|
Landflucht
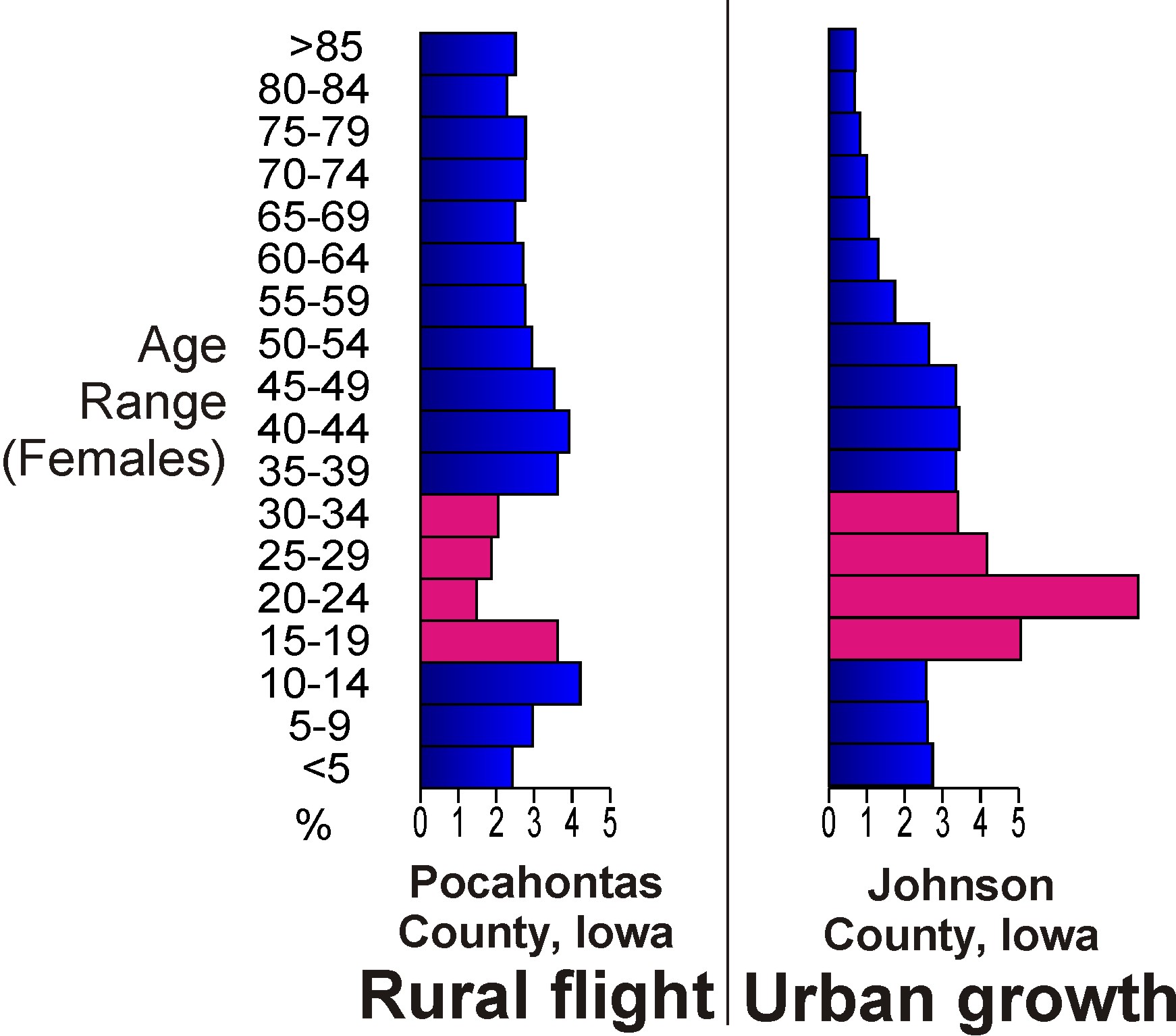
Landflucht (, "flight from the land") refers to the mass migration of peasants into the cities that occurred in Germany (and throughout much of Europe) in the late 19th century. Etymology The word ''landflucht'' has some negative connotations, as it was coined by agricultural employers (often of the German aristocracy), who were lamenting their labor shortages due to depopulation of rural areas. McLean, Kromkowski 1991, p. 56. Background In 1800, about 25% of the "German" population lived in cities, and about 75% lived in rural areas. Rankl 1999, p. 8. Beginning in the 1850s, ''ostflucht'' ("flight from the east"), reflected a growing migration from the less industrialized and urbanized east to the more developed west. The 1870s saw the beginning of the ''landflucht''—when the more industrialized regional cities became increasingly the focus of this migration. At the time, the rural population of Germany still constituted 64% of the population. By 1907, however, it had shrun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rural Flight
Rural flight (or rural exodus) is the migratory pattern of peoples from rural areas into urban areas. It is urbanization seen from the rural perspective. In industrializing economies like Britain in the eighteenth century or East Asia in the twentieth century, it can occur following the industrialization of primary industries such as agriculture, mining, fishing, and forestry—when fewer people are needed to bring the same amount of output to market—and related secondary industries (refining and processing) are consolidated. Rural exodus can also follow an ecological or human-caused catastrophe such as a famine or resource depletion. These are examples of push factors. The same phenomenon can also be brought about simply because of higher wages and educational access available in urban areas; examples of pull factors. Once rural populations fall below a critical mass, the population is too small to support certain businesses, which then also leave or close, in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostflucht
The ''Ostflucht'' (; "flight from the East") was the migration of Germans, in the later 19th century and early 20th century, from areas which were then eastern parts of Germany to more industrialized regions in central and western Germany. The migrants originated in East Prussia, West Prussia, Silesia, Pomerania and Posen; they moved to provinces along the Rhine and Ruhr rivers. Most of the migrants were ethnic Germans, but many migrants to the Ruhr were of Polish ethnicity, later known as ''Ruhrpolen''. Causes The United States, which had been the major destination of emigrants from the German East, lost much of its attraction when it stopped granting free land to settlers in 1893. At the same time, the Ruhr area prospered, leading to high demand for labor, especially in coal mining and heavy industries. This led to an East-to-West migration within the Kingdom of Prussia. Through 1907, 2,300,000 people emigrated from Prussia's eastern provinces (Pomerania, West Prussia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsches Reich (1871-1918)-en
German ''Reich'' (lit. German Realm, German Empire, from german: Deutsches Reich, ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty entirely from a continuing unitary German Volk ("national people"), with that authority and sovereignty being exercised at any one time over a unitary German "state territory" with variable boundaries and extent. Although commonly translated as "German Empire", the word ''Reich'' here better translates as "realm" or territorial "reach", in that the term does not in itself have monarchical connotations. The Federal Republic of Germany asserted, following its establishment in 1949, that within its boundaries it was the sole legal continuation of the German Reich, and consequently ''not'' a successor state. Nevertheless, the Federal Republic did not maintain the specific title ''German Reich'', and so consistently replaced the prefix ''Reich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Partition
The Prussian Partition ( pl, Zabór pruski), or Prussian Poland, is the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth acquired during the Partitions of Poland, in the late 18th century by the Kingdom of Prussia. The Prussian acquisition amounted to 141,400 km2 (54,600 sq mi) of land constituting formerly western territory of the Commonwealth. The First Partition of Poland, first partitioning led by Russian Empire, imperial Russia with Prussian participation took place in 1772; the Second Partition of Poland, second in 1793, and the Third Partition of Poland, third in 1795, resulting in Poland's elimination as a state for the next 123 years. History The Kingdom of Prussia acquired Polish territories in all three military partitions. The First Partition The First Partition of Poland in 1772 included the annexation of the formerly Polish Prussia by Frederick II of Prussia, Frederick II who quickly implanted over 57,000 German families West Prussia, there in order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Migrations
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Journal Of Sociology
The ''American Journal of Sociology'' is a Peer review, peer-reviewed bi-monthly academic journal that publishes original research and book reviews in the field of sociology and related social sciences. It was founded in 1895 as the first journal in its discipline. The current editor is Elisabeth S. Clemens. For its entire history, the journal has been housed at the University of Chicago and published by the University of Chicago Press. Past editors Past editors-in-chief of the journal have been: From 1926 to 1933, the journal was co-edited by a number of different members of the University of Chicago faculty including Ellsworth Faris, Robert E. Park, Ernest Burgess, Fay-Cooper Cole, Marion Talbot, Frederick Starr, Edward Sapir, Louis Wirth, Eyler Simpson, Edward Webster (sociologist), Edward Webster, Edwin Sutherland, William Fielding Ogburn, William Ogburn, Herbert Blumer, and Robert Redfield. Abstracting and indexing According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', its 2019 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868, and has been officially headquartered at the university's flagship campus in Berkeley, California, since its inception. As the non-profit publishing arm of the University of California system, the UC Press is fully subsidized by the university and the State of California. A third of its authors are faculty members of the university. The press publishes over 250 new books and almost four dozen multi-issue journals annually, in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, and maintains approximately 4,000 book titles in print. It is also the digital publisher of Collabra and Luminos open access (OA) initiatives. The University of California Press publishes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt (; HMH) is an American publisher of textbooks, instructional technology materials, assessments, reference works, and fiction and non-fiction for both young readers and adults. The company is based in the Financial District, Boston, Boston Financial District. It was formerly known as Houghton Mifflin Company, but it changed its name following the 2007 acquisition of Harcourt (publisher), Harcourt Publishing. Prior to March 2010, it was a subsidiary of EMPG, Education Media and Publishing Group Limited, an Irish-owned holding company registered in the Cayman Islands and formerly known as Riverdeep. History Ticknor and Allen, 1832 In 1832, William Ticknor and John Allen purchased a bookselling business in Boston and began to involve themselves in publishing; James T. Fields joined as a partner in 1843. Fields and Ticknor gradually gathered an impressive list of writers, including Ralph Waldo Emerson, Nathaniel Hawthorne, and Henry David Thoreau. The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Von Mises Institute
Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a libertarian nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, United States. It is named after the Austrian School economist Ludwig von Mises (1881–1973). It was founded in 1982 by Lew Rockwell. Its creation was funded by Ron Paul. History The Ludwig von Mises Institute was founded in 1982 by Lew Rockwell. Rockwell, who had previously served as editor for Arlington House Publishers, received the blessing of Margit von Mises during a meeting at the Russian Tea Room in New York City, and she was named the first chairman of the board. Early supporters of the institute included F.A. Hayek, Henry Hazlitt, Murray Rothbard, Ron Paul, and Burt Blumert. According to Rockwell, the motivation of the institute was to promote the specific contributions of Ludwig von Mises, who he feared was being ignored by libertarian institutions financed by Charles Koch and David Koch. As recounted by Justin Raimo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in England that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, Routledge, F1000 Research or Dovepress. It is a division of Informa plc, a United Kingdom–based publisher and conference company. Overview The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis joined Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the company was renamed Taylor & Francis Group to reflect the growing number of imprints. Taylor & Francis left the printing business in 1990, to concentrate on publishing. In 1998 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of Germany
The demography of Germany is monitored by the ''Statistisches Bundesamt'' (Federal Statistical Office of Germany). According to the most recent data, Germany's population is 84,079,811 (30 June 2022) making it the most populous country in the European Union, and the nineteenth-most populous country in the world. The total fertility rate was rated at 1.58 in 2021, which is far below the replacement rate of 2.1. For a long time Germany had one of the world's lowest fertility rates of around 1.3 to 1.4 however there has been a small increase in recent years. Due to the low birth rate there have been more deaths than births in Germany in every year since 1972, which means 2021 was the 50th consecutive year the German population would have decreased without immigration. But due to immigration the population has actually increased during the last half-century: in 2019 the number of people with a foreign background was 26%. Under this category there are counted foreigners, naturalize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
-en.png)

.jpg)

.jpg)