|
Lactobacillus Bulgaricus GLB44
''Lactobacillus delbrueckii'' subsp. ''bulgaricus'' is a bacterial subspecies traditionally isolated from European yogurts. ''Lactobacillus bulgaricus'' GLB44 differs from the rest of the ''L. bulgaricus'' strains as it was isolated from the leaves of '' Galanthus nivalis'' (snowdrop flower) in Bulgaria, becoming the only known strain of this subspecies that has vegan origin (not from yogurt) available as a commercial probiotic. Probiotics are health promoting bacteria which, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer a benefit on the host, normally associated with positive effects on the digestive and immune systems, and are usually prescribed during or after antibiotic treatment to alleviate the symptoms of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Probiotics are also associated with decreasing of the risk of traveler's diarrhea. General information: GLB44 As GLB44 is derived from leaves of the snowdrop flower found in European mountainous regions. Thus, GLB44 is capable of surviv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Subsp
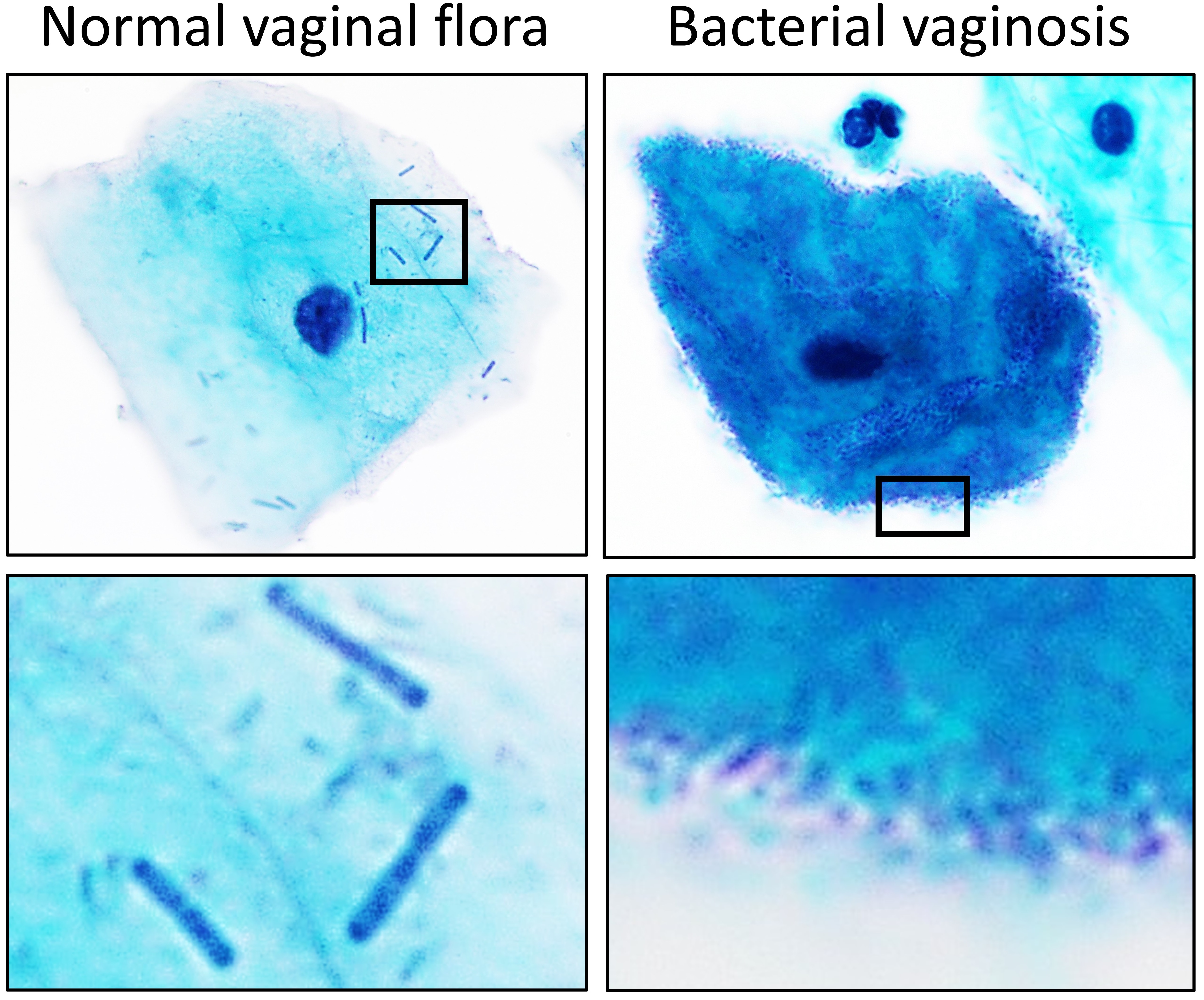
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distribution Of The Galanthus Species
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function, in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample * Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a category are accounted for *Distributivity, a property of binary operations that generalises the distributive law from elementary algebra *Distribution (number theory) *Distribution problems, a common type of problems in combinatorics where the goal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Nuts
A nut is a fruit consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, a wide variety of dry seeds are called nuts, but in a botanical context "nut" implies that the shell does not open to release the seed ( indehiscent). Most seeds come from fruits that naturally free themselves from the shell, but this is not the case in nuts such as hazelnuts, chestnuts, and acorns, which have hard shell walls and originate from a compound ovary. The general and original usage of the term is less restrictive, and many nuts (in the culinary sense), such as almonds, pecans, pistachios, walnuts, and Brazil nuts, are not nuts in a botanical sense. Common usage of the term often refers to any hard-walled, edible kernel as a nut. Nuts are an energy-dense and nutrient-rich food source. Botanical definition A seed is the mature fertilised ovule of a plant; it consists of three parts, the embryo which will develop into a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soya Bean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption). Etymology The word "soy" originated as a corruption of the Cantonese or J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar synthesized by galactose and glucose subunits and has the molecular formula C12H22O11. Lactose makes up around 2–8% of milk (by mass). The name comes from ' (gen. '), the Latin word for milk, plus the suffix ''-ose'' used to name sugars. The compound is a white, water-soluble, non-hygroscopic solid with a mildly sweet taste. It is used in the food industry. Structure and reactions Lactose is a disaccharide derived from the condensation of galactose and glucose, which form a β-1→4 glycosidic linkage. Its systematic name is β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-D-glucose. The glucose can be in either the α- pyranose form or the β-pyranose form, whereas the galactose can only have the β-pyranose form: hence α-lactose and β-lactose refer to the anomeric form of the glucopyranose ring alone. Detection reactions for lactose are the Woehlk- and Fearon's test. Both can be easily used in school experiments to visualise the different lactose co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, animal foods & feed and veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not directly related to food or drugs, but involves such things as regulating lasers, cellular phones, and condoms, as well as control of disease in contexts v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergens
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies. In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivity reaction in atopic individuals through immunoglobulin E (IgE) responses. Most humans mount significant Immunoglobulin E responses only as a defense against parasitic infections. However, some individuals may respond to many common environmental antigens. This hereditary predisposition is called atopy. In atopic individuals, non-parasitic antigens stimulate inappropriate IgE production, leading to type I hypersensitivity. Sensitivities vary widely from one person (or from one animal) to another. A very broad range of substances can be allergens to sensitive individuals. Types of allergens Allergens can be found in a variety of sources, such as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casein
Casein ( , from Latin ''caseus'' "cheese") is a family of related phosphoproteins ( αS1, aS2, β, κ) that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of the proteins in human milk. Sheep and buffalo milk have a higher casein content than other types of milk with human milk having a particularly low casein content. Casein has a wide variety of uses, from being a major component of cheese, to use as a food additive. The most common form of casein is sodium caseinate. In milk, casein undergoes phase separation to form colloidal casein micelles, a type of secreted biomolecular condensate. As a food source, casein supplies amino acids, carbohydrates, and two essential elements, calcium and phosphorus. Composition Casein contains a high number of proline amino acids which hinder the formation of common secondary structural motifs of proteins. There are also no disulfide bridges. As a result, it has relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grains that have been proved capable of triggering celiac disease. These include any species of wheat (such as common wheat, durum, spelt, khorasan, emmer and einkorn), barley, rye and some oat cultivars, as well as any cross hybrids of these grains (such as triticale). Gluten makes up 75–85% of the total protein in bread wheat. Glutens, especially Triticeae glutens, have unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties, which give dough its elasticity, helping it rise and keep its shape and often leaving the final product with a chewy texture. These properties, and its relatively low cost, make gluten valuable to both food and non-food industries. Wheat gluten is composed of mainly two types of proteins: the glutenins and the gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus Brevis
''Levilactobacillus brevis'' is a gram-positive, rod shaped species of lactic acid bacteria which is heterofermentative, creating CO2, lactic acid and acetic acid or ethanol during fermentation. ''L. brevis'' is the type species of the genus ''Levilactobacillus'' (previously ''L. brevis'' group), which comprises 24 specieshttp://www.lactobacillus.ualberta.ca/ http://www.lactobacillus.uantwerpen.be/).Pavlova, S. I., Kilic, A. O., Kilic, S. S., So, J. S., Nader‐Macias, M. E., Simoes, J. A., & Tao, L. (2002). Genetic diversity of vaginal lactobacilli from women in different countries based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 92(3), 451-459. It can be found in many different environments, such as fermented foods, and as normal microbiota. ''L.brevis'' is found in food such as sauerkraut and pickles. It is also one of the most common causes of beer spoilage. Ingestion has been shown to improve human immune function, and it has been patented several times. Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifidobacterium
''Bifidobacterium'' is a genus of gram-positive, nonmotile, often branched anaerobic bacteria. They are ubiquitous inhabitants of the gastrointestinal tract though strains have been isolated from the vagina and mouth ('' B. dentium'') of mammals, including humans. Bifidobacteria are one of the major genera of bacteria that make up the gastrointestinal tract microbiota in mammals. Some bifidobacteria are used as probiotics. Before the 1960s, ''Bifidobacterium'' species were collectively referred to as ''Lactobacillus bifidus''. History In 1899, Henri Tissier, a French pediatrician at the Pasteur Institute in Paris, isolated a bacterium characterised by a Y-shaped morphology ("bifid") in the intestinal microbiota of breast-fed infants and named it "bifidus". In 1907, Élie Metchnikoff, deputy director at the Pasteur Institute, propounded the theory that lactic acid bacteria are beneficial to human health. Metchnikoff observed that the longevity of Bulgarians was the result of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

