|
Lake 227
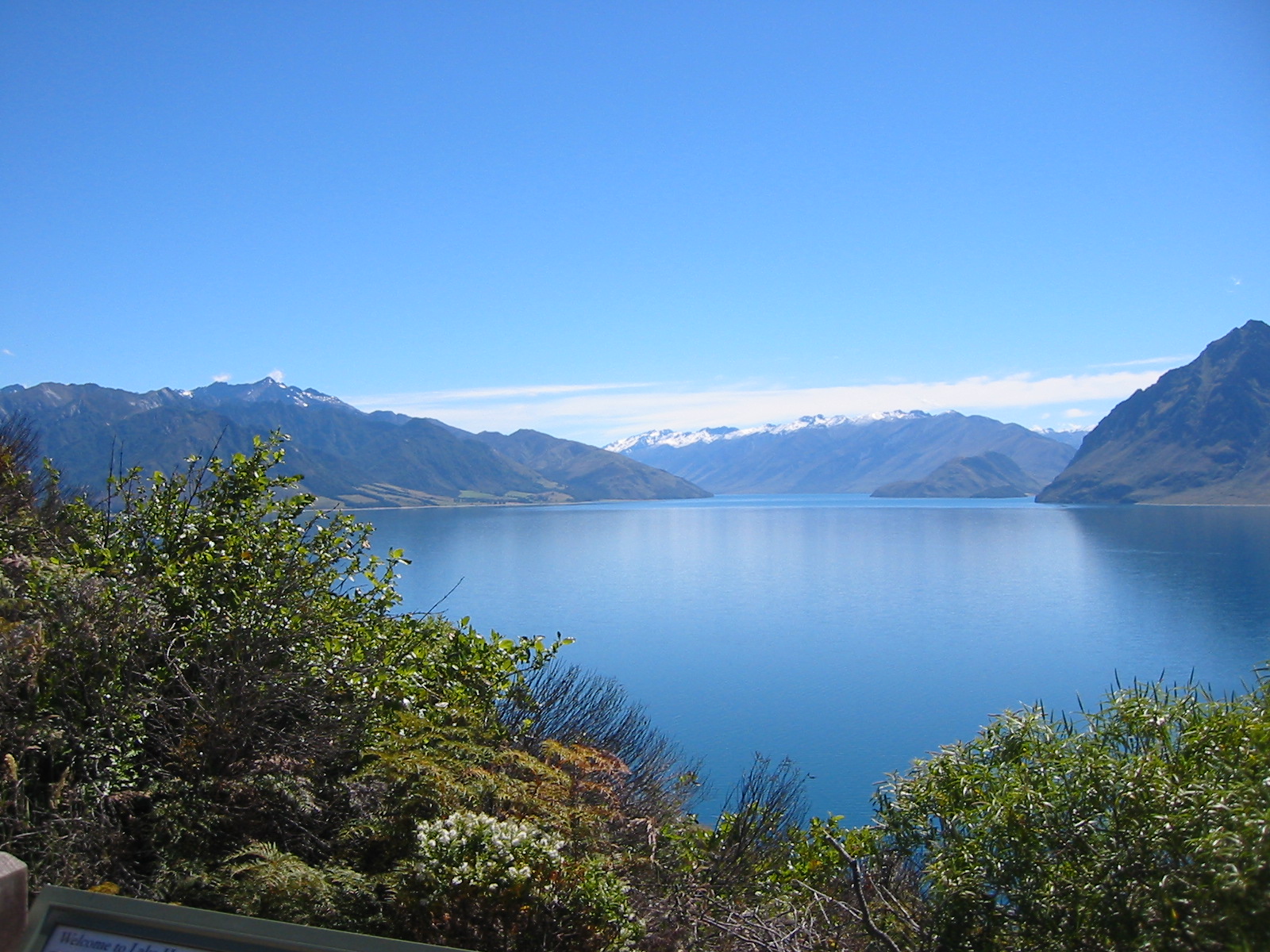
Lake 227 is one of 58 lakes located in the Experimental Lakes Area (ELA) in the Kenora District of Ontario, Canada. Lake 227 is one of only five lakes in the Experimental Lakes Area currently involved in long-term research projects, and is of particular note for its importance in long-term lake eutrophication studies. The relative absence of human activity and pollution makes Lake 227 ideal for limnological research, and the nature of the ELA makes it one of the few places in the world accessible for full lake experiments. At its deepest, Lake 227 is deep, and the area of the lake is approximately . Funding and governmental permissions for access to Lake 227 have been unstable in recent years, as control of the ELA was handed off by the Canadian government to the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD). Ecology Lake 227 is a freshwater lake. The ELA region is home to a variety of native fish, many of which are planktivorous. Fathead minnows, fine-scale dace, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Ontario Ridings 2018 - Kenora—Rainy River
Northern may refer to the following: Geography * North, a point in direction * Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe * Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States * Northern Province, Sri Lanka * Northern Range, a range of hills in Trinidad Schools * Northern Collegiate Institute and Vocational School (NCIVS), a school in Sarnia, Canada * Northern Secondary School, Toronto, Canada * Northern Secondary School (Sturgeon Falls), Ontario, Canada * Northern University (other), various institutions * Northern Guilford High School, a public high school in Greensboro, North Carolina Companies * Arriva Rail North, a former train operating company in northern England * Northern Bank, commercial bank in Northern Ireland * Northern Foods, based in Leeds, England * Northern Pictures, an Australian-based television production company * Northern Rail, a former train operating company in northern England * Northern Railway of Canada, a defunct railway in On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limnology
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems. The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristics of fresh and saline, natural and man-made bodies of water. This includes the study of lakes, reservoirs, ponds, rivers, springs, streams, wetlands, and groundwater.Wetzel, R.G. 2001. Limnology: Lake and River Ecosystems, 3rd ed. Academic Press () Water systems are often categorized as either running (lotic) or standing (lentic). Limnology includes the study of the drainage basin, movement of water through the basin and biogeochemical changes that occur en route. A more recent sub-discipline of limnology, termed landscape limnology, studies, manages, and seeks to conserve these ecosystems using a landscape perspective, by explicitly examining connections between an aquatic ecosystem and its drainage basin. Recently, the need to un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter And Paul Lakes
Paul and Peter are two connected lakes located in Michigan's upper peninsula near the Wisconsin border in Vilas County (WI) and Gogebic County (MI). Paul and Peter are kettle lakes, which is a type of lake formed by glaciers. Peter Lake is larger with an area of 6.24 acres and a maximum depth of 19.6 meters while Paul Lake has an area of 4.12 acres and a maximum depth of 15 meters. The lakes are a part of the University of Notre Dame Environmental Research Center (UNDERC). The lakes, bogs, streams, and marshes of the UNDERC are located within deciduous and coniferous forests. The surrounding forest is made up mostly of sugar maple, yellow birch, and balsam fir. The two lakes are ideal for performing whole lake experiments since one lake can receive treatments while the other can remain a control. No fishing is allowed making the two connected lakes ideal for studying their fish populations. The lakes' basins are also located within the UNDERC meaning that no outside interferen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake 226
Lake 226 is one lake in Canada's Experimental Lakes Area (ELA) in Ontario. The ELA is a freshwater and fisheries research facility that operated these experiments alongside Fisheries and Oceans Canada and Environment Canada. In 1968 this area in northwest Ontario was set aside for limnological research, aiming to study the watershed of the 58 small lakes in this area. The ELA projects began as a response to the claim that carbon was the limiting agent causing eutrophication of lakes rather than phosphorus, and that monitoring phosphorus in the water would be a waste of money. This claim was made by soap and detergent companies, as these products do not biodegrade and can cause buildup of phosphates in water supplies that lead to eutrophication. The theory that carbon was the limiting agent was quickly debunked by the ELA Lake 227 experiment that began in 1969, which found that carbon could be drawn from the atmosphere to remain proportional to the input of phosphorus in the water. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolimnology
Paleolimnology (from Greek: παλαιός, ''palaios'', "ancient", λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake", and λόγος, ''logos'', "study") is a scientific sub-discipline closely related to both limnology and paleoecology. Paleolimnological studies focus on reconstructing the past environments of inland waters (e.g., lakes and streams) using the geologic record, especially with regard to events such as climatic change, eutrophication, acidification, and internal ontogenic processes. Paleolimnological studies are mostly conducted using analyses of the physical, chemical, and mineralogical properties of sediments, or of biological records such as fossil pollen, diatoms, or chironomids. History Lake ontogeny Most early paleolimnological studies focused on the biological productivity of lakes, and the role of internal lake processes in lake development. Although Einar Naumann had speculated that the productivity of lakes should gradually decrease due to leaching of catchment soils, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
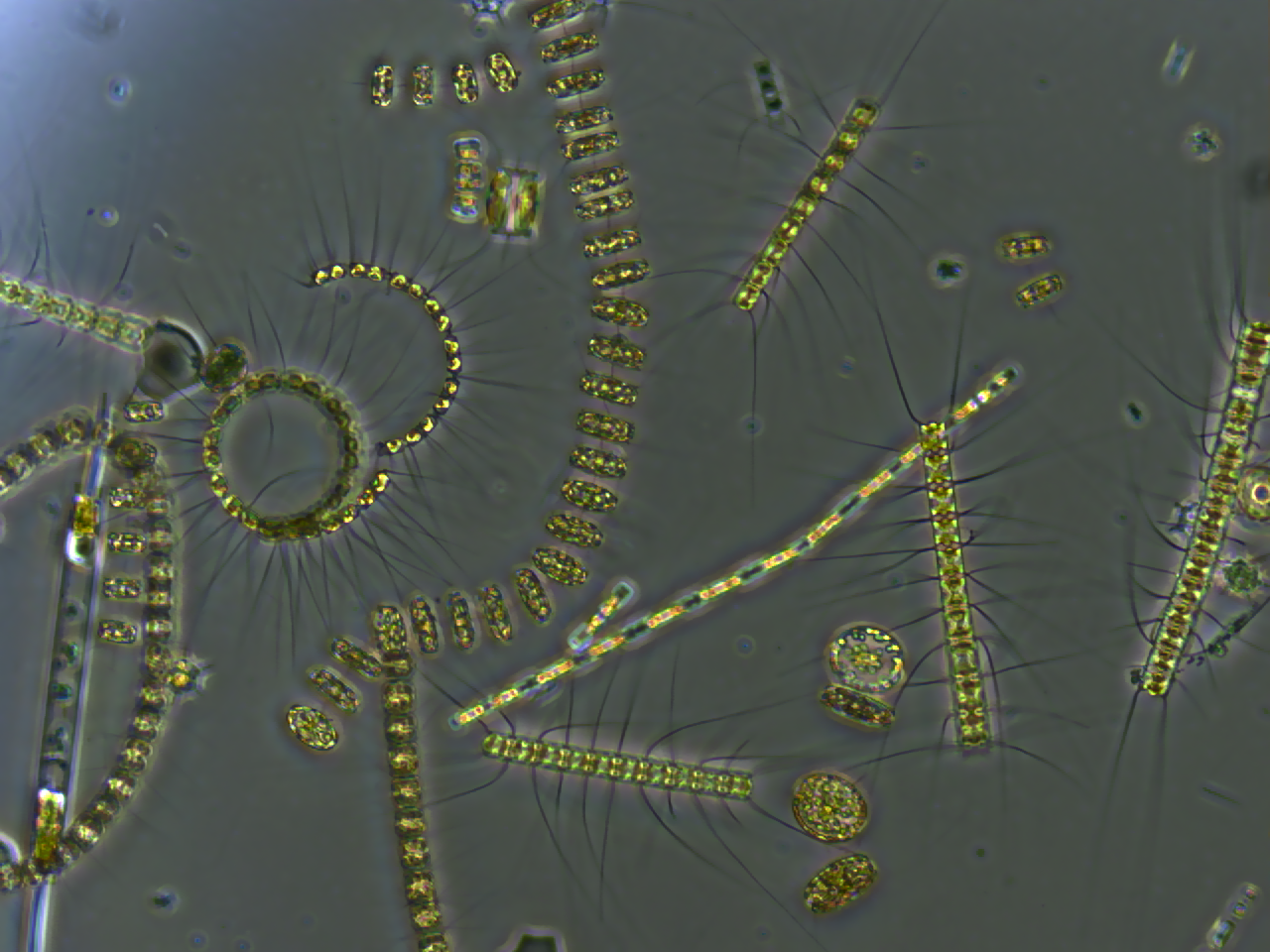
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Producers
An autotroph or primary producer is an organism that produces complex organic compounds (such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) using carbon from simple substances such as carbon dioxide,Morris, J. et al. (2019). "Biology: How Life Works", 3rd edition, W. H. Freeman. generally using energy from light (photosynthesis) or inorganic chemical reactions (chemosynthesis). They convert an abiotic source of energy (e.g. light) into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by other organisms (e.g. heterotrophs). Autotrophs do not need a living source of carbon or energy and are the producers in a food chain, such as plants on land or algae in water (in contrast to heterotrophs as consumers of autotrophs or other heterotrophs). Autotrophs can reduce carbon dioxide to make organic compounds for biosynthesis and as stored chemical fuel. Most autotrophs use water as the reducing agent, but some can use other hydrogen compounds such as hydrogen sulfide. The primary prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many industrially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the "Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Schindler
David William Schindler, , (August 3, 1940 – March 4, 2021) was an American/Canadian limnologist. He held the Killam Memorial Chair and was Professor of Ecology in the Department of Biological Sciences at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Alberta. He was notable for "innovative large-scale experiments" on whole lakes at the Experimental Lakes Area (ELA) which proved that "phosphorus controls the eutrophication (excessive algal blooms) in temperate lakes leading to the banning of phosphates in detergents. He was also known for his research on acid rain. In 1989, Schindler moved from the ELA to continue his research at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, with studies into fresh water shortages and the effects of climate disruption on Canada's alpine and northern boreal ecosystems. Schindler's research had earned him numerous national and international awards, including the Gerhard Herzberg Gold Medal, the First Stockholm Water Prize (1991) the Volvo Environment Prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IISD Experimental Lakes Area On The Banks Of Lake 239 In 2016
IISD is an acronym that may refer to: *International Institute for Sustainable Development The International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) is an independent think tank founded in 1990 working to shape and inform international policy on sustainable development governance. The institute has three offices in Canada - Win ... * International Indian School Dammam {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |