|
La Toma
''La Toma'' ( Spanish: ''The taking'') was a significant legal declaration made by Don Juan de Oñate on April 30, 1598. This event marked the formal assertion of Spanish sovereignty over the territories north of the Rio Grande, in present-day Texas, and laid the groundwork for the colonization of New Mexico. Background Don Juan de Oñate was a Spanish explorer and conquistador born in 1550 in what is now Mexico. He was the son of Cristóbal de Oñate, one of the founders of Zacatecas. In his youth, Oñate engaged in military campaigns against indigenous groups such as the Chichimecas. His ambitions led him to seek permission from the Spanish crown to explore and settle new territories in North America, which he received in 1595 from Viceroy Luis de Velasco. Oñate's expedition began in 1598, comprising over 400 Tlaxcaltecs, soldiers, priests, and supplies necessary for establishing a settlement. The expedition aimed not only to conquer but also to spread Christianity among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish (language)
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries, as well as one of the six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The country with the largest population of native speakers is Mexico. Spanish is part of the Ibero-Romance language group, in which the language is also known as ''Castilian'' (). The group evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in Iberia after the collapse of the Western R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy Of Spain
The monarchy of Spain or Spanish monarchy () is the constitutional form of government of Spain. It consists of a hereditary monarch who reigns as the head of state, being the highest office of the country. The Spanish monarchy is constitutionally referred to as The Crown (), and it comprises the reigning monarch, currently King Felipe VI, their family, and the Royal Household, which supports and facilitates the sovereign in the exercise of his duties and prerogatives. The royal family is currently represented by King Felipe VI, Queen Letizia, their daughters Leonor, Princess of Asturias, and Infanta Sofía, and the king's parents, King Juan Carlos I and Queen Sofía. The Spanish Constitution of 1978 re-established a constitutional monarchy as the form of government for Spain after the end of the dictatorship of Francisco Franco and the restoration of democracy in 1977. The 1978 constitution affirmed the role of the King of Spain as the living personification an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ácoma Massacre
The Acoma Massacre was a punitive expedition by Spanish conquistadors at the Acoma Pueblo in January, 1599 that resulted in the deaths of around 500 Acoma men and 300 women and children after a three-day battle. Of the Acoma who survived the attack, many were sentenced to 20-year terms of bondage, and 24 suffered amputations. The massacre was the result of a battle between Spanish colonizers and Native Americans from the Keres Acoma Nation in what is now New Mexico in retaliation for the killing of 12 Spanish soldiers by the Acoma in the previous year. Background In the late 1500s the Spanish Crown began ordering conquest expeditions into the territories of Pueblo peoples, areas of which Spain sought to gain control of as part of the colonization efforts in New Spain. In 1595, the conquistador Don Juan de Oñate was granted permission by King Philip II to colonize Santa Fe de Nuevo México, the present-day American state of New Mexico. The early years of Spanish exploits i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural list of regions of the United States, region of the United States that includes Arizona and New Mexico, along with adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by List of metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area are Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Texas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson, Arizona, Tucson. Before 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of New Mexico's pueblos and Santa Fe de Nuevo México#Regions and municipalities, Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of the area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854. While the regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Requirement Of 1513
The Spanish Requirement of 1513 (''Requerimiento'') was a declaration by the Spanish monarchy, written by the Council of Castile jurist Juan López de Palacios Rubios, of Castile's divinely ordained right to take possession of the territories of the New World and to subjugate, exploit and, when necessary, to fight the native inhabitants. The declaration was made on behalf of Ferdinand II of Aragon and his daughter, the Queen regnant Joanna of Castile. The ''Requerimiento'' (Spanish for "requirement" as in "demand") was read to Native Americans to inform them of Spain's rights to conquest. The Spaniards thus considered those who resisted as defying God's plan, and so used Catholic theology to justify their conquest.Todorov, Tzvetan (1984) "The Conquest of America." New York:HarperPerennial Historical context In 1452, Pope Nicholas V issued the papal bull '' Dum Diversas'', which legitimized the slave trade, at least as a result of war. It granted Afonso V of Portugal the right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pueblo
Pueblo refers to the settlements of the Pueblo peoples, Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, currently in New Mexico, Arizona, and Texas. The permanent communities, including some of the oldest continually occupied settlements in the United States, are called pueblos (lowercased). Spanish explorers of northern New Spain used the term ''pueblo'' to refer to permanent Indigenous towns they found in the region, mainly in New Mexico and parts of Arizona, in the former province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, Nuevo México. This term continued to be used to describe the communities housed in apartment structures built of stone, adobe, and other local material. The structures were usually multistoried buildings surrounding an open plaza. Many rooms were accessible only through ladders raised and lowered by the inhabitants, thus protecting them from break-ins and unwanted guests. Larger pueblos are occupied by hundreds to thousands of Puebloan people. Several federall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II Of Spain
Philip II (21 May 152713 September 1598), sometimes known in Spain as Philip the Prudent (), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and List of Sicilian monarchs, Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He was also ''jure uxoris'' King of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from Wedding of Mary I of England and Philip of Spain, his marriage to Queen Mary I in 1554 until her death in 1558. Further, he was Duke of Milan from 1540. From 1555, he was Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands, Netherlands. The son of Emperor Charles V and Isabella of Portugal, Holy Roman Empress, Isabella of Portugal, Philip inherited his father's Spanish Empire in 1556, and succeeded to the Kingdom of Portugal, Portuguese throne in 1580 following a dynastic crisis. The Spanish conquests Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, of the Inca Empire and of the Philippines, named in his honor by Ruy López de Villalobos, were completed during h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlaxcaltec
The Tlaxcallans, or Tlaxcaltec, are an indigenous Nahua people who originate from Tlaxcala, Mexico. The Confederacy of Tlaxcala was instrumental in overthrowing the Aztec Empire in 1521, alongside conquistadors from the Kingdom of Spain. The Tlaxcallans remained allies of the Spanish for 300 years until the Independence of Mexico in 1821. Pre-Colonial history The Tlaxcaltec were a Nahua group, one of the 7 tribes which migrated from their original homeland in the north alongside the Mexica and 5 other tribes. After settling in what is now called Tlaxcala they formed a conglomeration of three distinct ethnic groups who spoke Nahuatl, Otomi and Pinome that comprised the four city-states (''Altepetl'') of ''Tlaxcallān'' or Tlaxcala. Each of the four cities supposedly had equal say in this confederation, but eventually, the Nahuatl speakers became the dominant ethnic group. By the time of European contact, the city of Tizatlan was effectively controlling Tlaxcala. Despite ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis De Velasco, 1st Marquess Of Salinas Del Río Pisuerga
Luis de Velasco, 1st Marquess of Salinas del Río Pisuerga (c. 1534 – September 7, 1617) was a Spanish nobleman who was the ninth viceroy of New Spain from January 27, 1590 to November 4, 1595, and again from July 2, 1607, to June 10, 1611. In between he was viceroy of Peru for eight years, from July 24, 1596, to January 18, 1604. He was known as Luis de Velasco, hijo to distinguish him from his father, Luis de Velasco, the second viceroy of New Spain. Early life Born in Carrión de los Condes, Luis de Velasco remained in Spain with his mother and siblings when his father, Luis de Velasco, was appointed Viceroy of New Spain. His brother, don Antonio de Velasco, was a "gentilhombre de la boca" to Prince Philip. The two brothers accompanied Philip to England when he married Queen Mary. They traveled on with the court to Brussels, where young don Luis was admitted to the military-religious order of Santiago. In about 1560 he joined his father in Mexico City where he passed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' Spanish Empire, imperial era between 15th and 19th centuries. To the end of its imperial rule, Spain called its overseas possessions in the Americas and the Philippines "The Indies", an enduring remnant of Columbus's notion that he had reached Asia by sailing west. When these territories reach a high level of importance, the crown established the Council of the Indies in 1524, following the conquest of the Aztec Empire, asserting permanent royal control over its possessions. Regions with dense indigenous populations and sources of mineral wealth attracting Spanish settlers became colonial centers, while those without such resources were peripheral to crown interest. Once regions incorporated into the empire and their importance assessed, overseas possessions came under stronger or weaker crown co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
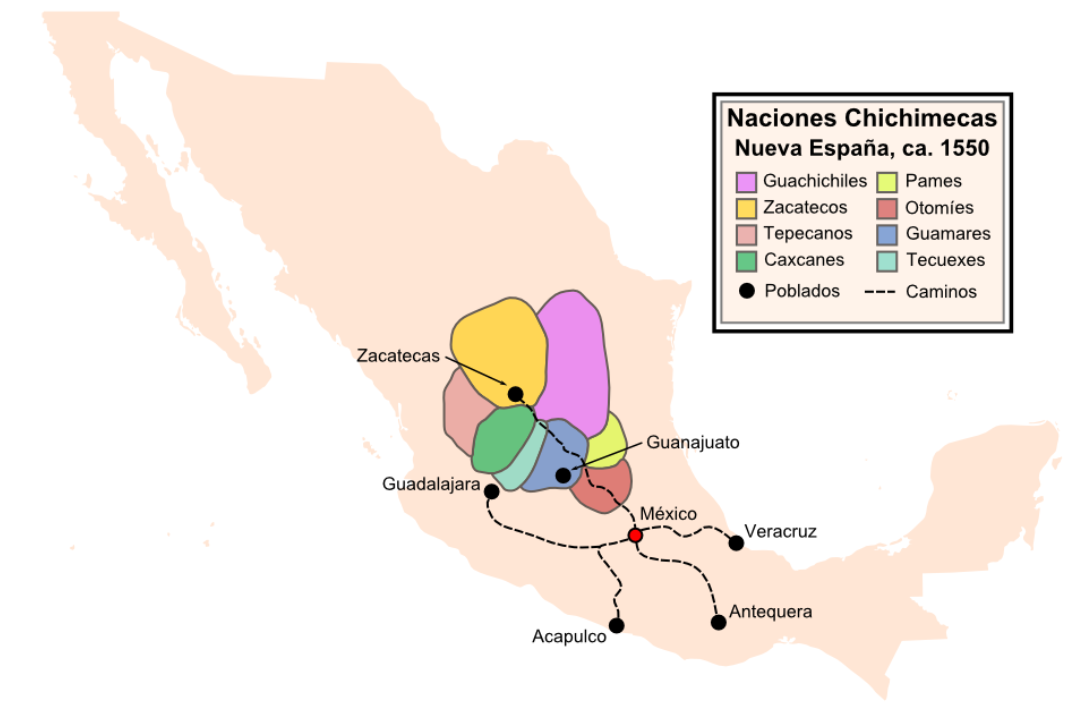
Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajío region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the same meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. In the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "for the Spanish, the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit."Gradie, Charlotte M. "Discovering the Chichimecas" ''Academy of American Franciscan History'', Vol 51, No. 1 (July 1994), p. 68 Gradie noted that Chichimeca was used as a broad and generalizing term by outsiders, writing, " twas used by both Spanish and Nahuatl speakers to refer collectively to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don (honorific)
The terms Don (in Spanish language, Spanish and Italian language, Italian), Dom (in Portuguese language, Portuguese), and Domn (in Romanian language, Romanian), are honorific prefixes derived from the Latin language, Latin ''Dominus'', meaning "lord" or "owner". The honorific is commonly used in Spain, Portugal, and Italy, as well as in the Spanish-speaking world and Portuguese-speaking world, as well as some other places formerly colonized by Spain or Portugal. The feminine equivalents are (), (), (Romanian) and (). The term is derived from the Latin : a master of a household, a title with background from the Roman Republic in classical antiquity. With the abbreviated form having emerged as such in the Middle Ages, traditionally it is reserved for Catholic clergy and nobles, in addition to certain educational authorities and persons of high distinction. Spanish-speaking world In Spanish, although originally a title reserved for royalty, select nobles, and church hierarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |