|
Lamit Company
Lamit Company is an independent satellite operator company in Europe, operating worldwide. The company provides satellite internet and telephony to primary schools and high schools, universities, government institutions etc. Areas of the world covered by the company are: Africa (whole), Europe (whole), Middle East (whole), Russia (major parts), Australia (northern part), Americas, India, Indonesia, etc. Satellite Internet for wind farms, photovoltaic, hydroelectric plants Maritime Satellite services and coverage The company manages and operates different capacities on multiple satellites and provides fully mobile maritime connection solutions. Lamit Company also provides services for yachts which are also applicable to small vessels, ferry boats or fishing vessels. The fleet can be constantly connected to the desired terrestrial network or to other vessels, allowing the development and centralization of on board applications. The VSAT maritime solution allows the cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privately-held Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in the respective listed markets, but rather the company's stock is offered, owned, traded, exchanged privately, or over-the-counter. In the case of a closed corporation, there are a relatively small number of shareholders or company members. Related terms are closely-held corporation, unquoted company, and unlisted company. Though less visible than their publicly traded counterparts, private companies have major importance in the world's economy. In 2008, the 441 largest private companies in the United States accounted for ($1.8 trillion) in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In 2005, using a substantially smaller pool size (22.7%) for comparison, the 339 companies on ''Forbes'' survey of closely held U.S. businesses sold a trillion dollars' worth of goods and services ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
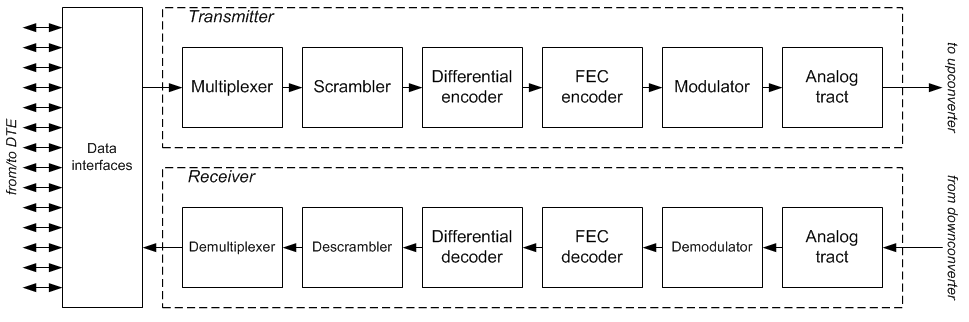
Satmodem
A satellite modem or satmodem is a modem used to establish data transfers using a communications satellite as a relay. A satellite modem's main function is to transform an input bitstream to a radio signal and vice versa. There are some devices that include only a demodulator (and no modulator, thus only allowing data to be downloaded by satellite) that are also referred to as "satellite modems." These devices are used in satellite Internet access (in this case uploaded data is transferred through a conventional PSTN modem or an ADSL modem). Satellite link A satellite modem is not the only device needed to establish a communication channel. Other equipment that is essential for creating a satellite link include satellite antennas and frequency converters. Data to be transmitted are transferred to a modem from data terminal equipment (e.g. a computer). The modem usually has intermediate frequency (IF) output (that is, 50-200 MHz), however, sometimes the signal is modulated d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companies Based In Bucharest
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared goals. Companies take various forms, such as: * voluntary associations, which may include nonprofit organizations * business entities, whose aim is generating profit * financial entities and banks * programs or educational institutions A company can be created as a legal person so that the company itself has limited liability as members perform or fail to discharge their duty according to the publicly declared incorporation, or published policy. When a company closes, it may need to be liquidated to avoid further legal obligations. Companies may associate and collectively register themselves as new companies; the resulting entities are often known as corporate groups. Meanings and definitions A company can be defined as an "artificial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Access
Internet access is the ability of individuals and organizations to connect to the Internet using computer terminals, computers, and other devices; and to access services such as email and the World Wide Web. Internet access is sold by Internet service providers (ISPs) delivering connectivity at a wide range of data signaling rate, data transfer rates via various networking technologies. Many organizations, including a growing number of municipal entities, also provide cost-free wireless access and landlines. Availability of Internet access was once limited, but has grown rapidly. In 1995, only percent of the world's population had access, with well over half of those living in the United States, and consumer use was through dial-up Internet access, dial-up. By the first decade of the 21st century, many consumers in developed nations used faster broadband technology, and by 2014, 41 percent of the world's population had access, broadband was almost ubiquitous worldwide, and glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a ''internetworking, network of networks'' that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and Web application, applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), email, electronic mail, internet telephony, telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to the development of packet switching and research commissioned by the United States Department of Defense in the 1960s to enable time-sharing of computers. The primary precursor network, the ARPANET, initially served as a backbone for interconnection of regional academic and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ku Band
The Ku band () is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies from 12 to 18 gigahertz (GHz). The symbol is short for "K-under" (originally german: Kurz-unten), because it is the lower part of the original NATO K band, which was split into three bands (Ku, K, and Ka) because of the presence of the atmospheric water vapor resonance peak at 22.24 GHz, (1.35 cm) which made the center unusable for long range transmission. In radar applications, it ranges from 12 to 18 GHz according to the formal definition of radar frequency band nomenclature in IEEE Standard 521–2002. Ku band is primarily used for satellite communications, most notably the downlink used by direct broadcast satellites to broadcast satellite television, and for specific applications such as NASA's Tracking Data Relay Satellite used for International Space Station (ISS) communications and SpaceX Starlink satellites. Ku band satellites are also u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-noise Blockconverter
A low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is the receiving device mounted on satellite dishes used for satellite TV reception, which collects the radio waves from the dish and converts them to a signal which is sent through a cable to the receiver inside the building. Also called a low-noise block, low-noise converter (LNC), or even low-noise downconverter (LND),Bains, Geoff. "Getting The Most Out Of An LNB" ''What Satellite & Digital TV'' (November, 2008) pp50-51 the device is sometimes inaccurately called a ''low-noise amplifier'' (''LNA''). The LNB is a combination of low-noise amplifier, frequency mixer, local oscillator and intermediate frequency (IF) amplifier. It serves as the RF front end of the satellite receiver, receiving the microwave signal from the satellite collected by the dish, amplifying it, and downconverting the block of frequencies to a lower block of intermediate frequencies (IF). This downconversion allows the signal to be carried to the indoor satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCPC
Single channel per carrier (SCPC) refers to using a single signal at a given frequency and bandwidth. Most often, this is used on broadcast satellites to indicate that radio stations are not multiplexed as subcarriers onto a single video carrier, but instead independently share a transponder. It may also be used on other communications satellites, or occasionally on non-satellite transmissions. In an SCPC system, satellite bandwidth is dedicated to a single source. This makes sense if it is being used for something like satellite radio, which broadcasts continuously. Another very common application is voice, where a small amount of fixed bandwidth is required. However, it does not make sense for burst transmissions like satellite internet access or telemetry, since a customer would have to pay for the satellite bandwidth even when they were not using it. Where multiple access is concerned, SCPC is essentially FDMA. Some applications use SCPC instead of TDMA, becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Television
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advancement and represented the first significant evolution in television technology since color television in the 1950s. Modern digital television is transmitted in high-definition television (HDTV) with greater resolution than analog TV. It typically uses a widescreen aspect ratio (commonly 16:9) in contrast to the narrower format of analog TV. It makes more economical use of scarce radio spectrum space; it can transmit up to seven channels in the same bandwidth as a single analog channel, and provides many new features that analog television cannot. A transition from analog to digital broadcasting began around 2000. Different digital television broadcasting standards have been adopted in different parts of the world; below are the more wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voip
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), also called IP telephony, is a method and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol (IP) networks, such as the Internet. The terms Internet telephony, broadband telephony, and broadband phone service specifically refer to the provisioning of communications services (voice, fax, SMS, voice-messaging) over the Internet, rather than via the public switched telephone network (PSTN), also known as plain old telephone service (POTS). Overview The steps and principles involved in originating VoIP telephone calls are similar to traditional digital telephony and involve signaling, channel setup, digitization of the analog voice signals, and encoding. Instead of being transmitted over a circuit-switched network, the digital information is packetized and transmission occurs as IP packets over a packet-switched network. They transport media streams using special media delivery proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Device Bandwidths
This is a list of interface bit rates, is a measure of information transfer rates, or digital bandwidth capacity, at which digital interfaces in a computer or network can communicate over various kinds of buses and channels. The distinction can be arbitrary between a ''computer bus'', often closer in space, and larger telecommunications networks. Many device interfaces or protocols (e.g., SATA, USB, SAS, PCIe) are used both inside many-device boxes, such as a PC, and one-device-boxes, such as a hard drive enclosure. Accordingly, this page lists both the internal ribbon and external communications cable standards together in one sortable table. Factors limiting actual performance, criteria for real decisions Most of the listed rates are theoretical maximum throughput measures; in practice, the actual effective throughput is almost inevitably lower in proportion to the load from other devices ( network/ bus contention), physical or temporal distances, and other overhead in da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to avoid orbital decay by the atmosphere. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |