|
La Macarena Fault
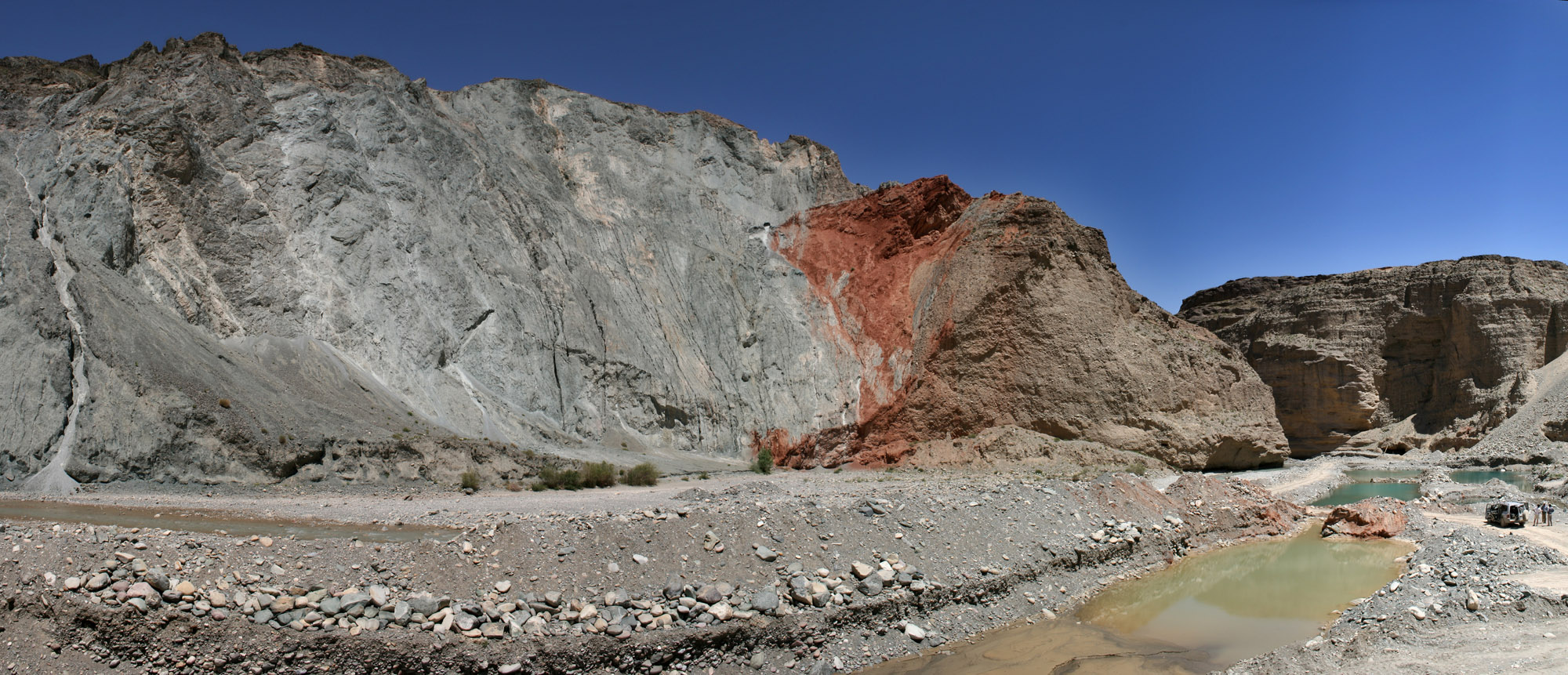
The La Macarena Fault () is a thrust fault in the department of Meta in Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average north to south strike of 000.6 ± 9 along the east side of the Serranía de la Macarena. Etymology The fault is named after the Serranía de la Macarena.Paris et al., 2000, p.47 Description The Macarena Fault extends along the eastern border of the Serranía de la Macarena, which is an isolated tectonic block to the east of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault thrusts Precambrian crystalline rocks and Tertiary oceanic rocks on the west over Tertiary and Pleistocene continental rocks on the east. The course of the Guayabero River is controlled by the fault, showing strong lineations. Pleistocene sediments and alluvial terraces are apparently offset. There is a prominent fault scarp on the west side of the river. See also * List of earthquakes in Colombia * Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault * Eastern Frontal Fault System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serranía De La Macarena
Serranía de la Macarena is an isolated mountain range located in the Meta Department, Colombia. It was named after the Virgin of Hope of Macarena. The mountains are separated by about at their northern extreme from the East Andes. The range is orientated from north to south and is in length and wide. The highest peak ("El Gobernador", the governor) reaches and is the highest point of the Orinoquía Region. The first national reserve in Colombia was established in the central part of the mountain range in accordance with a Congressional Law promulgated in 1948. The status of National Natural Park was designated in 1971 and the protected area encompasses . Biodiversity The national park encompasses the ecologically unique meeting point for the flora and fauna of the Amazon, Orinoco and Andes regions. The area is of tropical climate and temperatures range from 42 °F (5.5 °C) to 88 °F (31 °C). These aspects help to maintain a high level of biodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria, the Latinised name for Wales, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time. The Precambrian is an informal unit of geologic time, subdivided into three eons ( Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic) of the geologic time scale. It spans from the formation of Earth about 4.6 billion years ago ( Ga) to the beginning of the Cambrian Period, about million years ago ( Ma), when hard-shelled creatures first appeared in abundance. Overview Relatively little is known about the Precambrian, despite it making up roughly seven-eighths of the Earth's history, and what is known has largely been discovered from the 1960s onwards. The Precambrian fos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Faults
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or ''window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular ''klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
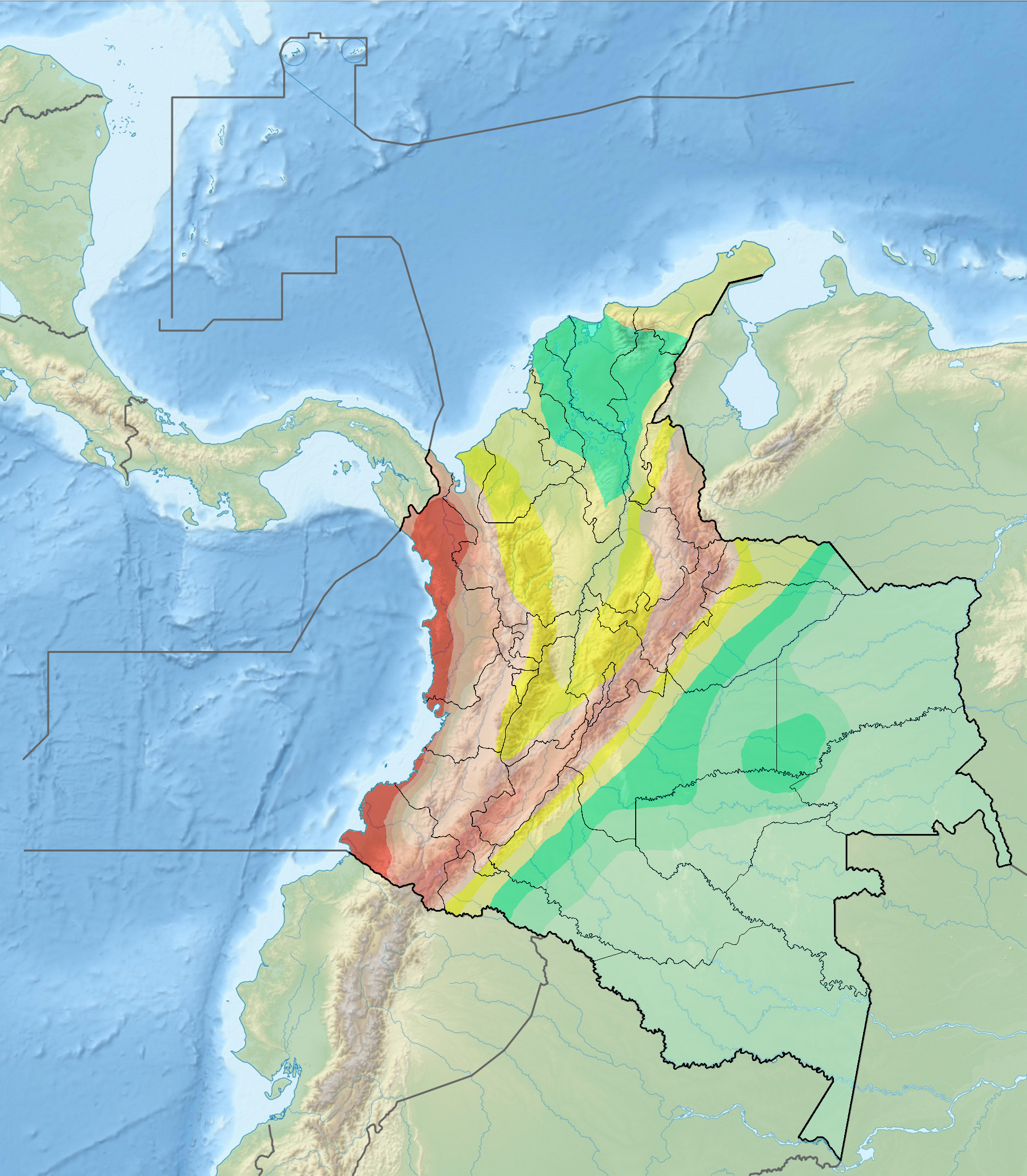
Seismic Faults Of Colombia
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning " earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Frontal Fault System
The Eastern Frontal Fault System ( es, Sistema de Fallas de la Falla Frontal de la Cordillera Oriental) is a megaregional system of oblique and thrust faults cross-cutting Colombia from Ecuador in the south to Venezuela in the north. The system from south to north covers ten out of 32 departments of Colombia; Nariño, Putumayo, Cauca, Huila, Caquetá, Cundinamarca, Meta, Boyacá, Casanare and Arauca. The Eastern Frontal Fault System underlies and affects the capitals of Putumayo, Mocoa, Caquetá, Florencia, Meta, Villavicencio and Casanare, Yopal. The fault system has a total length of with a cumulative length of the faults of and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 042.1 ± 19 bordering and crossing the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault system forms the boundary between the North Andes microplate and the South American Plate. Several segments of the fault system are active, with major earthquakes occurring in historical time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault
The Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault (BSMF, BSF) or Bucaramanga-Santa Marta Fault System ( es, (Sistema de) Falla(s) de Bucaramanga-Santa Marta) is a major oblique transpressional sinistral strike-slip fault (wrench fault) in the departments of Magdalena, Cesar, Norte de Santander and Santander in northern Colombia. The fault system is composed of two main outcropping segments, named Santa Marta and Bucaramanga Faults, and an intermediate Algarrobo Fault segment in the subsurface. The system has a total length of and runs along an average north-northwest to south-southeast strike of 341 ± 23 from the Caribbean coast west of Santa Marta to the northern area of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The fault system is a major bounding fault for various sedimentary basins and igneous and metamorphic complexes. The northern Santa Marta Fault segment separates the Sinú-San Jacinto Basin and Lower Magdalena Valley in the west from the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta to the east. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Colombia
This is a list of earthquakes in Colombia. Colombia is a seismically active country and has a large seismic risk in many areas of its territory due to its location at the boundaries of the Malpelo, Panama, Caribbean, North Andes (where most earthquakes occurred) and South American Plates along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The southeastern and extreme eastern portions of Colombia are not as seismically active as the rest of the country. The first historically registered earthquake felt in Colombia occurred on September 11, 1530, around 10:00 AM, probably with the epicentre near Cumaná, Venezuela. The earthquake was documented by Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés in his work ''La Historia general de las Indias'' and by friar Bartolomé de las Casas in his book ''Historia de Las Indias''.Ramírez, 1975, p.63 The first documented earthquake with its epicentre in present-day Colombia territory took place in 1566,Ramírez, 1975, p.65 with the epicentre estimated around San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Scarp
A fault scarp is a small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other. It is the topographic expression of faulting attributed to the displacement of the land surface by movement along faults. They are exhibited either by differential movement and subsequent erosion along an old ''inactive'' geologic fault (a sort of old rupture), or by a movement on a recent active fault. Characteristics Fault scarps often contain highly fractured rock of both hard and weak consistency. In many cases, bluffs form from the upthrown block and can be very steep. The height of the scarp formation is equal to the vertical displacement along the fault. Active scarps are usually formed by tectonic displacement, e.g. when an earthquake changes the elevation of the ground and can be caused by any type of fault, including strike-slip faults, whose motion is primarily horizontal. This movement is usually episodic, with the height of the bluf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined '' alluvion'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guayabero River
The Guayabero River is a river of Colombia. It is primarily located in the Meta Department, forming a portion of its border with the Guaviare Department. It is part of the Orinoco River basin. Its confluence with the Ariari River gives rise to the Guaviare River, one of the Orinoco's largest tributaries. See also *List of rivers of Colombia Atlantic Ocean Amazon River Basin * Amazon River ** Guainía River or Negro River *** Vaupés River or Uaupés River **** Papuri River **** Querary River *** Isana River or Içana River **** Cuiari River *** Aquio River ** Caquetá Rive ... References *Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993. Rivers of Colombia {{Colombia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |