|
Lake Wallenpaupack
Lake Wallenpaupack () is a reservoir in Northeastern Pennsylvania. After Raystown Lake, it is the second-largest lake contained entirely in Pennsylvania. It comprises of shoreline, with a length of and a maximum depth of , and has a surface area in excess of . It was created in 1926 by the PPL Corporation for hydroelectric purposes, as well as flood control, but it is best known as one of several major recreational destinations in the Pocono Mountains. It is located near the Borough of Hawley, and forms part of the boundary between Pike and Wayne Counties. See map. History The indigenous Lenape people named the area "Wallenpaupack"m which means "the Stream of Swift and Slow Water." William Penn later owned the land and then deeded it to his son Thomas Penn. Upon his death, it went to the Penn estate, which sold about in 1793 to James Wilson, one of the signers of the Declaration of Independence. To create the lake, PPL Corporation constructed a dam on Wallenpaupack Cree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pike County, Pennsylvania
Pike County is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 58,535. Its county seat is Milford, Pennsylvania, Milford. The county is part of the Northeastern Pennsylvania, Northeast Pennsylvania region of the state. Pike County is included in the New York metropolitan area. History Pike County was named for General Zebulon Pike. It was organized on March 26, 1814, from part of Wayne County, Pennsylvania. Some English settlement in the area had started during the colonial years. The longtime original inhabitants were the Lenape Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans, known by the English colonists as the Delaware Indians because their territory was along the Delaware River (as named by the colonists), as well as the coastal mid-Atlantic area. In 1694, Governor Benjamin Fletcher of the colony of New York sent Captain Arent Schuyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wilson (Founding Father)
James Wilson (September 14, 1742 – August 21, 1798) was a Scottish American American Founding Father of the United States, Founding Father, legal scholar, jurist, and statesman who served as an associate justice of the United States Supreme Court from 1789 to 1798. Wilson was elected twice to the Continental Congress, and was a signatory of the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence. In 1787 he was a major participant in drafting the United States Constitution, U.S. Constitution, and became one of only six people to sign both documents. A leading legal theorist, he was one of the first four Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, Associate Justices appointed to the Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court by George Washington. In his capacity as the first professor of law at the Academy and College of Philadelphia, College of Philadelphia (a year after he was appointed as a professor at the College of Philadelphia, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nor’easter
A nor'easter (also northeaster; see below) is a large-scale extratropical cyclone in the western North Atlantic Ocean. The name derives from the direction of the winds that blow from the northeast. Typically, such storms originate as a low-pressure area that forms within of the shore between North Carolina and Massachusetts. The precipitation pattern is similar to that of other extratropical storms, although nor'easters are usually accompanied by heavy rain or snow, and can cause severe coastal flooding, coastal erosion, hurricane-force winds, or blizzard conditions. They tend to develop most often and most powerfully between the months of November and March, because of the difference in temperature between the cold polar air mass coming down from central Canada and the warm ocean waters off the upper East Coast. The susceptible regions—the upper north Atlantic coast of the United States and the Atlantic Provinces of Canada—are generally impacted by nor'easters a few ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Storm
An ice storm, also known as a glaze event or a silver storm, is a type of winter storm characterized by freezing rain. The National Weather Service, U.S. National Weather Service defines an ice storm as a storm which results in the accumulation of at least of ice on exposed surfaces. They are generally not violent storms but instead are commonly perceived as gentle rains occurring at temperatures just below freezing. Formation The formation of ice begins with a layer of above-freezing air above a layer of sub-freezing temperatures closer to the surface. Frozen Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation melts to rain while falling into the warm air layer, and then begins to refreeze in the cold layer below. If the precipitate refreezes while still in the air, it will land on the ground as ice pellets, sleet. Alternatively, the liquid droplets can continue to fall without freezing, passing through the cold air just above the surface. This thin layer of air then cools the rain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
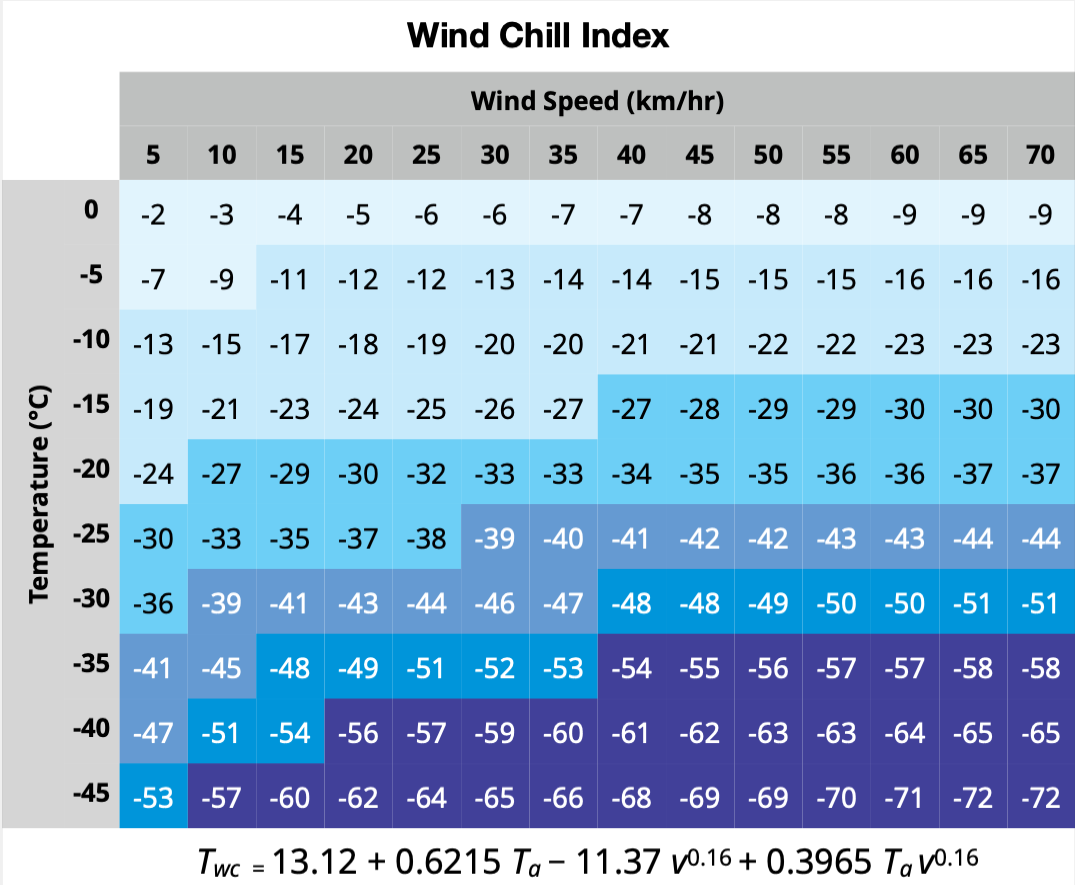
Wind Chill
Wind chill (popularly wind chill factor) is the sensation of cold produced by the wind for a given ambient air temperature on exposed skin as the air motion accelerates the rate of heat transfer from the body to the surrounding atmosphere. Its values are always lower than the air temperature in the range where the formula is valid. When the apparent temperature is higher than the air temperature, the heat index is used instead. Explanation A surface loses heat through conduction, evaporation, convection, and radiation. The rate of convection depends on both the difference in temperature between the surface and the fluid surrounding it and the velocity of that fluid with respect to the surface. As convection from a warm surface heats the air around it, an insulating boundary layer of warm air forms against the surface. Moving air disrupts this boundary layer, or epiclimate, carrying the warm air away, thereby allowing cooler air to replace the warm air against the surface and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the secretary of agriculture, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Brooke Rollins, who has served since February 13, 2025. Approximately 71% of the USDA's $213 billion budget goes towards nutrition assistance programs administered by the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS). The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (formerly known as the 'Food Stamp' program), which is the cornerstone of USDA's nutrition assistance. The United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
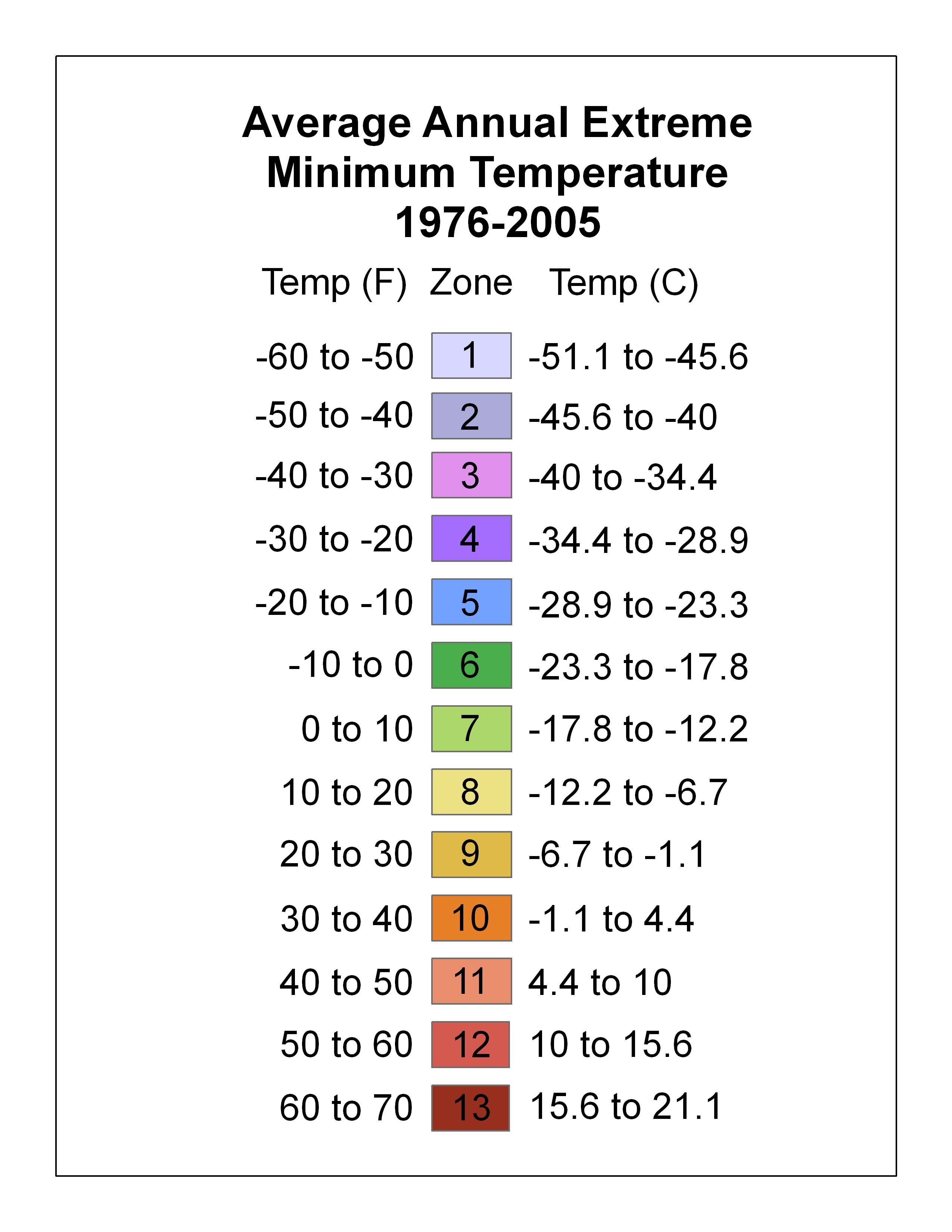
Plant Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. A plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of . Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. However, some confusion can exist in discussing buildings and HVAC, where "climate zone" can refer to the International Energy Conservation Code zones, where Zone 1 is warm and Zone 8 is cold. Other hardiness rating schemes have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustics, acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in cumulonimbus clouds. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce Heavy rain (meteorology), heavy rain and sometimes Thundersnow, snow, Ice pellets, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms can produce little or Dry thunderstorm, no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may thunderstorm training, line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or #Severe thunderstorms, severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dew Point
The dew point is the temperature the air needs to be cooled to (at constant pressure) in order to produce a relative humidity of 100%. This temperature depends on the pressure and water content of the air. When the air at a temperature above the dewpoint is cooled, its moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will Condensation, condense to form liquid water known as dew. When this occurs through the air's contact with a colder surface, dew will form on that surface. The dew point is affected by the air's humidity. The more moisture the air contains, the higher its dew point. When the temperature is below the freezing point of water, the dew point is called the frost point, as frost is formed via deposition (phase transition), deposition rather than condensation. In liquids, the analog to the dew point is the cloud point. Humidity If all the other factors influencing humidity remain constant, at ground level the relative humidity rises as the temperature falls; this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Index
The heat index (HI) is an index that combines air temperature and relative humidity, in shade (shadow), shaded areas, to posit a human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the Shade (shadow), shade. For example, when the temperature is with 70% relative humidity, the heat index is (see table below). The heat index is meant to describe experienced temperatures in the shade, but it does not take into account heating from direct sunlight, physical activity or cooling from wind. The human body normally cools itself by evaporation of perspiration, sweat. High relative humidity reduces evaporation and cooling, increasing discomfort and potential Hyperthermia, heat stress. Different individuals perceive heat differently due to body shape, metabolism, level of hydration, pregnancy, or other physical conditions. Measurement of perceived temperature has been based on reports of how hot subjects feel under controlled conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm to hot summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in central and eastern parts of the three northern-tier continents (North America, Europe, and Asia), typically in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 or 60 degrees north), often within large landmasses, where prevailing winds blow overland bringing some precipitation, and temperatures are not moderated by oceans. Continental climates occur mostly in the Northern Hemisphere due to the large landmasses found there. Most of northeastern China, eastern and southeastern Europe, much of Russia south of the Arctic Circle, central and southeastern Canada, and the central and northeastern United States have this type of climate. Continentality is a measure of the degree to which a region experiences this type of climate. In continental climates, precipitation tends to be moderate in amount, concentrated mostly in the warmer months. Only a few areas—in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trewartha Climate Classification
The Trewartha climate classification (TCC), or the Köppen–Trewartha climate classification (KTC), is a climate classification system first published by American geographer Glenn Thomas Trewartha in 1966. It is a modified version of the Köppen–Geiger system, created to answer some of its deficiencies. The Trewartha system attempts to redefine the middle latitudes to be closer to vegetation zoning and genetic climate systems. Scheme Trewartha's modifications to the 1884 Köppen climate system sought to reclass the middle latitudes into three groups, according to how many months have a mean temperature of or higher: * ''C'' (subtropical)—8 or more months; * ''D'' (temperate)—4 to 7 months; * ''E'' ( boreal climate)—1 to 3 months. The tropical climates and polar climates remained the same as in the original Köppen climate classification. The "highland" climate is ambiguously defined. Newer users of KTC generally omit this option. Group A: Tropical climates This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |