|
La Brea Tar Pits
La Brea Tar Pits comprise an active Paleontological site, paleontological research site in urban Los Angeles. Hancock Park was formed around a group of tar pits where natural Bitumen, asphalt (also called asphaltum, bitumen, or pitch; ''brea'' in Spanish) has seeped up from the ground for tens of thousands of years. Over many centuries, the bones of trapped animals have been preserved. The George C. Page Museum is dedicated to researching the tar pits and displaying specimens from the animals that died there. "La Brea Tar Pits" is a registered National Natural Landmark. Formation Tar pits are composed of Heavy crude oil, heavy oil fractions, called gilsonite, which seep from the earth as oil. Crude oil seeps up along the 6th Street Fault from the Salt Lake Oil Field, which underlies much of the Fairfax District north of Hancock Park. The oil reaches the surface and forms pools, becoming asphalt as the lighter fractions of the petroleum biodegrade or evaporate. The asphalt the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hancock Park
Hancock Park is a city park in the Miracle Mile section of the Mid-Wilshire neighborhood in Los Angeles, California. The park's destinations include the La Brea Tar Pits; the adjacent George C. Page Museum of La Brea Discoveries, which displays the fossils of Ice Age prehistoric mammals from the tar pits; and the Los Angeles County Museum of Art (LACMA) complex. They are among the most popular tourist attractions in Los Angeles. Geography In 1939, the Federal Writers' Project American Guide to Los Angeles described Hancock Park as a district bounded by "on the north side of Wilshire Blvd. between W. 6th St., Curson Ave., and Ogden Dr." Features The park has urban open spaces and landscaped areas for walking, picnicking, and other recreation. Located on Wilshire Boulevard just east of Fairfax Avenue, it extends across a large city block and around two museums. The landmark Park La Brea complex is across 6th Street on the north. The Hancock Park neighborhood, is approxim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfossil
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, is referred to as a macrofossil. Microfossils are a common feature of the geological record, from the Precambrian to the Holocene. They are most common in deposits of marine environments, but also occur in brackish water, fresh water and terrestrial sedimentary deposits. While every kingdom of life is represented in the microfossil record, the most abundant forms are protist skeletons or microbial cysts from the Chrysophyta, Pyrrhophyta, Sarcodina, acritarchs and chitinozoans, together with pollen and spores from the vascular plants. Overview A microfossil is a descriptive term applied to fossilized plants and animals whose size is just at or below the level at which the fossil can be analyzed by the naked e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of United States cities by population, 67th-most populous city in the U.S., with a population of 302,971 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city is located in Western Pennsylvania, southwestern Pennsylvania at the confluence of the Allegheny River and Monongahela River, which combine to form the Ohio River. It anchors the Greater Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh metropolitan area, which had a population of 2.457 million residents and is the largest metro area in both the Ohio Valley and Appalachia, the Pennsylvania metropolitan areas, second-largest in Pennsylvania, and the List of metropolitan statistical areas, 26th-largest in the U.S. Pittsburgh is the principal city of the greater Pittsburgh–New Castle–Weirton combined statistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorrance Publishing Co
Dorrance can refer to: People Surname * Anson Dorrance (born 1951), American former soccer coach * Arthur Calbraith Dorrance, American businessman, president of the Campbell Soup Company beginning in 1894 * Daniel G. Dorrance (1811–1896), American politician * Denise Dorrance, American-born British cartoonist, illustrator and graphic novelist * Ethel Smith Dorrance (1880–?), American writer * Harvie James Dorrance (1898–1961), Canadian politician * John Thompson Dorrance (1873–1930), American chemist who discovered a method to create condensed soup, president of the Campbell Soup Company * John Dorrance III (born 1943 or 1944), American-born Irish billionaire businessman and Campbell's Soup heir * Mary Alice Dorrance Malone (born 1949 or 1950), née Dorrance, American billionaire and Campbell's Soup heiress, granddaughter of John Thompson Dorrance * Michelle Dorrance (born 1979), American dancer and choreographer * Tom and Bill Dorrance (1906–1999 and 1910–2003, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Crespí
Juan Crespí, OFM (Catalan language, Catalan: ''Joan Crespí''; 1 March 1721 – 1 January 1782) was a Franciscan missionary and explorer of The Californias, Las Californias. Biography A native of Majorca, Crespí entered the Franciscan order at the age of seventeen. He came to New Spain in 1749, and accompanied explorers Francisco Palóu and Junípero Serra. In 1767 he went to the Baja California Peninsula and was placed in charge of the Misión La Purísima Concepción de Cadegomó. In 1769, Crespí joined the Portola expedition, expedition led by Gaspar de Portolá and Junípero Serra (see Timeline of the Portolá expedition). He traveled in the vanguard of the land expedition to San Diego, led by Captain Fernando Rivera y Moncada, where a presidio and mission were established. Crespí then continued north with Portolá and Rivera to identify the port of Monterey. Because he was the only one of the Franciscans to make the entire journey by land, Crespí became the first o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspar De Portolá
Captain Gaspar de Portolá y Rovira (January 1, 1716 – October 10, 1786) was a Spanish Army officer and colonial administrator who served as the first List of governors of California before 1850, governor of the Californias from 1767 to 1770. Born in Catalonia into an Spanish nobility, aristocratic family, he is best known for leading the Portolá expedition into California, which laid the foundations of Spanish rule in the region Californian cities like San Diego and Monterey, California, Monterey, and bestowed names to geographic features throughout California, many of which are still in use. Early life Gaspar de Portolá y Rovira was born on January 1, 1716 in Os de Balaguer, Catalonia, into a family of minor Spanish nobility. After he came of age, Portolá joined the Spanish Army, being commissioned as an Ensign (rank), ensign in 1734 and a lieutenant in 1743. He saw service in Italy during the War of the Austrian Succession and participated in the Spanish invasion of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portolá Expedition
thumbnail, 250px, Point of San Francisco Bay Discovery The Portolá expedition was a Spanish voyage of exploration in 1769–1770 that was the first recorded European exploration of the interior of the present-day California. It was led by Gaspar de Portolá, governor of '' Las Californias'', the Spanish colonial province that included California, Baja California, and other parts of present-day Mexico and the United States. The expedition led to the founding of Alta California and contributed to the solidification of Spanish territorial claims in the disputed and unexplored regions along the Pacific coast of North America. Background Although already inhabited by Native Americans, the territory that is now California was claimed by the Spanish Empire in 1542 by right of discovery when Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo explored the Pacific coast. Cabrillo's exploration laid claim to the coastline as far north as forty-two degrees north latitude. This northern limit was later confirmed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel Islands (California)
The Channel Islands () are an eight-island archipelago located within the Southern California Bight in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California. They define the Santa Barbara Channel between the islands and the California mainland. The four Northern Channel Islands are part of the Transverse Ranges geologic province, and the four Southern Channel Islands are part of the Peninsular Ranges province. Five of the islands are within the Channel Islands National Park. The waters surrounding these islands make up Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary. The Nature Conservancy was instrumental in establishing the Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary. There is evidence that humans have lived on the Northen Channel Islands for thousands of years. Radiocarbon dating shows that there was a continuous human presence between 8000-11000 years ago. The islands were inhabited primarily by two different Native American groups, the Chumash, and the Tongva/Gabrieleno .The Chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Barbara Channel
The Santa Barbara Channel is a portion of the Southern California Bight and separates the mainland of California from the northern Channel Islands. It is generally south of the city of Santa Barbara, and west of the Oxnard Plain in Ventura County. It trends east–west, is approximately long and averages about across, becoming narrowest at its easternmost extremity where Anacapa Island is about from the mainland. During the last ice age, the four northern Channel Islands, including Santa Rosa Island, were conjoined into Santa Rosae, a single island that was only five miles (8 km) off the coast. The islands are visible from the mainland on clear days. Excursion boats cross the channel, taking visitors to watch whales and visit the islands. In the perpendicular (east-west) direction, huge cargo ships and tankers occupy a major shipping lane on their way to or from the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach. The Channel is the location of numerous oil fields, some of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
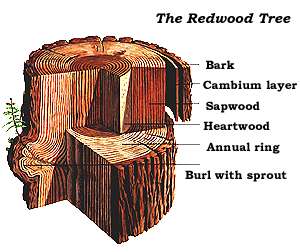
California Redwood
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995: 606–607 is the sole living species of the genus '' Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the longest-living trees on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. Being the tallest tree species, with a small range and an extremely long lifespan, many redwoods are preserved in various state and nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomol
A ''tomol'' or ''tomolo'' (Chumash) or ''te'aat'' or ''ti'at'' (Tongva/Kizh) are plank-built boats, historically and currently in the Santa Barbara, California and Los Angeles area. They replaced or supplemented tule reed boats. The boats were between in length and in width. The Chumash refer to the ''tomol'' as the "House of the Sea" for their reliability. Double-bladed kayak-like paddles are used to propel the boat through the ocean. Some sources suggest the boats may have origins at Santa Catalina Island (California), Catalina Island and have been in use for thousands of years. Others suggest an origin on the Northern Channel Islands during the first millennium CE. The ''tomol'' has been described as "the single most technologically complex watercraft built in North America" and as being unique to "the New World." The boats are still constructed by Chumash, Tongva/Kizh, and Acjachemen people today. Construction ''Tomols'' were preferably built out of redwood that had drift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongva
The Tongva ( ) are an Indigenous peoples of California, Indigenous people of California from the Los Angeles Basin and the Channel Islands of California, Southern Channel Islands, an area covering approximately . In the precolonial era, the people lived in as many as 100 villages and primarily identified by their village rather than by a pan-tribal name. During colonization, the Spanish referred to these people as Gabrieleño and Fernandeño, names derived from the Spanish missions in California, Spanish missions built on their land: Mission San Gabriel Arcángel and Mission San Fernando Rey de España. ''Tongva'' is the most widely circulated endonym among the people, used by Narcisa Higuera in 1905 to refer to inhabitants in the vicinity of Mission San Gabriel. Some people who identify as direct lineal descendants of the people advocate the use of their ancestral name ''Kizh'' as an Endonym and exonym, endonym. The Tongva, along with neighboring groups such as the Chumash peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |