|
LPHN3
Latrophilin 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ADGRL3'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of the latrophilin subfamily of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). Latrophilins may function in both cell adhesion and signal transduction. In experiments with non-human species, endogenous proteolytic cleavage within a cysteine-rich GPS (G-protein-coupled-receptor proteolysis site) domain resulted in two subunits (a large extracellular N-terminal cell adhesion subunit and a subunit with substantial similarity to the secretin/calcitonin family of GPCRs) being non-covalently bound at the cell membrane. Clinical significance A version of this gene has been linked to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). See also * Adhesion G protein-coupled receptors Adhesion G protein-coupled receptors (adhesion GPCRs) are a class of 33 human protein receptors with a broad distribution in embryonic and larval cells, cells of the reproductive tract, neurons, leu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latrophilin
Latrophilins are a group of highly conserved G-protein coupled receptors from the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor family. These receptors were originally identified based on their ability to bind to a component of black widow spider venom known as alpha-latrotoxin. This conserved family of membrane proteins has up to three homologues in chordate species, including humans. The precise functions of latrophilins remain unknown. Genetic defects in latrophilin genes have been associated with diseases such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and cancer. Human proteins containing this domain * Latrophilin 1 ( LPHN1) * Latrophilin 2 ( LPHN2) * Latrophilin 3 ( LPHN3) See also * ELTD1 Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor L4 is a latrophilin-like orphan receptor of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor family. In humans this protein is encoded by the ''ADGRL4'' gene. ADGRL4 appears to have a role in angiogenesis, both physiol ... References {{Acetylcholine metabo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretin Receptor Family
Secretin receptor family (class B GPCR subfamily) consists of secretin receptors regulated by peptide hormones from the glucagon hormone family. The family is different from adhesion G protein-coupled receptors. The secretin-receptor family of GPCRs include vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors and receptors for secretin, calcitonin and parathyroid hormone/parathyroid hormone-related peptides. These receptors activate adenylyl cyclase and the phosphatidyl-inositol-calcium pathway. The receptors in this family have seven transmembrane helices,; ; like rhodopsin-like GPCRs. However, there is no significant sequence identity between these two GPCR families and the secretin-receptor family has its own characteristic 7TM signature. The secretin-receptor family GPCRs exist in many animal species. Data mining with the Pfam signature has identified members in fungi, although due to their presumed non-hormonal function they are more commonly referred to as Adhesion G protein-coupled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and Developmental psychology, developmentally inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction. Impairments resulting from deficits in self-regulation such as time management, Cognitive inhibition, inhibition, task initiation, and sustained attention can include poor professional performance, relationship difficulties, and numerous health risks, collectively predisposing to a diminished Quality of life (healthcare), quality of life and a reduction in life expectancy. As a consequence, the disorder costs society hundreds of billions of US dollars each year, worldwide. It is associated with other mental disorders as well as non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment. While ADHD involves a lack of su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesion G Protein-coupled Receptors
Adhesion G protein-coupled receptors (adhesion GPCRs) are a class of 33 human protein receptors with a broad distribution in embryonic and larval cells, cells of the reproductive tract, neurons, leukocytes, and a variety of tumours. Adhesion GPCRs are found throughout metazoans and are also found in single-celled colony forming choanoflagellates such as ''Monosiga brevicollis'' and unicellular organisms such as Filasterea. The defining feature of adhesion GPCRs that distinguishes them from other GPCRs is their hybrid molecular structure. The extracellular region of adhesion GPCRs can be exceptionally long and contain a variety of structural domains that are known for the ability to facilitate cell and matrix interactions. Their extracellular region contains the membrane proximal GAIN (GPCR-Autoproteolsis INducing) domain. Crystallographic and experimental data has shown this structurally conserved domain to mediate autocatalytic processing at a GPCR-proteolytic site (GPS) prox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
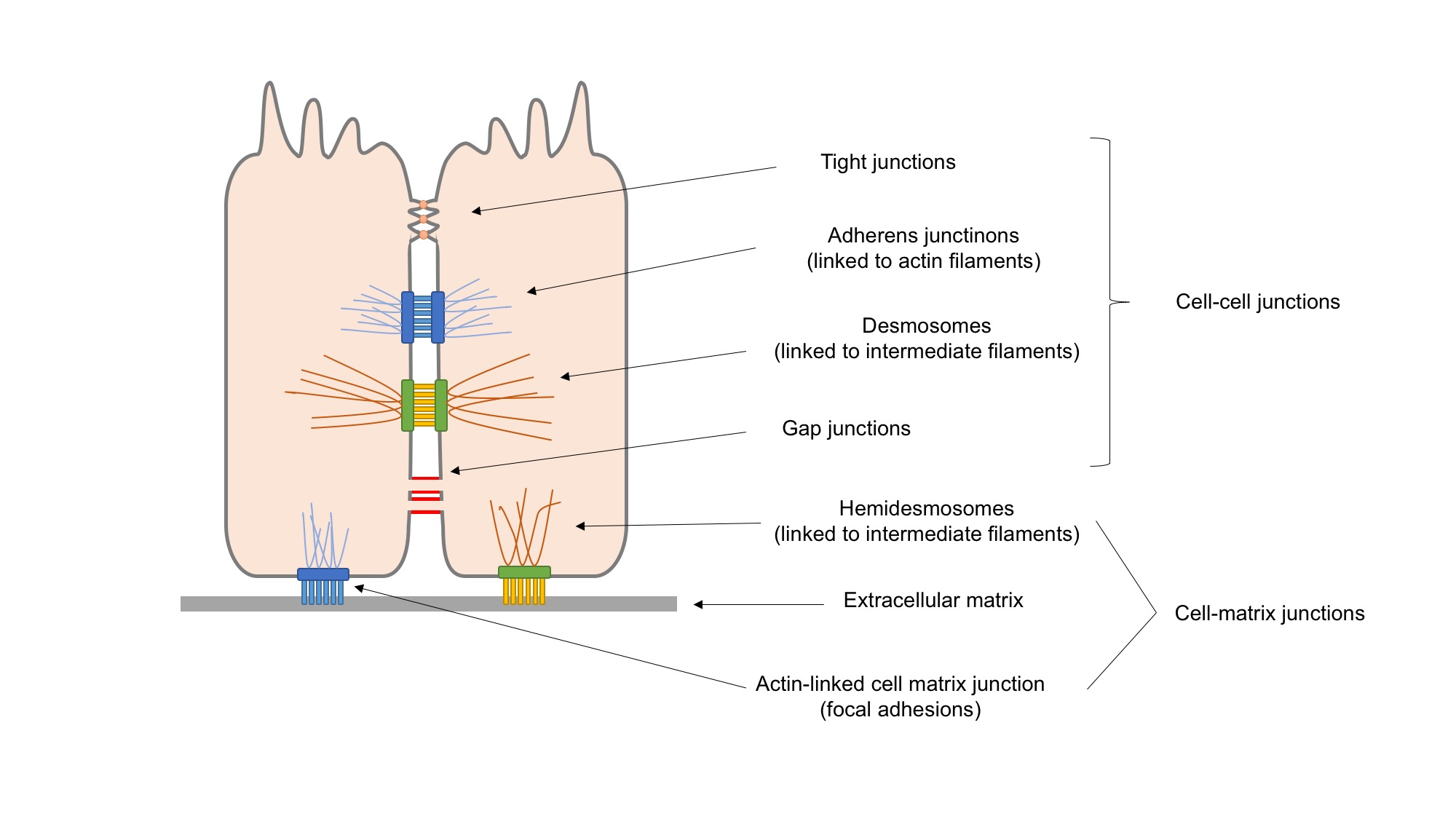
Cell Adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junctions or indirect interaction, where cells attach to surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM), a gel-like structure containing molecules released by cells into spaces between them. Cells adhesion occurs from the interactions between cell adhesion molecules, cell-adhesion molecules (CAMs), transmembrane proteins located on the cell surface. Cell adhesion links cells in different ways and can be involved in signal transduction for cells to detect and respond to changes in the surroundings. Other cellular processes regulated by cell adhesion include cell migration and tissue development in multicellular organisms. Alterations in cell adhesion can disrupt important cellular processes and lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and arthrit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a biochemical cascade, series of molecular events. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptor (biology), receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand (biochemistry), ligand binding (or signal sensing) in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a Cell signaling#Signaling pathways, signaling pathway. When signaling pathways interact with one another they form networks, which allow cellular responses to be coordinated, often by combinatorial signaling events. At the molecular level, such responses include changes in the transcription (biology), transcription or translation (biology), translation of genes, and post-translational modification, post-translational and conformational changes in proteins, as well as changes in their location. These molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |