|
Laminaria Stick
Osmotic dilators, also known as hygroscopic dilators, are medical implements used to dilate the uterine cervix by swelling as they absorb fluid from surrounding tissue. They may be composed of natural or synthetic materials. A laminaria stick or tent is a thin rod made of the stems of dried ''Laminaria'', a genus of kelp. Laminaria sticks can be generated from ''Laminaria japonica'' and ''Laminaria digitata''. Second generation dilators such as Dilapan-S are composed of polyacrylonitrile, a plastic polymer. The hygroscopic nature of the polymer causes the dilator to absorb fluid and expand. Use in obstetrics and gynecology Osmotic dilators are most commonly used to slowly dilate and soften the cervix prior to surgical abortion, a process referred to as cervical preparation. Adequate cervical preparation is important prior to surgical abortions because it helps to prevent complications of dilation and evacuation (D&E), such as laceration of the cervix. Cervical preparation can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmotic Dilators 1
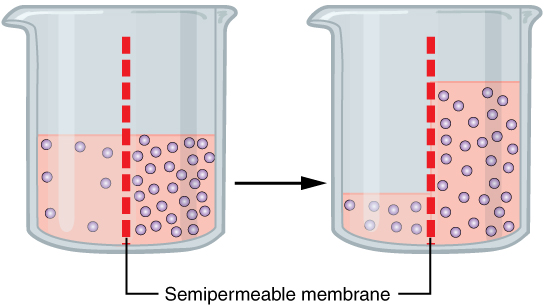
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to prevent net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman's life cycle. For example, women in the fertile years of their reproductive cycle tend to have larger cervixes than postmenopausal women; likewise, women who have produced offspring have a larger cervix than those who have not. In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the ''internal os'' and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the ''external os''. Between them is a conduit commonly called the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminaria
''Laminaria'' is a genus of brown algae, brown seaweed in the order Kelp, Laminariales (kelp), comprising 31 species native to the north Atlantic and northern Pacific Oceans. This economically important genus is characterized by long, leathery Lamina (algae), laminae and relatively large size. Some species are called Devil's apron, due to their shape, or sea colander, due to the perforations present on the Lamina (algae), lamina. Others are referred to as ''tangle''. ''Laminaria'' form a habitat for many fish and invertebrates. The life cycle of ''Laminaria'' has wikt:heteromorphic, heteromorphic alternation of generations which differs from ''Fucus''. At meiosis the male and female zoospores are produced separately, then germinate into male and female gametophytes. The female egg matures in the oogonium until the male sperm fertilizes it. Life-Cycle: The most apparent form of ''Laminaria'' is its sporophyte phase, a structure composed of the holdfast (biology), holdfast, the Sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelp
Kelps are large brown algae or seaweeds that make up the order (biology), order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genus, genera. Despite its appearance and use of photosynthesis in chloroplasts, kelp is technically not a plant but a stramenopile (a group containing many protists). Kelp grow from stalks close together in kelp forest, very dense areas like forests under shallow temperate and Arctic oceans. They were previously thought to have appeared in the Miocene, 5 to 23 million years ago based on fossils from California. New fossils of kelp holdfasts from early Oligocene rocks in Washington State show that kelps were present in the northeastern Pacific Ocean by at least 32 million years ago. The organisms require nutrient-rich water with temperatures between . They are known for their high growth rate—the genera ''Macrocystis'' and ''Nereocystis'' can grow as fast as half a metre a day (that is, about 20 inches a day), ultimately reaching .Thomas, D. 2002. ''Seaweed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylonitrile
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula (CH2CHCN)n. Almost all PAN resins are copolymers with acrylonitrile as the main monomer. PAN is used to produce large variety of products including ultra filtration membranes, hollow fibers for reverse osmosis, fibers for textiles, and oxidized PAN fibers. PAN fibers are the chemical precursor of very high-quality carbon fiber. PAN is first thermally oxidized in air at 230 °C to form an oxidized PAN fiber and then carbonized above 1000 °C in inert atmosphere to make carbon fibers found in a variety of both high-tech and common daily applications such as civil and military aircraft primary and secondary structures, missiles, solid propellant rocket motors, pressure vessels, fishing rods, tennis rackets and bicycle frames. It is a component repeat unit in several important copolymers, such as styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology And Minimally Invasive Therapy ...
External linksList of journals on Medknow Publications website * Medknow Publications Medknow Publications also known as Wolters Kluwer Medknow or simply Medknow, is a publisher of academic journals on behalf of learned societies and associations. Previously an independent Indian publisher, Medknow is now part of within Wolters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption (chemistry), absorption or adsorption from the surrounding Natural environment, environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g. changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they dissolve in the water they absorb, forming an aqueous solution. Hygroscopy is essential for many plant and animal species' attainment of hydration, nutrition, reproduction and/or seed dispersal. Biological evolution created hygroscopic solutions for water harvesting, filament tensile strength, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilation And Evacuation
Dilation and evacuation (D&E) or dilatation and evacuation (British English) is the dilation of the cervix and surgical evacuation of the uterus (potentially including the fetus, placenta and other tissue) after the first trimester of pregnancy. It is the most common method and procedure for abortions in the second trimester of pregnancy. The procedure can also be used to remove a miscarried fetus from the womb. In various health care centers it may be called by different names: * D&E (dilation and evacuation) * ERPOC (evacuation of retained products of conception) * TOP or STOP ((surgical) termination of pregnancy) D&E normally refers to a specific second trimester procedure. However, some sources use the term D&E to refer more generally to any procedure that involves the processes of dilation and evacuation, which includes the first trimester procedures of manual and electric vacuum aspiration. Intact dilation and extraction (D&X) is a different procedural variation on D&E. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is the inspection of the uterine cavity by endoscopy with access through the cervix. It allows for the diagnosis of intrauterine pathology and serves as a method for surgical intervention (operative hysteroscopy). Hysteroscope A hysteroscope is an endoscope that carries optical and light channels or fibers. It is introduced in a sheath that provides an inflow and outflow channel for insufflation of the uterine cavity. In addition, an operative channel may be present to introduce scissors, graspers or biopsy instruments. A hysteroscopic resectoscope is similar to a transurethral resectoscope and allows entry of an electric loop to shave off tissue, for instance to eliminate a fibroid. A ''contact hysteroscope'' is a hysteroscope that does not use distention media. Procedure Hysteroscopy has been carried out in hospitals, surgical centers and doctors' offices. It is best carried out when the endometrium is relatively thin, that is after a menstruation. Both diagnost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilation And Curettage
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to: Physiology or medicine * Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc. * Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex * Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and surgical removal of the contents of the uterus * Dilation and evacuation, the dilation of the cervix and evacuation of the contents of the uterus * Esophageal dilation, a procedure for widening a narrowed esophagus * Pupillary dilation (also called mydriasis), the widening of the pupil of the eye * Vasodilation, the widening of luminal diameter in blood vessels Mathematics * Dilation (affine geometry), an affine transformation * Dilation (metric space), a function from a metric space into itself * Dilation (operator theory), a dilation of an operator on a Hilbert space * Dilation (morphology), an operation in mathematical morphology * Scaling (geometry) In affine geometry, uniform scaling (or isotropic scaling) is a linear tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmotic Dilators 3
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to prevent net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeable. In general, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculum (medical)
A speculum (Latin for 'mirror'; : specula or speculums) is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision. History Vaginal and anal specula were used by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans, and speculum Artifact (archaeology), artifacts have been found in Pompeii. The modern vaginal speculum, developed by J. Marion Sims, consists of a hollow cylinder with a rounded end that is divided into two hinged parts, somewhat like the beak of a duck. This speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate it for examination of the vagina and cervix. A more modern vaginal speculum was developed by Marie Boivin (1773–1841), a French midwife, inventor, and obstetrics writer who has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |