|
La Mère Catherine
La Mère Catherine () is a brasserie in the 18th arrondissement of Paris, France. It is the oldest still-operating restaurant at the Place du Tertre. It is situated in a building that previously served as the church presbytery of Saint-Pierre de Montmartre. History Founded in 1793, it is one of the oldest restaurants in Paris. A plaque at its entrance gives a folk etymology of the word "bistro": that on March 30, 1814, while a group of Russian soldiers were dining at Mère Catherine, they asked for drinks, (Cyrillic: ''быстро''; Russian: "quickly"). Thereafter, "bistro" became a description of a restaurant where you could get food or drink quickly. In the early twentieth century, the bistro was managed by Mr. Lemoine and owned by Père Labille. During the French Revolution, Georges Danton met his disciples at Mère Catherine. During the Nazi occupation of Paris, 1941-1944, Ernst Jünger was a patron. At one time, guests could enjoy a game of billiards at Mère Catherine; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris 75018 Place Du Tertre 20120101 La Mère Catherine
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasserie
In France, Flanders, and the Francophone world, a brasserie () is a type of French restaurant with a relaxed setting, which serves dishes and other meals. The word ''brasserie'' is French for "brewery" and, by extension, "the brewing business". Although most brasseries still serve a large selection of beers, most of them offer a wider choice of beverages such as wines and liquors. A brasserie can be expected to have professional service, printed menus, and, traditionally, white linen—unlike a bistro which may have none of these. Typically, a brasserie is open every day and serves the same menu, generally composed of a few traditional French dishes, all day. A classic example of a brasserie dish is steak frites. Etymology The term ''brasserie'' is French for "brewery", from Middle French ''brasser'' "to brew", from Old French ''bracier'', from -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Arrondissement Of Paris
The 18th arrondissement of Paris (''XVIIIe arrondissement'') is one of the 20 Arrondissements of Paris, arrondissements, or administrative districts, of Paris, the capital city of France. In spoken French, this arrondissement is referred to as ''dix-huitième''. The arrondissement, known as Butte-Montmartre, is located on the Rive Droite, right bank of the River Seine. It is mostly known for hosting the large hill of Montmartre, which is known for its artistic history, the where Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque, and Amedeo Modigliani lived and worked in the early 20th century, the house of music diva Dalida, the Moulin Rouge cabaret, other historic features, and the prominent Basilique du Sacré-Cœur, Paris, Sacré Cœur basilica which sits atop the hill. The 18th arrondissement also contains Goutte d'Or district, which has large numbers of residents of North and sub-Saharan African origins, and which is famous for its market, the marché Barbès, which sells products from Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Du Tertre
The Place du Tertre () is a square in the 18th arrondissement of Paris, France. Only a few streets away from the Basilica of the Sacré Cœur and the Lapin Agile cabaret, it is near the summit of the city's elevated Montmartre quarter. History The Place du Tertre was the heart of the prestigious Benedictine Montmartre Abbey, established in 1133 by King Louis VI. Montmartre Abbey thrived through the centuries and until the French Revolution under the patronage of the Kings of France. The Place du Tertre was opened to the public in 1635 as Montmartre village central square. From the end of the 18th century until World War I, the whole Montmartre Bohème could be seen there: painters, songwriters and poets. With its many artists setting up their easels each day for the tourists, the Place du Tertre is a reminder of the time when Montmartre was the mecca of modern art. At the beginning of the 20th century, many painters including Pablo Picasso, Amedeo Modigliani, and Maurice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbytery (residence)
A clergy house is the residence, or former residence, of one or more priests or ministers of a given religion, serving as both a home and a base for the occupant's ministry. Residences of this type can have a variety of names, such as manse, parsonage, presbytery, rectory, or vicarage. Function A clergy house is typically owned and maintained by a church, as a benefit to its clergy. This practice exists in many denominations because of the tendency of clergy to be transferred from one church to another at relatively frequent intervals. Also, in smaller communities, suitable housing is not always available. In addition, such a residence can be supplied in lieu of salary, which may not be able to be provided (especially at smaller congregations). Catholic clergy houses in particular may be lived in by several priests from a parish. Clergy houses frequently serve as the administrative office of the local parish, as well as a residence. They are normally located next to, or at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-Pierre De Montmartre
Saint-Pierre de Montmartre () is the second oldest surviving church in Paris, after the Abbey of Saint-Germain-des-Pres. It is one of the two main churches on Montmartre, the other being the more famous 19th-century Sacré-Cœur Basilica, just above it. Saint-Pierre de Montmartre, begun in 1133, was the church of the prestigious Montmartre Abbey, destroyed in the French Revolution.Dumoulin, Ardisson, Maingard and Antonello, ''Églises de Paris (2010)'', pp 180-183 According to the earliest biography of Saint Ignatius Loyola, the martyrium of Montmartre Abbey was the location where the vows were taken that led to the founding of the Society of Jesus. History According the traditional history of the church, it was founded by Saint Denis in the third century, but only scattered signs of Gallo-Roman occupation have been detected at the much-disturbed site, Merovingian sarcophagi and column capitals dating from the 7th century indicate that there was a church on the summit of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Etymology
Folk etymology – also known as (generative) popular etymology, analogical reformation, (morphological) reanalysis and etymological reinterpretation – is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more familiar one through popular usage. The form or the meaning of an archaic, foreign, or otherwise unfamiliar word is reinterpreted as resembling more familiar words or morphemes. The term ''folk etymology'' is a loan translation from German ''Volksetymologie'', coined by Ernst Förstemann in 1852. Folk etymology is a productive process in historical linguistics, language change, and social interaction. Reanalysis of a word's history or original form can affect its spelling, pronunciation, or meaning. This is frequently seen in relation to loanwords or words that have become archaic or obsolete. Folk/popular etymology may also refer to a popular false belief about the etymology of a word or phrase that does not lead to a change in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistro
A bistro or bistrot (), in its original Parisian form, is a small restaurant serving moderately priced, simple meals in a modest setting. In more recent years, the term has become used by restaurants considered, by some, to be pretentious. Style In a 2007 survey of national cuisines, a bistro is characterised as typically: A Paris newspaper in 1892 referred to dishes served at a bistro, including escargots, veal with sauce ravigote, navarin of lamb, hachis Parmentier, eggs, sausages and hot roast chicken. The '' Oxford Companion to Food'' comments that the idea of simple inexpensive food served in a French atmosphere has wide appeal, so that by the end of the 20th century the term had "begun to be annexed by more pretentious premises". Etymology The etymology is unclear. The ''Dictionnaire de l'Académie française'' dates the word from the 19th century term, ''bistro'', "innkeeper", and suggests that it may be linked to the Poitevin word ''bistraud'' ("little servant"), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Danton
Georges Jacques Danton (; ; 26 October 1759 – 5 April 1794) was a leading figure of the French Revolution. A modest and unknown lawyer on the eve of the Revolution, Danton became a famous orator of the Cordeliers Club and was raised to governmental responsibilities as the French Minister of Justice following the fall of the monarchy on the tenth of August 1792, and was allegedly responsible for inciting the September Massacres. He was tasked by the National Convention to intervene in the military conquest of Belgium led by General Dumouriez, and in the spring of 1793 supported the foundation of a Revolutionary Tribunal, becoming the first president of the Committee of Public Safety. During the Insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793, Danton changed his mind on the use of force and lost his seat in the committee afterwards, which solidified the rivalry between him and Maximilien Robespierre. In early October 1793, Danton left politics but was urged to return to Paris to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Jünger
Ernst Jünger (; 29 March 1895 – 17 February 1998) was a German author, highly decorated soldier, philosopher, and entomology, entomologist who became publicly known for his World War I memoir ''Storm of Steel''. The son of a successful businessman and chemist, Jünger rebelled against an affluent upbringing and sought adventure in the ''Wandervogel'' German youth movement, before running away to briefly serve in the French Foreign Legion, which was an illegal act in Germany. However, he escaped prosecution due to his father's efforts and was able to enlist in the German Army (German Empire), German Army on the outbreak of World War I in 1914. During an ill-fated offensive in 1918 Jünger was badly wounded and was awarded the ''Pour le Mérite'', a rare decoration for one of his rank. Since new awards of the military class ceased with the end of the Prussian monarchy in November 1918, Jünger, who died in 1998, was the last living recipient of the military class award. He wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
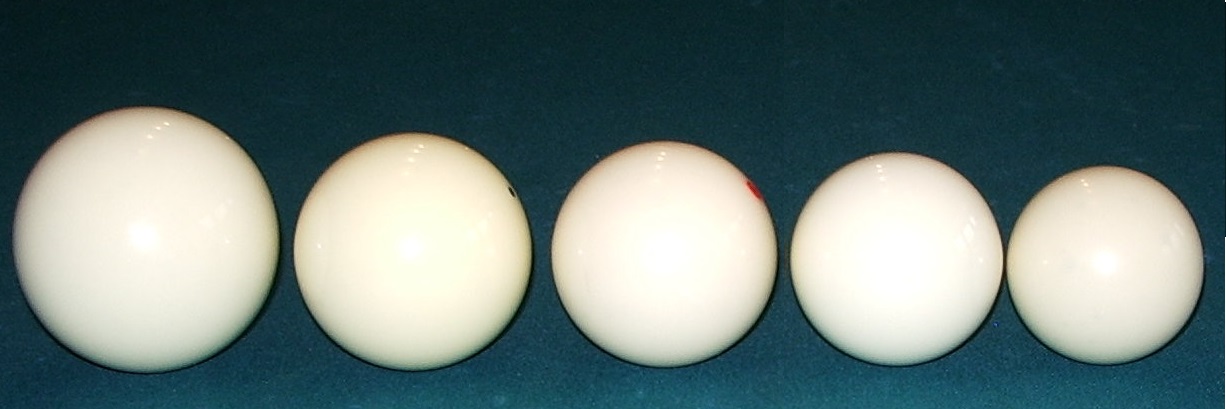
Billiards
Cue sports are a wide variety of games of skill played with a cue stick, which is used to strike billiard balls and thereby cause them to move around a cloth-covered table bounded by elastic bumpers known as . Cue sports, a category of stick sports, may collectively be referred to as billiards, though this term has more specific connotations in some English dialects. There are three major subdivisions of games within cue sports: * Carom billiards, played on tables without , typically ten feet in length, including straight rail, balkline, one-cushion carom, three-cushion billiards, artistic billiards, and four-ball * Pocket billiards (or pool), played on six-pocket tables of seven, eight, nine, or ten-foot length, including among others eight-ball (the world's most widely played cue sport), nine-ball (the dominant professional game), ten-ball, straight pool (the formerly dominant pro game), one-pocket, and bank pool *Snooker, English billiards, and Russian pyra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |