|
Lambda Pegasi
Lambda Pegasi (λ Peg, λ Pegasi) is a fourth-magnitude star in the constellation Pegasus. λ Pegasi is a yellow giant with stellar classification G8II-III. With a mass of and radius that is , the star boasts a bolometric luminosity that is roughly . Its apparent magnitude was calibrated in 1983 at 3.96, yielding an absolute magnitude of -1.45. Parallax calculations place the star at a distance of roughly 112 parsecs from Earth, or 365 ± 10 light years away, about three times the distance of its line-of-sight double μ Pegasi. In the constellation, Lambda and Mu lie to the southwest of Beta Pegasi Beta Pegasi (β Pegasi, abbreviated Beta Peg, β Peg), formally named Scheat , is a red giant star and the second-brightest star (after Epsilon Pegasi) in the constellation of Pegasus. It forms the upper right corner of the Great Square ..., the nearest bright star. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Lambda Pegasi Pegasi, Lambda G-type giants Pegasus (conste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pegasus (constellation)
Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognised today. With an apparent magnitude varying between 2.37 and 2.45, the brightest star in Pegasus is the orange supergiant Epsilon Pegasi, also known as Enif, which marks the horse's muzzle. Alpha (Markab), Beta (Scheat), and Gamma (Algenib), together with Alpha Andromedae (Alpheratz) form the large asterism known as the ''Square of Pegasus''. Twelve star systems have been found to have exoplanets. 51 Pegasi was the first Sun-like star discovered to have an exoplanet companion. Mythology The Babylonian constellation IKU (field) had four stars of which three were later part of the Greek constellation ''Hippos'' (Pegasus). Pegasus, in Greek mythology, was a winged horse with magical powers. One myth regarding his powers says that his hooves dug o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparcos Objects
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the first high-precision measurements of the intrinsic brightnesses (compared to the less precise apparent brightness), proper motions, and parallaxes of stars, enabling better calculations of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial velocity measurements from spectroscopy, astrophysicists were able to finally measure all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting ''Hipparcos Catalogue'', a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision ''Tycho Catalogue'' of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. ''Hipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flamsteed Objects
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called '' Atlas Coelestis'', both published posthumously. He also made the first recorded observations of Uranus, although he mistakenly catalogued it as a star, and he laid the foundation stone for the Royal Greenwich Observatory. Life Flamsteed was born in Denby, Derbyshire, England, the only son of Stephen Flamsteed and his first wife, Mary Spadman. He was educated at the free school of Derby and at Derby School, in St Peter's Churchyard, Derby, near where his father carried on a malting business. At that time, most masters of the school were Puritans. Flamsteed had a solid knowledge of Latin, essential for reading the scientific literature of the day, and a love of history, leaving the school in May 1662.Birks, John L. (1999) ''John Flamsteed, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-type Bright Giants
Gaea Gaea is one of the Elder Gods of Earth. Gaia Gaia, also known as the Guardian of the Universal Amalgamator, is a fictional superhero, depicted as possibly being a mutant or extraterrestrial. Created by Larry Hama, she first appeared in ''Generation X'' #37. Not much is known about Gaia's origin besides her having spent thousands of years chained to the Universal Amalgamator at the end of Time, a device that would be used to merge all sentient consciousnesses into one being.''Generation X'' #37 Gaia was apparently the safeguard that was supposed to prevent the Amalgamator from being activated by malicious people. She even claimed that her entire galaxy was wiped out at one point for her refusing to activate the Amalgamator.''Generation X'' #38 However, when M-Plate, the synthesis of Emplate and M, tried to have Synch use his power to tap into Gaia's and activate the Amalgamator, Everett refused. The Citadel of the Universal Amalgamator began to crumble around them and Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-type Giants
Gaea Gaea is one of the Elder Gods of Earth. Gaia Gaia, also known as the Guardian of the Universal Amalgamator, is a fictional superhero, depicted as possibly being a mutant or extraterrestrial. Created by Larry Hama, she first appeared in '' Generation X'' #37. Not much is known about Gaia's origin besides her having spent thousands of years chained to the Universal Amalgamator at the end of Time, a device that would be used to merge all sentient consciousnesses into one being.''Generation X'' #37 Gaia was apparently the safeguard that was supposed to prevent the Amalgamator from being activated by malicious people. She even claimed that her entire galaxy was wiped out at one point for her refusing to activate the Amalgamator.''Generation X'' #38 However, when M-Plate, the synthesis of Emplate and M, tried to have Synch use his power to tap into Gaia's and activate the Amalgamator, Everett refused. The Citadel of the Universal Amalgamator began to crumble around them and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer Objects
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceuticals; consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the Euro Stoxx 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer and dyer Friedrich Weskott. As was common in this era, the company was established as a dyestuffs producer. The versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand their business into other areas, and in 1899 Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. In 1904 Bayer received a trademark for the "Bayer Cross" logo, which was subsequently stamped onto each aspirin tablet, creating an iconic product that is still sold by Bayer. Other commonly known p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
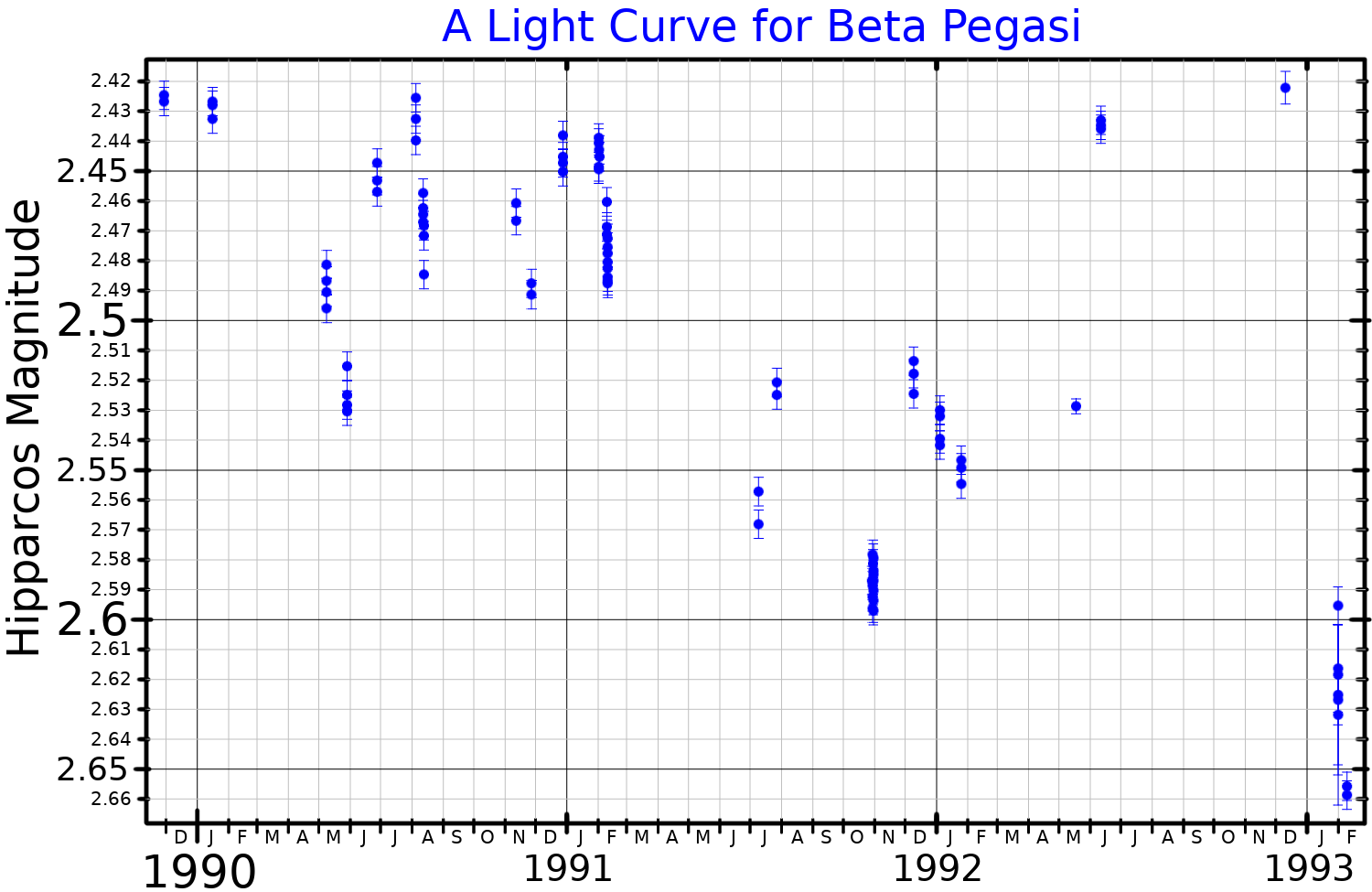
Beta Pegasi
Beta Pegasi (β Pegasi, abbreviated Beta Peg, β Peg), formally named Scheat , is a red giant star and the second-brightest star (after Epsilon Pegasi) in the constellation of Pegasus. It forms the upper right corner of the Great Square of Pegasus, a prominent rectangular asterism. Nomenclature ''β Pegasi'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Pegasi'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name of ''Scheat'', a name that had also been used for Delta Aquarii. The name was derived from the Arabic ''Al Sā'id'' "the upper arm", or from ''Sa'd''. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organised a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardise proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Scheat'' for this star (the name ''Skat'' was later approved for Delta Aquarii). In Chinese, (), meaning '' Encampment'', refers to an asterism consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mu Pegasi
Mu Pegasi or μ Pegasi, formally named Sadalbari (), is a star in the northern constellation of Pegasus. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is 3.5, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye even on a moonlit night. Based upon parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately from the Sun. Nomenclature ''μ Pegasi'' ( Latinised to ''Mu Pegasi'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Sadalbari'', which derives from ar, سعد بارع ''saʿd al-bāriʿ'', the “auspicious star of the splendid one.” In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Sadalbari'' for this star on 21 August 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Resting Palace'', refers to an asterism consisting of Mu Pegasi, Lambda Pegasi, Omicron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (au), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 au subtends an angle of one arcsecond ( of a degree). This corresponds to astronomical units, i.e. 1\, \mathrm = 1/\tan \left( \ \mathrm \right)\, \mathrm. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about from the Sun. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand. The word ''parsec'' is a portmanteau of "parallax of one second" and was coined by the British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913 to make calculations of astronomical distances from only raw observational data easy for astronomers. Partly for this reason, it is the unit preferred in astronomy and astrophysics, though the light-year remains prominent in popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects when observed from different positions, so parallax can be used to determine distances. To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder. Parallax also affects opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)