|
Labna
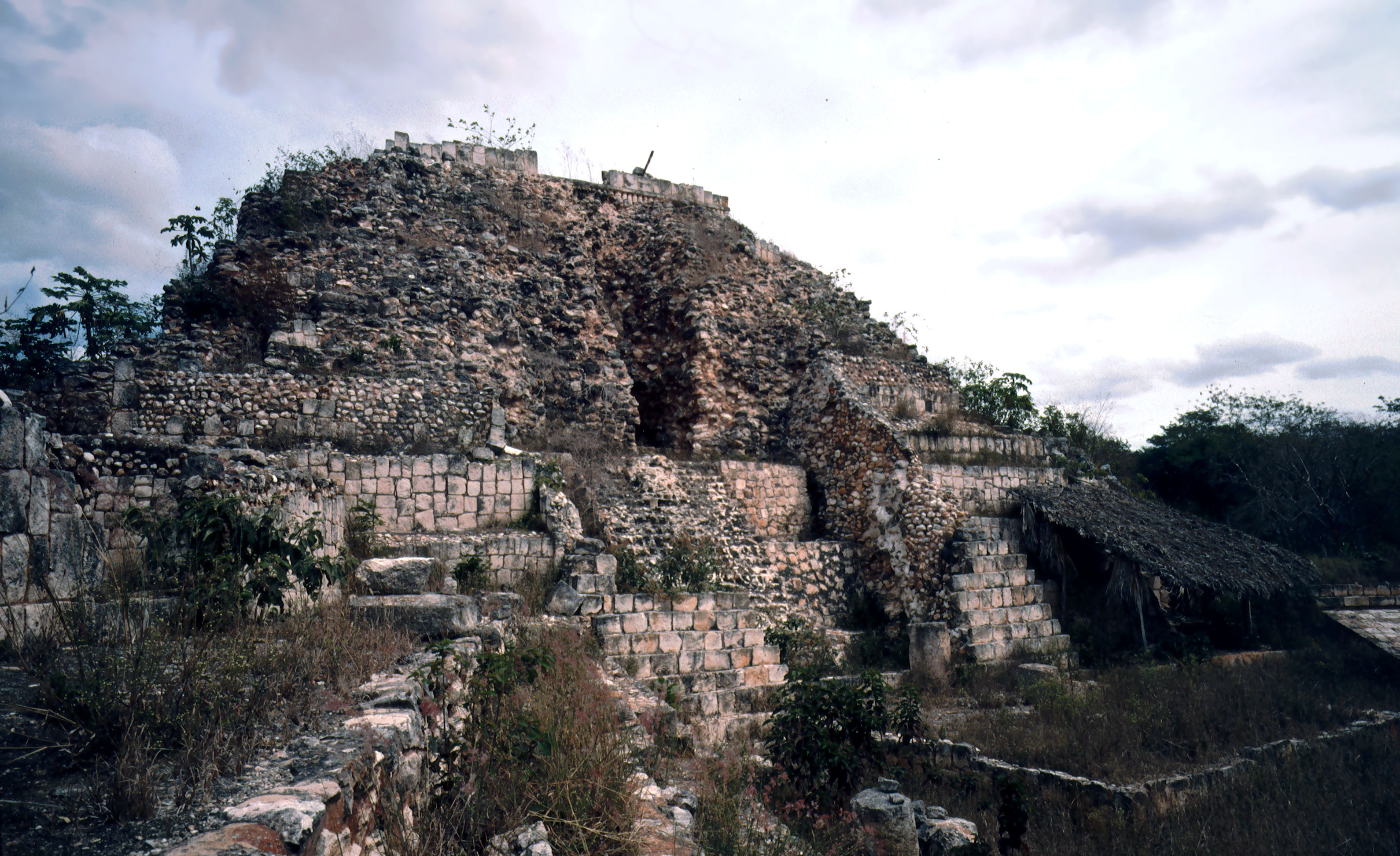
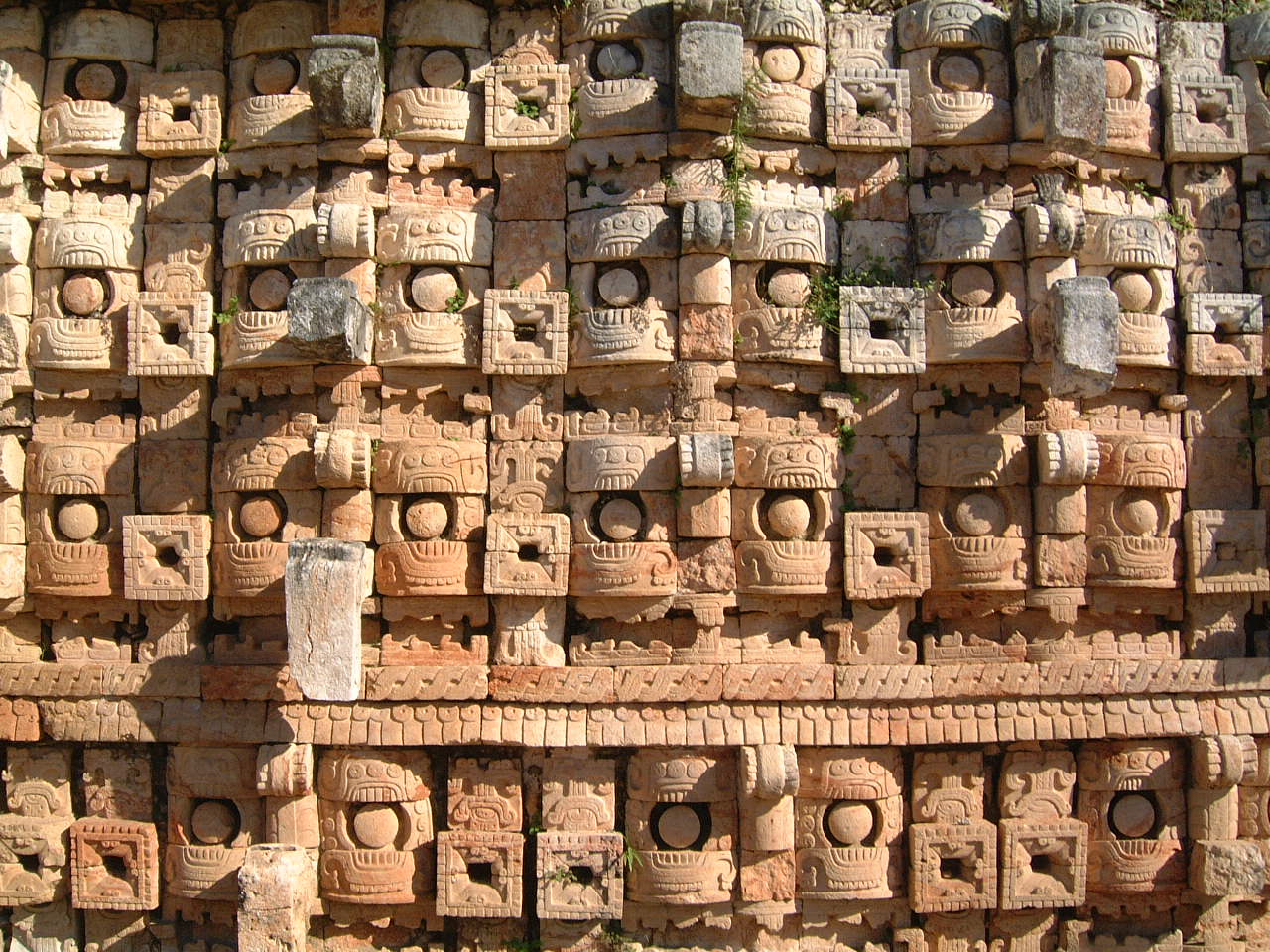
Labna (or Labná in Writing system of Spanish, Spanish orthography) is a Mesoamerican archaeological site and ceremonial center of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization, located in the Puuc Hills region of the Yucatán Peninsula. It is situated to the south of the large Maya site of Uxmal, in the southwest of the present-day state of Yucatán (state), Yucatán, Mexico. Labna, Sayil and Kabah (Maya site), Kabah were incorporated with Uxmal as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. History The city existed from 200 to 1000 AD. It reached its peak in the period from 800 to 1000 AD. It undoubtedly had a complex social organization and shares style and decorative elements with other cities in the region (Uxmal, Sayil, Kabah). It is estimated that about 3,000 inhabitants lived in Labna. The first written report of Labna was by John Lloyd Stephens who visited it with artist Frederick Catherwood in 1842. Thanks to this, drawings illustrating the state of the ruins from that period have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from antiquity to the early modern period. It is known by its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayil
Sayil was a pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal Classic period. It is located in the Mexican state of Yucatán, in the southwest of the state, south of Uxmal. Sayil, Kabah and Labna were incorporated together with Uxmal as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. Sayil flourished principally, albeit briefly, in the Terminal Classic period. The city reached its greatest extent c. 900 and had a population of 10,000 with an additional 5,000–7,000 living in the surrounding area. A number of badly damaged monuments suggest that Sayil was governed by a local royal dynasty,Sharer & Traxler 2006, p.545. with wealth among lineages based, at least in part, upon control of the best agricultural lands.Carmean ''et al.'' 2005, p.435 The ruins of Sayil include a prominent example of monumental Puuc style architecture, the partially ruined Grand Palace of Sayil. Location The site is located in the karst limestone hills of the Puuc region of the northern Yuca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and northwestern part of Costa Rica. As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures. In the pre-Columbian era, many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous societies flourished in Mesoamerica for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas began on Hispaniola in 1493. In world history, Mesoamerica was the site of two historical transformations: (i) primary urban generation, and (ii) the formation of New World cultures from the mixtures of the indigenous Mesoamerican peoples with the European, African, and Asian peoples who were introduced by the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puuc
Puuc is the name of a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán (state), Yucatán and a Maya architecture, Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word ''puuc'' is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was extended to encompass the large karstic range of hills in the southern portion of the state, hence the terms Puuc region or Puuc hills. The Puuc hills extend into northern Campeche and western Quintana Roo. The term Puuc is also used to designate the Mesoamerican architecture, architectural style of ancient Maya sites located within the Puuc hills, hence the term Puuc architecture. This architectural style began at the end of the Mesoamerican chronology#Late Classic, Late Classic period but experienced its greatest extent during the Mesoamerican chronology#Terminal Classic, Terminal Classic period. Puuc architecture In the florescence of Puuc architecture (such as at the ancient Maya civilization, Maya site o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vision Serpent
The Vision Serpent is an important creature in Pre-Columbian Maya mythology, although the term itself is now slowly becoming outdated. The serpent was a very important social and religious symbol, revered by the Maya. Maya mythology describes serpents as being the vehicles by which celestial bodies, such as the sun and stars, cross the heavens. The shedding of their skin made them a symbol of rebirth and renewal. They were so revered, that one of the main Mesoamerican deities, Quetzalcoatl, was represented as a feathered serpent. The name means "Precious/feathered serpent" (from Nahuatl, "quetzalli" is used to describe the bird, its feathers, or something precious depending on the context and "coatl" meaning snake or serpent.). The Vision Serpent is thought to be the most important of the Maya serpents. "It was usually bearded and had a rounded snout. It was also often depicted as having two heads or with the spirit of a god or ancestor emerging from its jaws." During Maya blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian, prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian (first human habitation until 3500 BCE); the Archaic (before 2600 BCE), the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE – 250 CE), the Classic (250–900 CE), and the Postclassic (); as well as the post European contact Colonial Period (1521–1821), and Postcolonial, or the period after independence from Spain (1821–present). The periodisation of Mesoamerica by researchers is based on archaeological, ethnohistorical, and modern cultural anthropology research dating to the early twentieth century. Archaeologists, ethnohistorians, historians, and cultural anthropologists continue to work to develop cultural histories of the region. Overview Paleo-Indian period 18000–8000 BCE The Paleo-Indian (less frequently, ''Lithic stage, Lithic'') period or era is that which spans from the first signs of human presence in the region, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Architecture
The Mayan architecture of the Maya civilization spans across several thousands of years, several eras of political change, and architectural innovation before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Often, the buildings most dramatic and easily recognizable as creations of the Maya peoples are the step pyramids of the Terminal Preclassic Maya period and beyond. Based in general Mesoamerican architecture, Mesoamerican architectural traditions, the Maya utilized geometric proportions and intricate carving to build everything from simple houses to ornate temples. This article focuses on the more well-known Mesoamerican chronology, pre-classic and Mesoamerican chronology, classic examples of Maya architecture. The temples like the ones at Palenque, Tikal, and Uxmal represent a zenith of Maya art and architecture. Through the observation of numerous elements and stylistic distinctions, remnants of Maya architecture have become an important key to understanding their religious beliefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabah (Maya Site)
Kabah (also spelled Kabaah, Kabáh, Kahbah and Kaba) is a Maya archaeological site in the Puuc region of western Yucatan, south of Mérida. It was incorporated together with Uxmal, Sayil and Labna as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. Kabah is south of Uxmal, connected to that site by an long raised causeway wide with monumental arches at each end. Kabah is the second largest ruin of the Puuc region after Uxmal. The site is on Fed. 261, approximately south from Mérida, Yucatán, towards Campeche, Campeche, and is a popular tourism destination. Ruins extend for a considerable distance on both sides of the highway; many of the more distant structures are little visited, and some are still overgrown with forest. , a program was ongoing to clear and restore more buildings, as well as archeological excavations under the direction of archeologist Ramón Carrasco. Kabah was declared a Yucatán state park in 1993. History The name ''Kabah'' or ''Kabaah'' was first sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lloyd Stephens
John Lloyd Stephens (November 28, 1805October 13, 1852) was an American explorer, writer, and diplomat. He was a pivotal figure in the rediscovery of Maya civilization throughout Middle America (Americas), Middle America and in the planning of the Panama railway, Panama railroad. Early life John Lloyd Stephens was born November 28, 1805, in the township of Shrewsbury, New Jersey. He was the second son of Benjamin Stephens, a successful New Jersey merchant, and Clemence Lloyd, daughter of an eminent local judge. The following year the family moved to New York City. There Stephens received an education in the Classics at two privately tutored schools. At the age of 13, he enrolled at Columbia College of Columbia University, Columbia College, graduating at the top of his class four years later in 1822. After studying law with an attorney for a year, he attended the Litchfield Law School. He passed the bar exam after completing his course of study and practiced in New York City. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
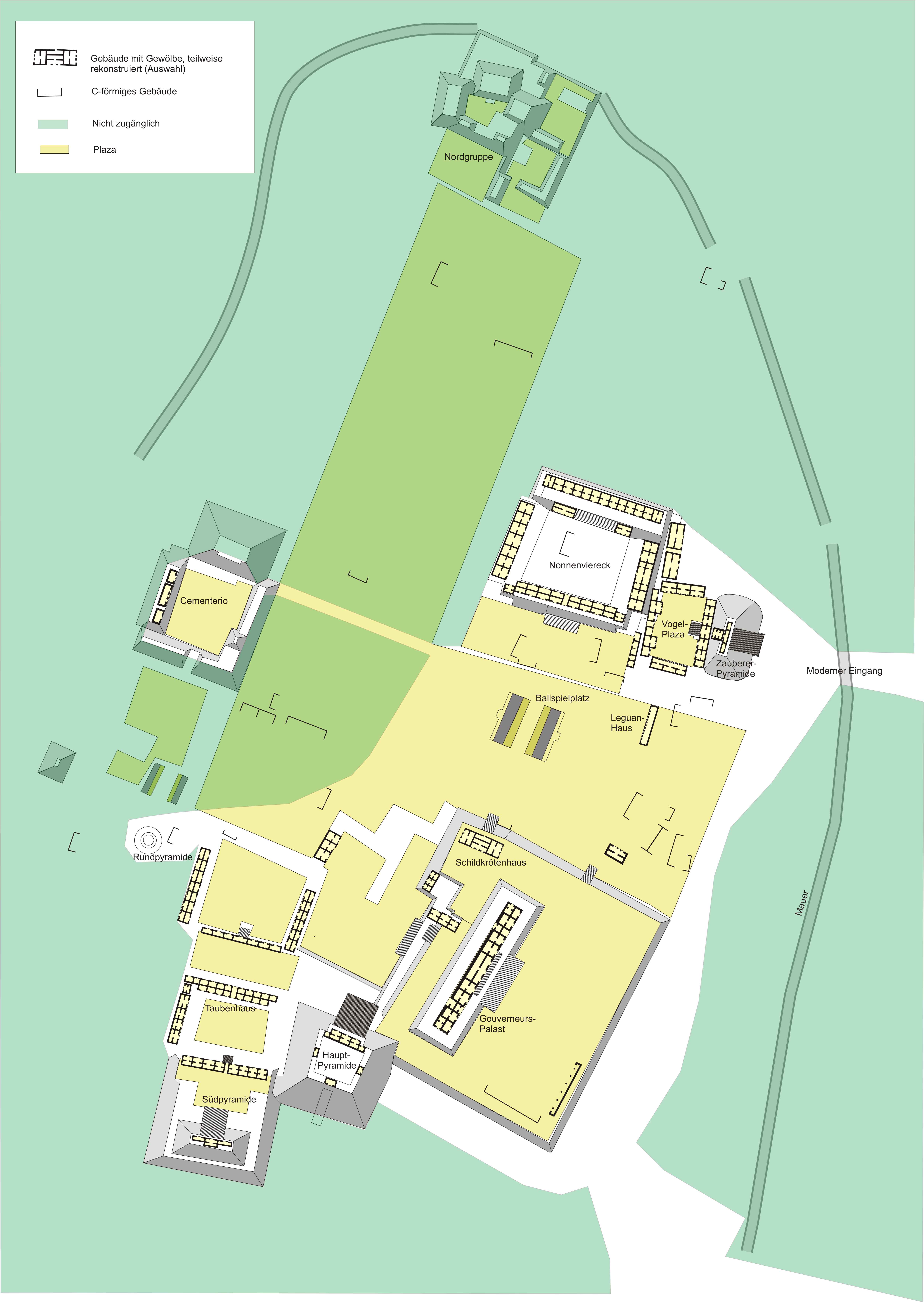
Uxmal
Uxmal (Yucatec Maya: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya civilization, Maya city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichen Itza and Calakmul in Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in Belize, and Tikal in Guatemala. It is located in the Puuc, Puuc region of the western Yucatán Peninsula, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site along with the nearby ruins of Kabah (Maya site), Kabah, Sayil and Labna. Uxmal is located 62 km south of Mérida, Yucatán, Mérida, capital of Yucatán state in Mexico. Its buildings are noted for their size and decoration. Ancient roads called ''sacbes'' connect the buildings, and also were built to other cities in the area such as Chichén Itzá in modern-day Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in modern-day Belize, and Tika ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Classic Period
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian (first human habitation until 3500 BCE); the Archaic (before 2600 BCE), the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE – 250 CE), the Classic (250–900 CE), and the Postclassic (); as well as the post European contact Colonial Period (1521–1821), and Postcolonial, or the period after independence from Spain (1821–present). The periodisation of Mesoamerica by researchers is based on archaeological, ethnohistorical, and modern cultural anthropology research dating to the early twentieth century. Archaeologists, ethnohistorians, historians, and cultural anthropologists continue to work to develop cultural histories of the region. Overview Paleo-Indian period 18000–8000 BCE The Paleo-Indian (less frequently, '' Lithic'') period or era is that which spans from the first signs of human presence in the region, which many believe to have happen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |