Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument in 2006 and 2007, including an adult skull and Postcrania, postcranial skeleton and partial subadults. In 2010, the adult was made the holotype of the new genus and species ''Kosmoceratops richardsoni''; the generic name means "ornate horned face", and the specific name honors Scott Richardson, who found the specimens. The find was part of a spate of ceratopsian discoveries in the early 21st century, and ''Kosmoceratops'' was considered significant due to its elaborate skull Biological ornament, ornamentation. ''Kosmoceratops'' had an estimated length of and a weight of . As a ceratopsid, it would have been quadrupedal with a heavily constructed skeleton. It had a triangular beak with a pointed ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appalachia (landmass)
During most of the Late Cretaceous (100.5 to 66 million years ago) the eastern half of North America formed Appalachia (named for the Appalachian Mountains), an island land mass separated from Laramidia to the west by the Western Interior Seaway. This seaway had split North America into two massive landmasses due to a multitude of factors such as tectonism and sea-level fluctuations for nearly 40 million years. The seaway eventually expanded, divided across the Dakotas, and by the end of the Cretaceous, it retreated towards the Gulf of Mexico and the Hudson Bay. This left the island masses joined in the continent of North America as the Rocky Mountains rose. From the Cenomanian to the end of the Campanian ages of the Late Cretaceous, Appalachia was separated from the rest of North America. As the Western Interior Seaway retreated in the Maastrichtian, Laramidia and Appalachia eventually connected. Until this connection, its fauna was isolated, and developed very differently fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, or the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea (geology), inland sea that existed roughly over the present-day Great Plains of North America, splitting the continent into two landmasses, i.e. Laramidia to the west and Appalachia (landmass), Appalachia to the east. The ancient sea, which existed for 34 million years from the early Late Cretaceous (100 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma) to the earliest Paleocene (66 Ma), connected the Gulf of Mexico (then a marginal sea of the Central American Seaway) to the Arctic Ocean. At its largest extent, the seaway was deep, wide and over long. Origin and geology By the late Cretaceous, Eurasia and the Americas had separated along the south Atlantic, and subduction on the west coast of the Americas had commenced, resulting in the Laramide orogeny, the early phase of growth of the modern Rocky Mountains. The Western Interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utahceratops
''Utahceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 76.4~75.5 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period (geology), period in what is now Utah. ''Utahceratops'' was a large-sized, robustly-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated long. Discovery The genus name ''Utahceratops'', means "horned face from Utah", and is derived from the state of Utah and Greek language, Greek words "keras" (κέρας) meaning "horn" and "ops" (ὤψ) referring to the "face". The specific name (zoology), specific name ''gettyi'', is derived from the name of Mike Getty, who discovered the holotype and has played a pivotal role in the recovery of fossils from the Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument (GSENM). It was first named by Scott D. Sampson, Mark A. Loewen, Andrew A. Farke, Eric M. Roberts, Catherine Forster, Catherine A. Forster, Joshua A. Smith and Alan L. Titus in 2010 in paleontology, 2010, and the typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in North Africa during the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Late Cretaceous. The two main families of ankylosaurians, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae primarily originated from the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia), but the more basal Parankylosauria originated from southern Gondwana (South America, Australia and Antarctica) during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), also hadrosaurs or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as ''Edmontosaurus'' and ''Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Late Jurassic/Early Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, and South America. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a Glossary of dinosaur anatomy#predentary, predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycephalosauria
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephalosaurs lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, dating between about 85.8 and 66 million years ago. They are exclusive to the Northern Hemisphere, all of them being found in North America and Asia. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/omnivorous animals with thick skulls. Skulls can be domed, flat, or wedge-shaped depending on the species, and are all heavily ossified. The domes were often surrounded by nodes and/or spikes. Partial skeletons have been found of several pachycephalosaur species, but to date no complete skeletons have been discovered. Often isolated skull fragments are the only bones that are found. Candidates for the earliest-known pachycephalosaur include ''Ferganocephale adenticulatum'' from Middle Jurassic Period strata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
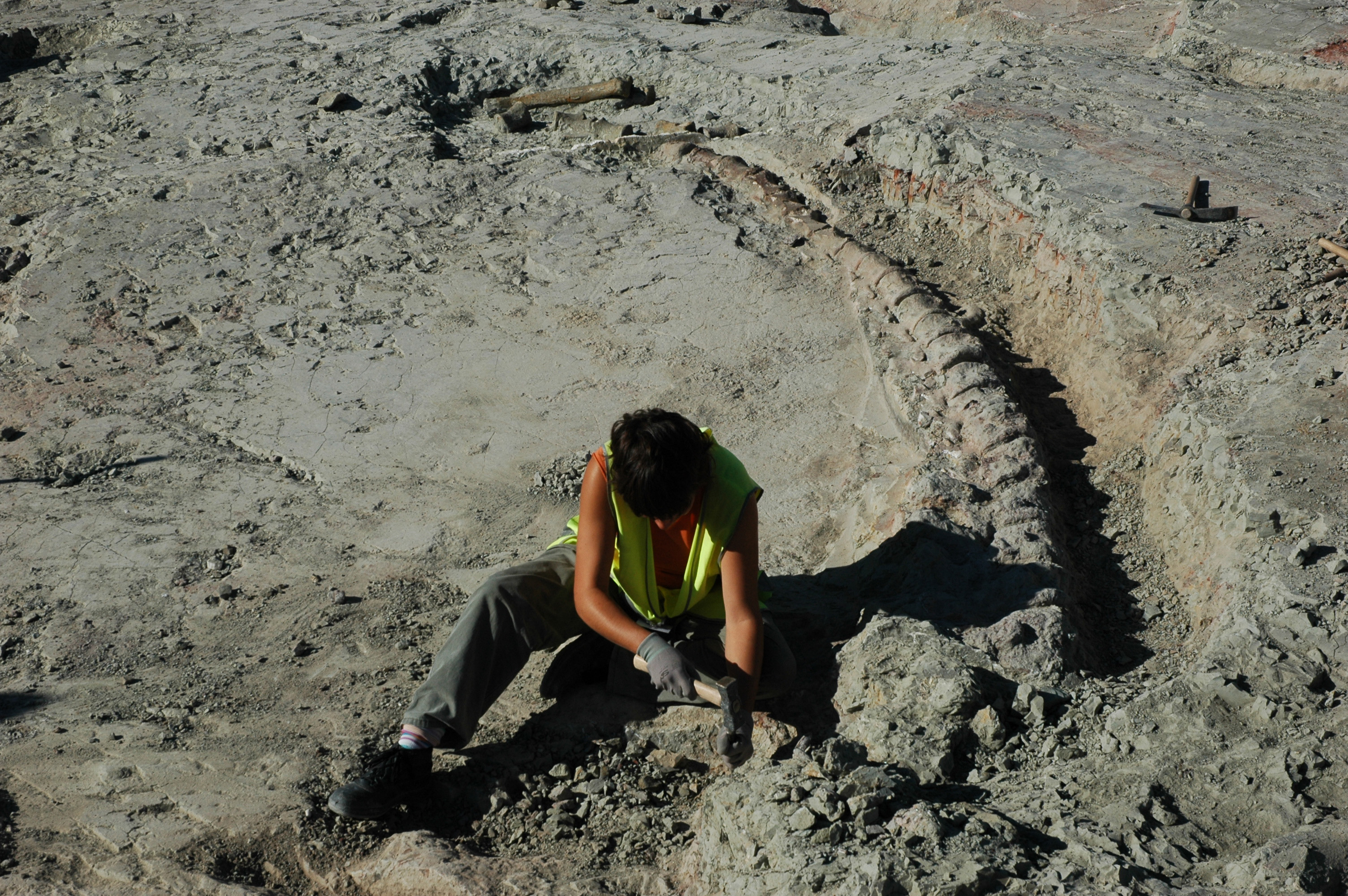
Titanosauria
Titanosaurs (or titanosaurians; members of the group Titanosauria) were a diverse group of Sauropoda, sauropod dinosaurs, including genera from all seven continents. The titanosaurs were the last surviving group of long-necked sauropods, with taxa still thriving at the time of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous. This group includes some of the Largest land animal, largest land animals known to have ever existed, such as ''Patagotitan'', estimated at long with a mass of , and the comparably-sized ''Argentinosaurus'' and ''Puertasaurus'' from the Patagonia, same region. The group's name alludes to the mythological Titan (mythology), Titans of ancient Greek mythology, via the type genus (now considered a ''nomen dubium)'' ''Titanosaurus''. Together with the Brachiosauridae, brachiosaurids and relatives, titanosaurs make up the larger sauropod clade Titanosauriformes. Titanosaurs have long been a poorly-known group, and the rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Ancient Greek, Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivore, herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Asia and Europe, during the Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Late Jurassic of Asia. The earliest known ceratopsian, ''Yinlong downsi'', lived between 161.2 and 155.7 million years ago.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2011) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages,'Winter 2010 Appendix./ref> The last ceratopsian species, ''Triceratops prorsus'', became extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, . ''Triceratops'' is by far the best-known ceratopsian to the general public. It is traditional for ceratopsian genus names to end in "''-ceratops''", although this is not always the case. One of the first named genera was ''Ceratops'' itself, which lent its name to the group, although it is considered a ''nomen dubium'' tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of North America With The Western Interior Seaway During The Campanian (Upper Cretaceous)
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropoda
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from ''wikt:sauro-, sauro-'' + ''wikt:-pod, -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their body), and four thick, pillar-like legs. They are notable for the enormous sizes attained by some species, and the group includes the largest animals to have ever lived on land. Well-known genus, genera include ''Apatosaurus'', ''Argentinosaurus'', ''Alamosaurus'', ''Brachiosaurus'', ''Camarasaurus'', ''Diplodocus,'' and ''Mamenchisaurus''. The oldest known unequivocal sauropod dinosaurs are known from the Early Jurassic. ''Isanosaurus'' and ''Antetonitrus'' were originally described as Triassic sauropods, but their age, and in the case of ''Antetonitrus'' also its sauropod status, were subsequently questioned. Sauropod-like sauropodomorph tracks from the Fleming Fjord Formation (Greenland) might, however, indicate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |