|
Land Day
Land Day ( ar, يوم الأرض, ''Yawm al-ʾArḍ''; he, יוֹם הַאֲדָמָה, ''Yom HaAdama''), March 30, is a day of commemoration for Arab citizens of Israel and Palestinians of the events of that date in 1976 in Israel. In 1976, in response to the Israeli government's announcement of a plan to expropriate thousands of dunams of land for state purposes, a general strike and marches were organized in Arab towns from the Galilee to the Negev.Levy and Weiss, 2002, p. 200. In the ensuing confrontations with the Israeli army and police, six unarmed Arab citizens were killed, about one hundred were wounded, and hundreds of others arrested.Israeli Arab leader on Land Day: We'll fight Israel's 'rising fascism' by Yoav Stern and Jack Khouri, '' |
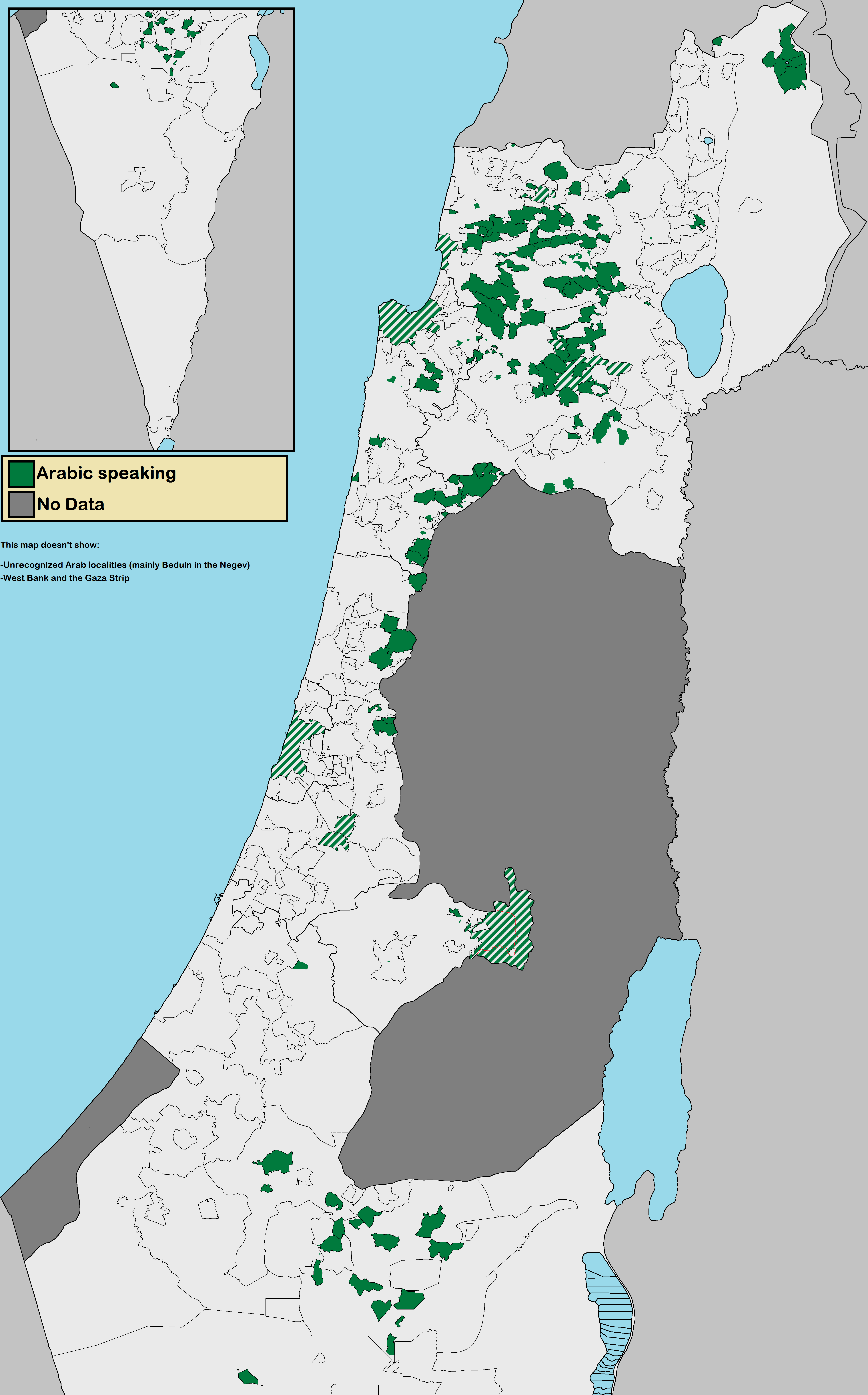
Arab Citizens Of Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel are the Demographics of Israel#Arabs, largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizenship law, Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian Citizenship Order 1925, Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee Bedouin, Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze in Israel, Druze people, and Christianity in Israel, Arab Christians and Islam in Israel, Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Green Line (Israel), Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the Palestine (region), region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and French Third Republic, France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oren Yiftachel
Oren Yiftachel ( he, אורן יפתחאל, born 1956) is an Israeli professor of political and legal geography, urban studies and urban planning at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, in Beersheba. He holds the Lynn and Lloyd Hurst Family Chair in Urban Studies. Life and career Yiftachel was born in Haifa and grew up on kibbutz Matzuva. During the 1980s and early 1990s, Yiftachel studied in Australia and Israel, specializing in urban studies and political geography. In 1990, he received a Doctor of Philosophy from the Department of Geography, the University of Western Australia, Perth, and the Faculty of Architecture and Town Planning, the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa.'Prof. Oren Yiftachel: Curriculum vita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salman Abu-Sitta
Salman Abu Sitta ( ar, سلمان ابو ستة; born 1937) is a Palestinian researcher. He is most known for mapping Palestine and developing a practical plan for implementing the right of return of Palestinian refugees. Early life Salman Abu Sitta was born in 1937 into a Palestinian family. His family's land and the village bore their name, Ma'in Abu Sitta (the Abu Sitta springwell), in Beer Sheba District of Mandatory Palestine. One morning in April 1948, he and other schoolboys were sent home for safety reasons, after they were summoned by the headmaster and told that the Jews had occupied central Palestine. Abu Sitta made the 40 km journey from Beer Sheba town to his home on foot, and six weeks later the family was attacked by the Jewish militia before Israel was declared a country. They became refugees in the Gaza Strip. Abu Sitta graduated from al-Saidiya secondary school in Cairo, Egypt, ranking first in Egypt. After graduating from Cairo University's Faculty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internally Displaced
An internally displaced person (IDP) is someone who is forced to leave their home but who remains within their country's borders. They are often referred to as refugees, although they do not fall within the legal definitions of a refugee. At the end of 2014, it was estimated there were 38.2 million IDPs worldwide, the highest level since 1989, the first year for which global statistics on IDPs are available. As of 3 May 2022 the countries with the largest IDP populations were Ukraine (8 million), Syria (7.6 million), Ethiopia (5.5 million), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (5.2 million), Colombia (4.9 million), Yemen (4.3 million), Afghanistan (3.8 million), Iraq (3.6 million), Sudan (2.2 million), South Sudan (1.9 million), Pakistan (1.4 million), Nigeria (1.2 million) and Somalia (1.1 million). The United Nations and the UNHCR support monitoring and analysis of worldwide IDPs through the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre. Definition Whereas 'refu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Present-absentees
Present absentees are Arab internally displaced persons (IDPs) who fled or were expelled from their homes in Mandatory Palestine during the 1947–1949 Palestine war but remained within the area that became the state of Israel. The term applies also to the descendants of the original IDPs.Davis, 1997, p. 49. 'Children of "absentees", whether born inside or outside of the State of Israel, are similarly classified as "absentees".' In 1950, 46,000 out of the 156,000 Israeli Arabs in Israel were considered Present absentees. According to 2015 estimates from Palestinian NGO BADIL, there are 384,200 IDPs in Israel and 334,600 IDPs in the Palestinian territories. IDPs are not permitted to live in the homes they formerly lived in, even if they were in the same area, the property still exists, and they can show that they own it. They are regarded as absent by the Israeli government because they were absent from their homes on a particular day, even if they did not intend to leave them fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land And Property Laws In Israel
Land and property laws in Israel are the property law component of Israeli law, providing the legal framework for the ownership and other ''in rem'' rights towards all forms of property in Israel, including real estate (land) and movable property. Besides tangible property, economic rights are also usually treated as property, in addition to being covered by the law of obligations. Principles The Jewish state was proclaimed on 14 May 1948 with its Declaration of Independence. The Provisional State Council's first legislative act was the "Law and Administration Ordinance of 1948", a reception statute. The act adopted all existing laws "with such modifications as may result from establishment of the State or its authorities." In respect of land law matters, Ottoman laws, as had been modified by British land law during the Mandate period, continued to apply. Most of these laws have been repealed by the last quarter of the 20th century. Over time, a modern set of codificative stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Refugees
This article lists expulsions, refugee crises and other forms of displacement that have affected Jews. Timeline The following is a list of Jewish expulsions and events that prompted significant streams of Jewish refugees. Assyrian captivity ;733/2 Common Era, BCE: Tiglath-Pileser III, King of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, sacked the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel and annexed the Transjordan (Bible), territory of the tribes of Tribe of Reuben, Reuben, Tribe of Gad, Gad and Tribe of Manasseh, Manasseh in Gilead. People from these tribes were taken captive and resettled in the region of the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River, in Halah, Habor, Hara and Tell Halaf, Gozan (). Tiglath-Pileser also captured the territory of Naphtali and the city of Janohah, Janoah in Tribe of Ephraim, Ephraim, and an Assyrian governor was placed over the region of Naphtali. According to , the population of Naphtali was deported to Assyria. ;722 Common Era, BCE: In 720s BC, 722 BCE, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action—emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel—is referred to in the Hebrew language as '' yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to various historical conflicts that led to their persecution alongside multiple instances of expu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Return
The Law of Return ( he, חֹוק הַשְׁבוּת, ''ḥok ha-shvūt'') is an Israeli law, passed on 5 July 1950, which gives Jews, people with one or more Jewish grandparent, and their spouses the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship. Section 1 of the Law of Return declares that "every Jew has the right to come to this country as an ''oleh'' mmigrant. In the Law of Return, the State of Israel gave effect to the Zionist movement's "credo" which called for the establishment of Israel as a Jewish state. In 1970, the right of entry and settlement was extended to people with at least one Jewish grandparent and a person who is married to a Jew, whether or not they are considered Jewish under Orthodox interpretations of Jewish law. On the day of arrival in Israel, or occasionally at a later date, a person who enters Israel under the Law of Return as an ''oleh'' would receive a certificate confirming their ''oleh'' status. The person then has three months ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian People
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=none, ), are an ethnonational group descending from peoples who have inhabited the region of Palestine over the millennia, and who are today culturally and linguistically Arab. Despite various wars and exoduses, roughly one half of the world's Palestinian population continues to reside in the territory of former British Palestine, now encompassing the West Bank and the Gaza Strip (the Palestinian territories) as well as Israel. In this combined area, , Palestinians constituted 49 percent of all inhabitants, encompassing the entire population of the Gaza Strip (1.865 million), the majority of the population of the West Bank (approximately 2,785,000 versus some 600,000 Israeli settlers, which includes about 200,000 in East Jerusalem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had been issued earlier that day, and a military coalition of Arab states entered the territory of British Palestine in the morning of 15 May. The day after the 29 November 1947 adoption of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine – which planned to divide Palestine into an Arab state, a Jewish state, and the Special International Regime encompassing the cities of Jerusalem and Bethlehem – an ambush of two buses carrying Jews took place in an incident regarded as the first in the civil war which broke out after the UN decision. The violence had certain continuities with the past, the Fajja bus attack being a direct response to a Lehi massacre on 19 November of five members of an Arab family, suspected of being British infor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |