|
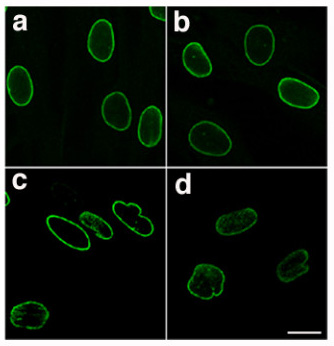
Lamin B2
Lamin B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LMNB2'' gene. It is the second of two type B nuclear lamins, and it is associated with laminopathies. See also * Lamin B receptor Lamin-B receptor is a protein, and in humans, it is encoded by the ''LBR'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ERG4/ ERG24 family. It localizes to the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope and anchors the lamina a ... * Barraquer–Simons syndrome * Pelger–Huët anomaly External links * References Genes mutated in mice {{biochemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Lamins
Lamins, also known as nuclear lamins, are fibrous proteins in type V intermediate filaments, providing structural function and transcriptional regulation in the cell nucleus. Nuclear lamins interact with inner nuclear membrane proteins to form the nuclear lamina on the interior of the nuclear envelope. Lamins have elastic and mechanosensitive properties, and can alter gene regulation in a feedback response to mechanical cues. Lamins are present in all animals but are not found in microorganisms, plants or fungi. Lamin proteins are involved in the disassembling and reforming of the nuclear envelope during mitosis, the positioning of nuclear pores, and programmed cell death. Mutations in lamin genes can result in several genetic laminopathies, which may be life-threatening. History Lamins were first identified in the cell nucleus, using electron-microscopy. However, they were not recognized as vital components of nuclear structural support until 1975. During this time period, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laminopathies
Laminopathies ('' lamino-'' + '' -pathy'') are a group of rare genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes encoding proteins of the nuclear lamina. Since the first reports of laminopathies in the late 1990s, increased research efforts have started to uncover the vital role of nuclear envelope proteins in cell and tissue integrity in animals. Laminopathies are a group of degenerative diseases, other disorders associated with inner nuclear membrane proteins are known as ''nuclear envelopathies''. Symptoms and signs Laminopathies and other nuclear envelopathies have a large variety of clinical symptoms including skeletal and/or cardiac muscular dystrophy, lipodystrophy and diabetes, dysplasia, dermo- or neuropathy, leukodystrophy, and progeria (premature aging). Most of these symptoms develop after birth, typically during childhood or adolescence. Some laminopathies however may lead to an early death, and mutations of lamin B1 ( LMNB1 gene) may be lethal before or at birth. Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamin B Receptor
Lamin-B receptor is a protein, and in humans, it is encoded by the ''LBR'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the ERG4/ ERG24 family. It localizes to the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope and anchors the lamina and the heterochromatin to the membrane. It may mediate the interaction between chromatin and lamin B. Mutations of this gene has been associated with autosomal recessive HEM/Greenberg skeletal dysplasia. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified. Clinical significance There is evidence tying it to Greenberg dysplasia and Pelger-Huet anomaly. Interactions Lamin B receptor has been shown to interact with CBX3 and CBX5. LBR also interacts with long non-coding RNA XIST in mouse cells and potentially assist the spreading XIST across X chromosome The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barraquer–Simons Syndrome
Barraquer–Simons syndrome is a rare form of lipodystrophy, which usually first affects the head, and then spreads to the thorax. It is named for Luis Barraquer Roviralta (1855–1928), a Spanish physician, and Arthur Simons (1879–1942), a German physician. Some evidence links it to '' LMNB2''. Causes The etiology of this condition has not been fully elucidated. Lipodystrophy is often associated with glomerulonephritis, low C3 serum complement levels, and the presence of a C3 nephritic factor. C3 nephritic factor is a serum immunoglobulin G that interacts with the C3bBb alternative pathway convertase to activate C3. C3 nephritic factor induces the lysis of adipocytes that secrete adipsin, a product identical to complement factor D. The distribution of the lipoatrophy is postulated to be dictated by the variable amounts of adipsin secreted by the adipocytes at different locations. Human PTRF mutations may cause secondary deficiency of caveolins, resulting in generalized lipodys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelger–Huët Anomaly
Pelger–Huët anomaly is a blood laminopathy associated with the lamin B receptor, wherein several types of white blood cells (neutrophils and eosinophils) have nuclei with unusual shape (being bilobed, peanut or dumbbell-shaped instead of the normal trilobed shape) and unusual structure (coarse and lumpy). It is a genetic disorder with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Heterozygotes are clinically normal, although their neutrophils may be mistaken for immature cells which may cause mistreatment in a clinical setting. Homozygotes tend to have neutrophils with rounded nuclei that do have some functional problems. Congenital Pelger–Huët anomaly Is a benign dominantly inherited defect of terminal neutrophil differentiation as a result of mutations in the lamin B receptor gene. The characteristic leukocyte appearance was first reported in 1928 by Karel Pelger (1885-1931), a Dutch Hematologist, who described leukocytes with dumbbell-shaped bilobed nuclei, a reduced num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |