|
Lampropeltis Splendida
The desert kingsnake (''Lampropeltis splendida'') is a species of kingsnake native to Texas, Arizona, and New Mexico, United States. It is not venomous, colored yellow and black. The desert kingsnake's diet consists of rodents, lizards, and smaller snakes, including rattlesnakes. They normally grow 3–4 ft long, but have been known to grow up to 6.8 ft. They are docile creatures when confronted by humans. If they do not try to escape, often they "play dead" by flipping over onto their backs and lying motionless. Some who domesticate kingsnakes, such as ranchers, do so in the hopes that the kingsnakes will feed on other snakes, which might present more of a threat. It was previously considered a subspecies of the common kingsnake. The desert kingsnake belongs to the Colubridae family, which is the largest family of snakes in the world. Appearance The snake's glossy dorsum is black or very dark brown colored, finely speckled with off-white or yellow. These pale flecks form d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spencer Fullerton Baird
Spencer Fullerton Baird (; February 3, 1823 – August 19, 1887) was an American naturalist, ornithologist, ichthyologist, Herpetology, herpetologist, and museum curator. Baird was the first curator to be named at the Smithsonian Institution. He eventually served as assistant Secretary of the Smithsonian from 1850 to 1878, and as Secretary from 1878 until 1887. He was dedicated to expanding the natural history collections of the Smithsonian which he increased from 6,000 specimens in 1850 to over 2 million by the time of his death. He also served as the U.S. United States Fish Commission, Commissioner of Fish and Fisheries from 1871 to 1887 and published over 1,000 works during his lifetime. Early life and education Spencer Fullerton Baird was born in Reading, Pennsylvania in 1823. His mother was a member of the prominent Philadelphia Biddle family; he was a nephew of Speaker of the Pennsylvania Senate Charles B. Penrose and a first cousin, once removed, of U.S. Senator Boies Penr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genus, genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small animals such as birds and rodents. Rattlesnakes receive their name from the #Rattle, rattle located at the end of their tails, which makes a loud rattling noise when tail vibration, vibrated that deters predators. Rattlesnakes are the leading contributor to snakebite injuries in North America, but rarely bite unless provoked or threatened; if treated promptly, the bites are seldom fatal. The 36 known List of rattlesnake species and subspecies, species of rattlesnakes have between 65 and 70 subspecies, all native to the Americas, ranging from central Argentina to southern Canada. The largest rattlesnake, the Eastern diamondback rattlesnake, eastern diamondback, can measure up to in length. Rattlesnakes are preyed upon by hawks, wease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Described In 1854
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern cladistic taxonomy regards that group as paraphyletic, since genetic and paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among reptiles from an evolutionary perspective. Many cladistic systems therefore redefine Reptilia as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of The Southwestern United States
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the " Sonoran Desert fauna" or the " Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Modern Greek equivalent of fauna (πανίς or rather πανίδα). ''Fauna'' is also the word for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Diamondback Rattlesnake
The western diamondback rattlesnake or Texas diamond-backWright AH, Wright AA. (1957). ''Handbook of Snakes''. Comstock Publishing Associates. (7th printing, 1985). . (''Crotalus atrox'') is a rattlesnake species and member of the viper family, found in the southwestern United States and Mexico. Like all other rattlesnakes and all other vipers, it is venomous. It is likely responsible for the majority of snakebite fatalities in northern Mexico and the greatest number of snakebites in the U.S.Norris R. (2004) "Venom Poisoning in North American Reptiles" in Campbell JA, Lamar WW. ''The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere''. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca and London. . No subspecies are currently recognized. It lives in elevations from below sea level up to . This species ranges throughout the Southwestern United States and northern half of Mexico. Currently, western diamondback rattlesnakes are not threatened or endangered. Common names Other common names for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamondback Rattlesnake
Diamondback rattlesnake may refer to: *'' Crotalus adamanteus'', a.k.a. the eastern diamondback rattlesnake, a venomous pitviper species found in the southeastern United States. *'' Crotalus atrox'', a.k.a. the western diamondback rattlesnake, a venomous pit viper species found in the southwestern United States and Mexico. *'' Crotalus oreganus'', a.k.a. the western rattlesnake, a venomous pitviper species found in North America in the western United States, parts of British Columbia and northwestern Mexico. *'' Crotalus ruber'', a.k.a. the red diamond rattlesnake, a venomous pitviper species found in southwestern California in the United States and Baja California in Mexico. {{SIA, snakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitviper
The Crotalinae, commonly known as pit vipers,Mehrtens JM (1987). ''Living Snakes of the World in Color''. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. . or pit adders, are a subfamily of vipers found in Asia and the Americas. Like all other vipers, they are venomous. They are distinguished by the presence of a heat-sensing pit organ located between the eye and the nostril on both sides of the head. Currently, 23 genera and 155 species are recognized: These are also the only viperids found in the Americas. The groups of snakes represented here include rattlesnakes, lanceheads, and Asian pit vipers. The type genus for this subfamily is ''Crotalus'', of which the type species is the timber rattlesnake, ''C. horridus''. These snakes range in size from the diminutive hump-nosed viper, '' Hypnale hypnale'', that grows to a typical total length (including tail) of only , to the bushmaster, ''Lachesis muta'', a species known to reach a maximum total length of in length. This subfamily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
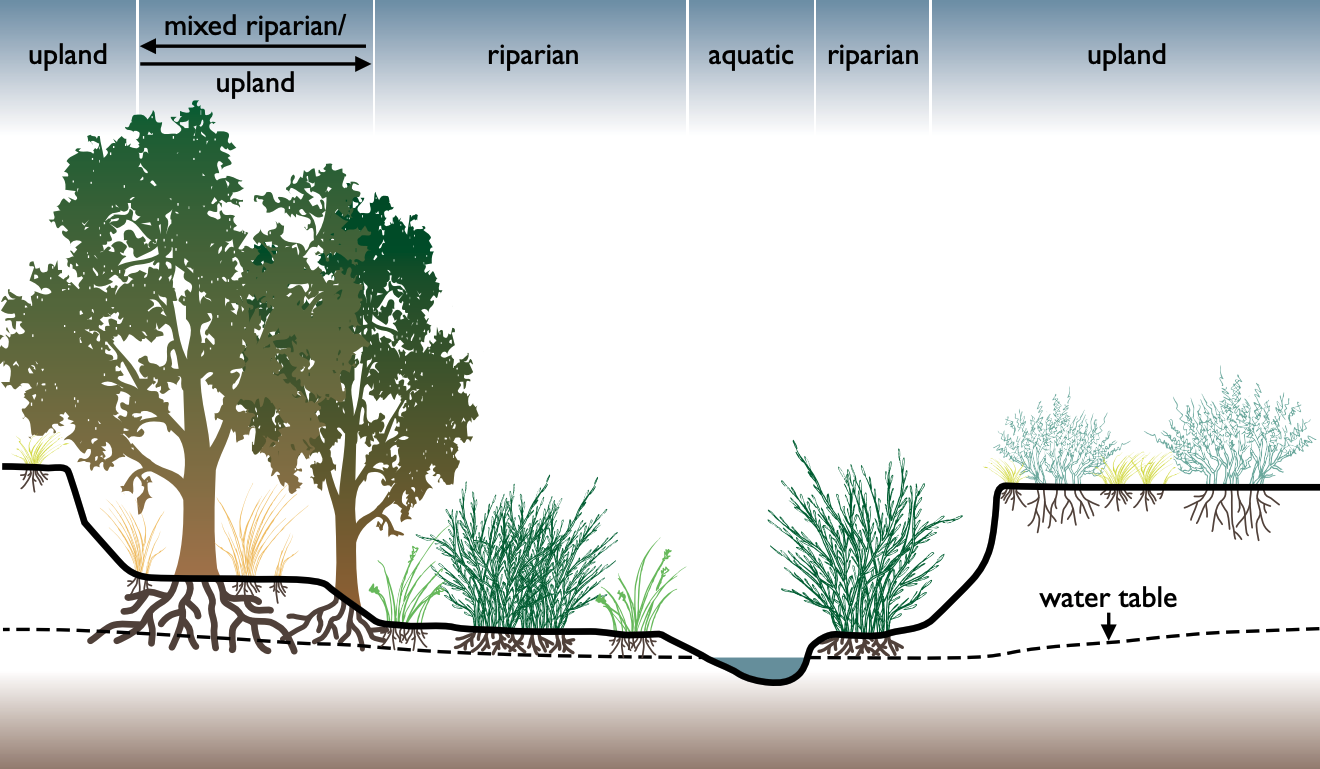
Riparian Corridor
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin '' ripa'', meaning "river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural or engineered for soil stabilization or restoration. These zones ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesic Habitat
In ecology, a mesic habitat is a type of habitat with a well-balanced or moderate supply of moisture throughout the growing season (e.g., a mesic forest, temperate hardwood forest, or dry-mesic prairie). The term derives from the Greek ''mesos'', meaning middle, indicating its relative moisture content between hydric (moist) and xeric (dry) habitats. The word "mesic" can apply to the plants or soils within the mesic habitat (i.e. mesic plants, mesic soils). Mesic habitats provide a moderate moisture content that remains relatively constant during crucial growing periods. A variety of outside factors contribute to the presence of water in the system, including streams and their offshoots, wet meadows, springs, seeps, irrigated fields, and high-elevation habitats. These factors effectively provide drought insurance during the growing season against climatic factors such as increasing temperatures, lack of rain, and the effects of urbanization. Other habitat types, such as m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |