|
Lake Finland
Finnish Lakeland or the Finnish lake district ( , "Lake Finland", ) is a large landscape region in central eastern Finland. The hilly, forest-covered landscape of Lakeland Finland's lake plateau is dominated by drumlins and by long sinuous eskers. Both are glacial remnants deposited after the continental glaciers that scoured and gouged the country's surface receded about 10,000 years ago. The lake basins of the lakeland originate from the joint work of weathering and erosion of fractures in the bedrock. The erosion that made the depressions occurred before and during the Quaternary ice ages. Erosion along fractures has produced linear inlets among the lakes. Demarcation The district occupies most of the central and East Finland and is bounded to the south by the Salpausselkä Ridges. These ridges are terminal moraines, which trap networks of thousands of lakes separated by hilly forested countryside. The lake district turns into the Coastal Finland district to the West an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salpausselkä Ridges
Salpausselkä (; "Bar Ridge") is an extensive ridge system left by the ice age in Southern Finland. It is a large terminal moraine formation that formed in front of the Baltic ice lake during the Younger Dryas period about 12,250–10,400 years ago. All together the formation is close to from end to end, and the ridges can be as tall as in some places. It runs from Hanko hundreds of kilometers to the east. It traps the extensive river and lake systems of Central Finland known as Finnish Lakeland (, "Lake Finland") and forces the water to flow through few breaches in the ridge. The Vuoksi River flows from lake Saimaa into Lake Ladoga () in Russia. From there the water subsequently flows through river Neva into the Gulf of Finland, bypassing the Salpausselkä. The Kymi River flows from Päijänne into the Gulf of Finland. An artificial breach from the Lakeland is the Saimaa Canal, from Saimaa at Lappeenranta into the Gulf of Finland at Vyborg. Salpausselkä has been used for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pieksämäki
Pieksämäki () is a town and municipality of Finland. It is located in the Southern Savonia region, about north of Mikkeli, east of Jyväskylä and south of Kuopio. The town has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . Neighbouring municipalities are Hankasalmi, Joroinen, Juva, Kangasniemi, Leppävirta, Mikkeli, Rautalampi and Suonenjoki. Formation Pieksämäki was granted town privileges in 1962 and enlarged on 1 January 2007 with the consolidation of the Pieksämäki and Pieksänmaa municipalities. Transport Pieksämäki railway station is an important junction for the Finnish railway network, and Savo Railway Museum is located in the area. Education Diaconia University of Applied Sciences has one of its five campuses in Pieksämäki. Politics Results of the 2023 Finnish parliamentary election in Pieksämäki: * Finns Party 21.5 * Social Democratic Party 21.0% * Centre Party 18.4% * National Coalition Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikkeli
Mikkeli (; ; ; ) is a List of cities and towns in Finland, city in, and the regional capital of, South Savo, Finland, located in the Finnish Lakeland. The population is approximately , while the Mikkeli sub-region of Southern Savonia has a population of approximately . Mikkeli is the most-populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality of Finland and the 19th most-populous List of urban areas in Finland by population, urban area in the country. Mikkeli is located on the shores of Saimaa, Lake Saimaa, the largest List of lakes of Finland, lake in the country, and List of largest lakes of Europe, Europe's fourth largest. Prior to being located within South Savonia, the city was in Mikkeli Province (until 1997), before becoming part of Eastern Finland Province (1997-2009). The city covers an area of , of which is water. Mikkeli is one of the largest towns in the South Savo region, and one of the main hubs in the region's Healthcare in Finland, hospital districts, along with Savonli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
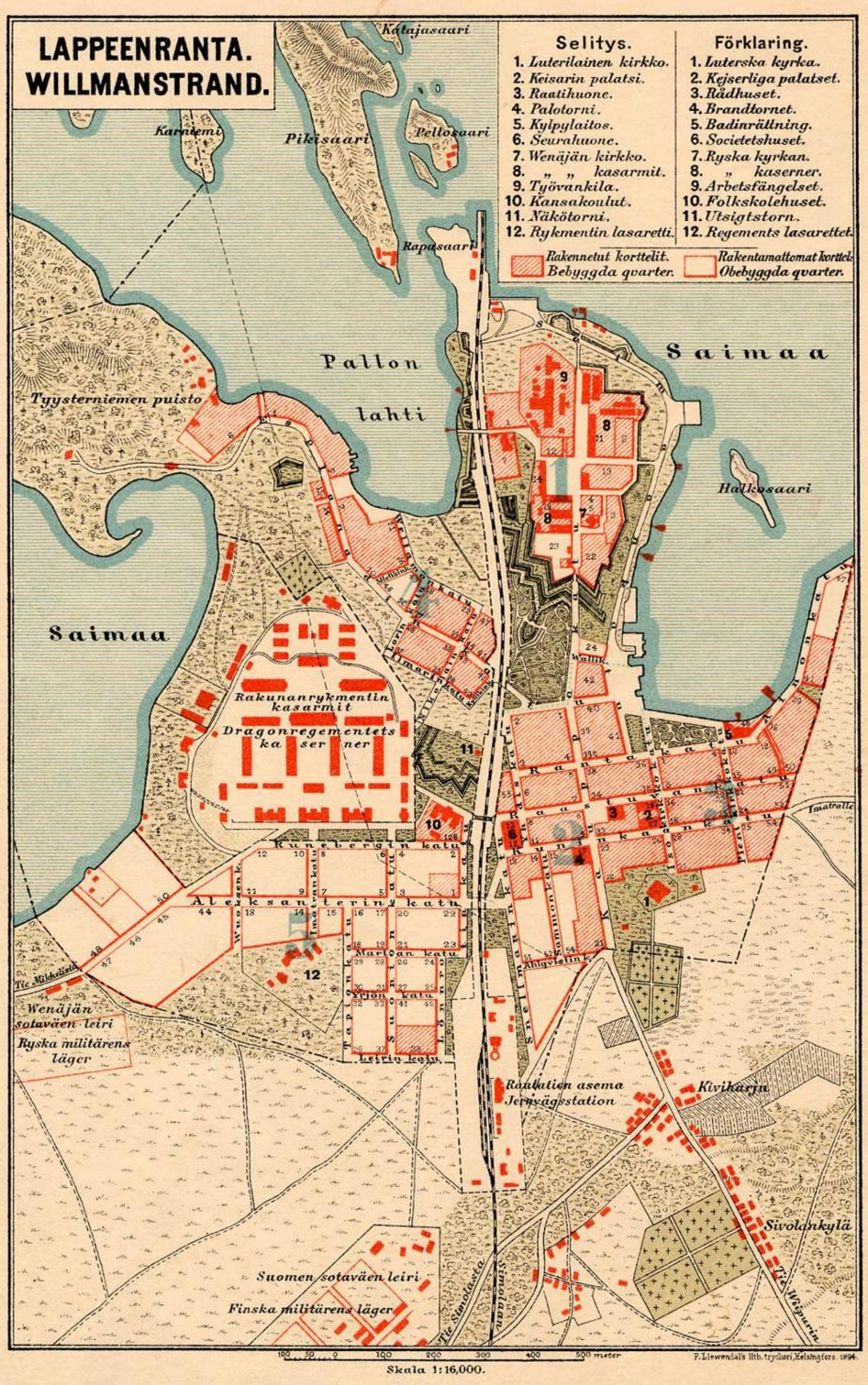
Lappeenranta
Lappeenranta (; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of South Karelia. It is located in the southeastern interior of the country and in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Lappeenranta is approximately , while the Lappeenranta sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is the most populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality in Finland, and the 11th most populous List of urban areas in Finland by population, urban area in the country. Lappeenranta is located on the shore of Lake Saimaa, from the Finnish–Russian border, Russian border and from the city of Vyborg. Lappeenranta is one of the most important urban centres in the entire Saimaa region, together with the cities of Imatra, Mikkeli and Savonlinna. Lappeenranta incorporated the late municipalities of Lappee and Lauritsala in 1967, Nuijamaa in 1989, Joutseno in 2009 and Ylämaa in 2010. Lappeenranta, the region's tourism centre, is the second most visited city in Finland by Russians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuopio
Kuopio ( , ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of North Savo. It is located in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Kuopio is approximately , while the Kuopio sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is the most populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality in Finland, and the seventh most populous List of urban areas in Finland by population, urban area in the country. Kuopio has a total area of , of which is water and half is forest. Although the city's population density, population is spread over , the city's urban areas are comparatively densely populated (urban area: 1,618 /km²), making Kuopio the second most densely populated city in Finland. At the end of 2018, its urban area had a population of approximately 90,000. Together with Joensuu, Kuopio is one of the major urban, economic and cultural centres of Eastern Finland. Kuopio is nationally known as one of the most important education in Finland, study cities and centres of attra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyväskylä
Jyväskylä () is a city in Finland and the regional capital of Central Finland. It is located in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Jyväskylä is approximately , while the Jyväskylä sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is Finland's most populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality, and fifth most populous List of urban areas in Finland by population, urban area. Jyväskylä is located about northeast of Tampere, the third largest city in Finland; and about north of Helsinki, the national capital. The Jyväskylä sub-region includes Jyväskylä, Hankasalmi, Laukaa, Muurame, Petäjävesi, Toivakka, and Uurainen. Other neighbouring municipalities of Jyväskylä are Joutsa, Jämsä and Luhanka. Jyväskylä is the largest city in the Central Finland and Finnish Lakeland region. Jyväskylä was one of the fastest growing cities in Finland during the 20th century; in 1940, there were only 8,000 inhabitants in Jyväskylä. Elias Lönnrot, the auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joensuu
Joensuu (; ; ) is a city in Finland and the regional capital of North Karelia. It is located in the eastern interior of the country and in the Finnish Lakeland. The population of Joensuu is approximately , while the sub-region has a population of approximately . It is the most populous municipality in Finland, and the ninth most populous urban area in the country. Joensuu was founded in 1848 by the Russian Emperor Nicholas I. The city is located on the northern shore of Lake Pyhäselkä, the northern part of Lake Saimaa, at the mouth of the River Pielinen. The nearest major city, Kuopio in North Savonia, is located to the west. From Joensuu, the distance to Lappeenranta, the capital of South Karelia, is along Highway 6. As is typical of cities in Eastern Finland, Joensuu is monolingually Finnish. Along with Kuopio, Joensuu is one of major urban, economic, and cultural hubs of Eastern Finland. Joensuu is a student city with a subsidiary of the University of Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imatra
Imatra is a city in Finland, located in the southeastern interior of the country. Imatra is located in the region of South Karelia, on Saima, Lake Saimaa and the River Vuoksi. The population of Imatra is approximately , while the Imatra sub-region, sub-region has a population of approximately . It is the most populous Municipalities of Finland, municipality in Finland. Imatra lies on the Finland–Russia border, border with Russia. On the other side of the border, away from the centre of Imatra, lies the Russian town of Svetogorsk. The city of Saint Petersburg, St. Petersburg is situated to the southeast, the Finnish capital Helsinki is away and Lappeenranta, the nearest Finnish city, is away. The main employers are the pulp and paper manufacturer Stora Enso, Stora Enso Oyj, the City of Imatra, the engineering steel manufacturer Ovako Bar Oy Ab and the Finnish Border Guard. , the total number of employees was 12,423. , 1,868 people were employed by the City of Imatra. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of , with a population of 533,121 residents. Its capital city, capital is Petrozavodsk. The modern Karelian Republic was founded as an autonomous republic within the Russian SFSR, by the Resolution of the Presidium of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee (VTsIK) on 27 June 1923 and by the Decree of the VTsIK and the Council of People's Commissars of 25 July 1923, from the Karelian Labor Commune, Karelian Labour Commune. From 1940 to 1956, it was known as the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic, one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, republics of the Soviet Union. In 1956, it was once again made an autonomous republic and remained part of Russia following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Etymology "Karelia" deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus (; ; ) is the approximately stretch of land situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva. Its northwestern boundary is a line from the Bay of Vyborg to the westernmost point of Lake Ladoga, Pekonlahti. If the Karelian Isthmus is defined as the entire territory of present-day Saint Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast to the north of the Neva and also a tiny part of the Republic of Karelia, the area of the isthmus is about . The smaller part of the isthmus to the southeast of the old Russia-Finland border is considered historically as Northern Ingria, rather than part of the Karelian Isthmus itself. The rest of the isthmus was historically a part of Finnish Karelia. This was conquered by the Russian Empire during the Great Northern War in 1712 and included within the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland (1809–1917) of the Russian Empire. When Finland became independent in 1917, the isthmus (excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |