|
Lapwing (1787 Sloop)
''Lapwing'' was a sloop launched in 1787, that in 1790 traded between London and Africa. She then disappeared from ''Lloyd's Register'' between 1793 and 1798. She reappeared in 1799 as a Bristol coaster and was last listed in 1804. Origins ''Lloyd's Register'' gave her master as Williams and her owner as "G. Sharpe". Granville Sharp acquired ''Lapwing'' to facilitate the work of the St George's Bay Company in providing a safe haven for destitute Africans in Sierra Leone and elsewhere. The broker for the company purchased ''Lapwing'' for £186 on 12 February 1790 at the Customs House. ''Lapwing'' herself was in the " condemned hold", a location in Wapping, London where ships seized for smuggling were held before Customs disposed of them. The ''Lapwing'' Expedition ''Lapwing'' set sail for Sierra Leone in late 1790 carrying relief supplies for the settlers there. She was at Bance Island when the enslaving ship arrived in June 1791 carrying as passengers Dr. Alexander Falco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granville Sharp
Granville Sharp (10 November 1735 – 6 July 1813) was one of the first Kingdom of Great Britain, British campaigners for the Abolitionism in the United Kingdom, abolition of the slave trade. He also involved himself in trying to correct other social injustices. Sharp formulated the plan to settle black people in Sierra Leone, and founded the St George's Bay Company, a forerunner of the Sierra Leone Company. His efforts led to both the founding of the Province of Freedom, and later on Freetown, Sierra Leone, and so he is considered to be one of the founding fathers of Sierra Leone. He was also a biblical scholar, a classicism, classicist, and a talented musician. Life Granville Sharp was the son of Judith Wheler (d. 1757) and Thomas Sharp (archdeacon), Thomas Sharp (1693–1759), Archdeacon of Northumberland, prolific theological writer and biographer of his father, John Sharp (archbishop), John Sharp, Archbishop of York. Judith was the daughter of travel writer George Wheler ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clapham Sect
The Clapham Sect, or Clapham Saints, were a group of social reformers associated with Clapham in the period from the 1780s to the 1840s. Despite the label "sect", most members remained in the established (and dominant) Church of England, which was highly interwoven with offices of state. However, its successors were in many cases outside of the established Anglican Church. History The Clapham movement grew from 18th-century evangelical trends in the Church of England (the Anglican Church) and started to coalesce around residents of Clapham, especially during the rectorship there of John Venn (in office: 1792-1813) and came to engage in systematically advocating social reform. In the course of time the growth of evangelical Christian revivalism in England and the movement for Catholic emancipation fed into a waning of the old precept that every Englishman automatically counted as an Anglican. Some new Christian groups (such as the Methodists and the Plymouth Brethren) mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1787 Ships
Events January–March * January 9 – The North Carolina General Assembly authorizes nine commissioners to purchase of land for the seat of Chatham County. The town is named Pittsborough (later shortened to Pittsboro), for William Pitt the Younger. * January 11 – William Herschel discovers Titania and Oberon, two moons of Uranus. * January 19 – Mozart's '' Symphony No. 38'' is premièred in Prague. * February 2 – Arthur St. Clair of Pennsylvania is chosen as the new President of the Congress of the Confederation.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p167 * February 4 – Shays' Rebellion in Massachusetts fails. * February 21 – The Confederation Congress sends word to the 13 states that a convention will be held in Philadelphia on May 14 to revise the Articles of Confederation. * February 28 – A charter is gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Sail Sloops
Age or AGE may refer to: Time and its effects * Age, the amount of time someone or something has been alive or has existed ** East Asian age reckoning, an Asian system of marking age starting at 1 * Ageing or aging, the process of becoming older ** Senescence, the gradual deterioration of biological function with age ** Human development (biology) * Periodization, the process of categorizing the past into discrete named blocks of time ** Ages of Man, the stages of human existence on the Earth according to Greek mythology and its subsequent Roman interpretation **Prehistoric age Places * AGE, the IATA airport code for Wangerooge Airfield, in Lower Saxony, Germany People * Åge, a given name * Aage, a given name * Agenore Incrocci, an Italian screenwriter Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * ''Ages'', worlds in the ''Myst'' video game series Music * "Age" (song), a song by Jim and Ingrid Croce Periodicals * ''Age'' (journal), a scientific journal on ageing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas, Isle Of Man
Douglas ( gv, Doolish, ) is the capital and largest town of the Isle of Man, with a population of 26,677 (2021). It is located at the mouth of the River Douglas, and on a sweeping bay of . The River Douglas forms part of the town's harbour and main commercial port. Douglas was a small settlement until it grew rapidly as a result of links with the English port of Liverpool in the 18th century. Further population growth came in the following century, resulting during the 1860s in a staged transfer of the High Courts, the Lieutenant Governor's residence, and finally the seat of the legislature, Tynwald, to Douglas from the ancient capital, Castletown. The town is the Island's main hub for business, finance, legal services, shipping, transport, shopping, and entertainment. The annual Isle of Man TT motorcycle races start and finish in Douglas. History Early history In the absence of any archaeological data, the origins of the town may be revealed by analysis of the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Thornton (reformer)
Henry Thornton (10 March 1760 – 16 January 1815) was an English economist, banker, philanthropist and parliamentarian. Early life He was the son of John Thornton (1720–1790) of Clapham, London, who had been one of the early patrons of the evangelical movement in Britain. At the age of five, Henry attended the school of Mr Davis at Wandsworth Common, and later with Mr Roberts at Point Pleasant, Wandsworth. From 1778 he was employed in the counting house of his cousin Godfrey Thornton, two years later joining his father's company, where he later became a partner. Career In 1784 Thornton joined the banking firm of Down and Free of London, later becoming a partner of the company which became known as Down, Thornton and Free. It was under his direction that this became one of the largest banking firms in London, with regional offices in other British cities. In 1782 Henry Thornton had been urged to seek a seat in Parliament, and applied to contest one of the two seats for Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Naimbanna
John Naimbanna (17??–1793) was a Temne Prince who visited London in 1791–1793. John was the son of Naimbanna II, the Obai (King) of the Temne people of Robanna, near Sierra Leone. The king had three sons and resolved to send one each to Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, Portugal and the Ottoman Empire to study Protestantism, Catholicism and Islam respectively. Thus in 1791 John was sent to England on the small merchant sloop ''Lapwing''. There he came under the tutelage of the reformer Henry Thornton. While in London he became a Christian, adopting the forenames Henry and Granville to honour Henry Thornton and Granville Sharp Granville Sharp (10 November 1735 – 6 July 1813) was one of the first Kingdom of Great Britain, British campaigners for the Abolitionism in the United Kingdom, abolition of the slave trade. He also involved himself in trying to correct other .... Naimbanna died of unknown causes in July 1793. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Naimbanna, John 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temne People
The Temne, also called Atemne, Témené, Temné, Téminè, Temeni, Thaimne, Themne, Thimni, Timené, Timné, Timmani, or Timni, are a West African ethnic group, They are predominantly found in the Northern Province of Sierra Leone.Temne people Encyclopædia Britannica Some Temne are also found in Guinea. The Temne constitute the largest ethnic group in , at 35.5% of the total population, which is slightly bigger than the Mend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granville Town, Sierra Leone
Cline Town is an area in Freetown, Sierra Leone. The area is named for Emmanuel Kline, a Hausa Liberated African who bought substantial property in the area. The neighborhood is in the vicinity of Granville Town, a settlement established in 1787 and re-established in 1789 prior to the founding of the Freetown settlement on 11 March 1792. Granville Town, as Cline Town was known at the time, was established in 1787 by the London-based Committee for the Relief of the Black Poor. They arranged for the transport of London's so-called Black Poor to Sierra Leone where they were amongst its original settlers. Many of these Black Poor were Black Loyalists who had decided or were forced to leave the United States after the American War of Independence; some came via several years in Nova Scotia, another British North American colony and so are known as Black Nova Scotians. All asserted a British identity. Some were formerly West Indian enslaved Africans. Some British wives also were part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Effecting The Abolition Of The Slave Trade
The Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade, also known as the Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, and sometimes referred to as the Abolition Society or Anti-Slavery Society, was a British abolitionist group formed on 22 May 1787. Slavery was abolished in all British colonies in 1833 as a result. Historians posit that this anti-slavery movement is the first peaceful social movement which all modern social movements are built upon. The society was established by twelve men; including prominent campaigners Thomas Clarkson and Granville Sharp, who, as Anglicans, were able to be more influential in Parliament than the more numerous Quaker founding members. The society worked to educate the public about the abuses of the slave trade, and achieved abolition of the international slave trade when the British Parliament passed the Slave Trade Act 1807, at which time the society ceased its activities. (The United States also prohibited the African slave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Maria Falconbridge
Anna Maria (Horwood) Falconbridge (1769-1835), was the first English woman to give a narrative account of experiences in Africa. She was born in All Saints Lane Bristol, England in 1769. Her father Charles was a local clock maker. After her parents’ death, she married Alexander Falconbridge surgeon and slave ship surgeon turned abolitionist on 16 October 1788 aged 19, in Easton in Gordano, against her family's and friends' wishes. After their marriage Anna Maria accompanied her husband to Sierra Leone twice. Once there she “described her experiences in a series of lively, informative letters”.1 Later she had the letters published. In her work ''Narrative of Two Voyages'' she defends the slave trade and ridicules her abolitionist-supporting dead husband. Visits to Africa During Anna Maria's first trip to Africa, she visited a slave-trading fort, Bance Island, in the Sierra Leone River. It would seem that Anna Maria, came from a family that took part in the slave trade but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Builder's Old Measurement
Builder's Old Measurement (BOM, bm, OM, and o.m.) is the method used in England from approximately 1650 to 1849 for calculating the cargo capacity of a ship. It is a volumetric measurement of cubic capacity. It estimated the tonnage of a ship based on length and maximum beam. It is expressed in "tons burden" ( en-em , burthen , enm , byrthen ), and abbreviated "tons bm". The formula is: : \text = \frac where: * ''Length'' is the length, in feet, from the stem to the sternpost; * '' Beam'' is the maximum beam, in feet. The Builder's Old Measurement formula remained in effect until the advent of steam propulsion. Steamships required a different method of estimating tonnage, because the ratio of length to beam was larger and a significant volume of internal space was used for boilers and machinery. In 1849, the Moorsom System was created in the United Kingdom. The Moorsom system calculates the cargo-carrying capacity in cubic feet, another method of volumetric measurem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


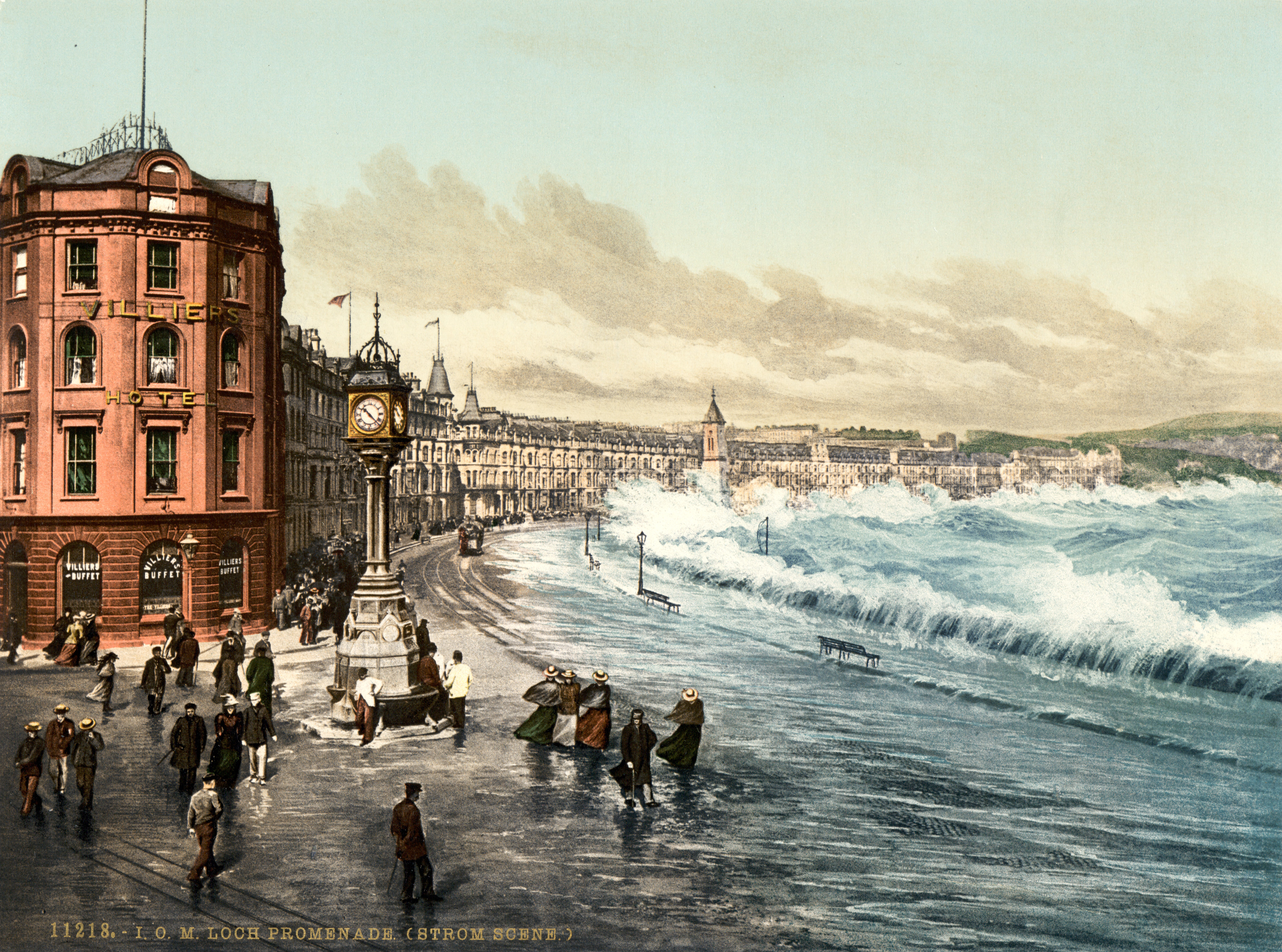


.jpg)