|
LNER Class D49
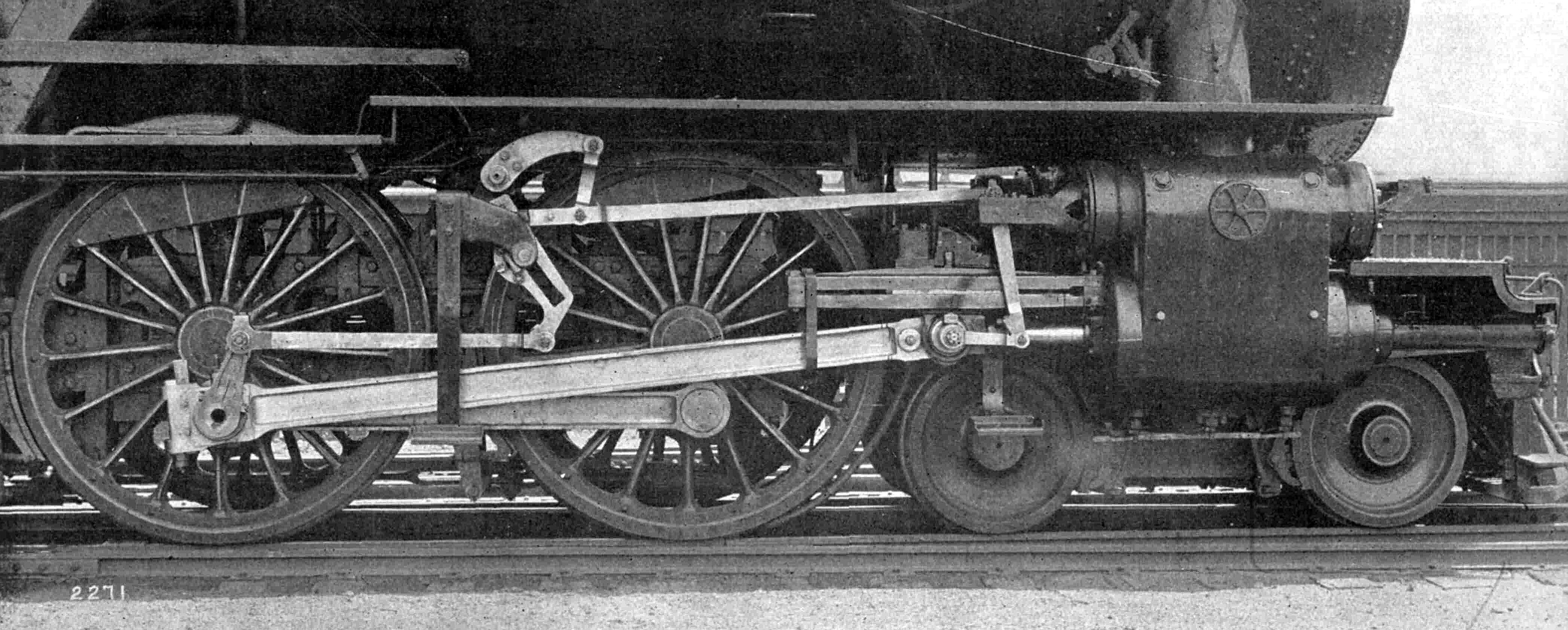
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) D49 Class is a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives designed by Nigel Gresley. They were named after fox hunts and shires. One, 246/62712 ''Morayshire'' has been preserved on the Bo'ness and Kinneil Railway. Sub-classes * D49/1 Introduced 1927 with Walschaerts and, Gresley conjugated valve gear with piston valves * D49/2 Introduced 1928 with Lentz rotary-cam poppet valves * D49/3 Introduced 1928 with Lentz oscillating-cam poppet valves * D class Introduced 1941 with Stephenson valve Gear and 8-inch(203 mm) piston valves Names and numbers Accidents and incidents *On 3 January 1931, locomotive No. 2758 ''Northumberland'' was hauling a passenger train that was derailed at Carlisle, Cumberland due to excessive speed through a curve. Three people were killed. *On August 16, 1952, the single D class locomotive No. 62768 ''The Morpeth'' was involved in a collision between a light engine and a passenger train at Dragon Junction near Starbeck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigel Gresley
Sir Herbert Nigel Gresley (19 June 1876 – 5 April 1941) was a British railway engineer. He was one of Britain's most famous steam locomotive engineers, who rose to become Chief Mechanical Engineer (CME) of the London and North Eastern Railway (LNER). He was the designer of some of the most famous steam locomotives in Britain, including the LNER Class A1 and LNER Class A4 4-6-2 Pacific engines. An A1 Pacific, '' Flying Scotsman'', was the first steam locomotive officially recorded over 100 mph in passenger service, and an A4, number 4468 '' Mallard'', still holds the record for being the fastest steam locomotive in the world (126 mph). Gresley's engines were considered elegant, both aesthetically and mechanically. His invention of a three-cylinder design with only two sets of Walschaerts valve gear, the Gresley conjugated valve gear, produced smooth running and power at lower cost than would have been achieved with a more conventional three sets of Walschaerts ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Lentz
Hugo Lentz (1859–1944) was an Austrian mechanical engineer, born in South Africa. He was the inventor of many award-winning improvements to the steam engine. The correct spelling of his name is Lenz but it has been Anglicised to Lentz in English-speaking countries. Life and career Lentz was born on 21 July 1859 in South Africa. When he was six years old, his father died and the family returned to relatives in Germany. He became an engineer in the Prussian Navy. In 1888, Lentz founded his own machine factory in Vienna. At an exposition in honour of Alessandro Volta in Como in 1899, his first steam engine won the first prize. At the Exposition Universelle (1900) in Paris, it won the ''Grand Prix'' while Lentz himself was awarded the gold medal. From 1907, ''Davey, Paxman & Co'', [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1927
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preserved London And North Eastern Railway Steam Locomotives
Preservation may refer to: Heritage and conservation * Preservation (library and archival science), activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record while making as few changes as possible * ''Preservation'' (magazine), published by the National Trust for Historic Preservation * Historic preservation, endeavor to preserve, conserve and protect buildings, objects, landscapes or other artifacts * Conservation and restoration of cultural heritage, protection and care of tangible cultural heritage Mathematics and computer science * Type preservation, property of a type system if evaluation of expressions does not cause their type to change * Case preservation, when computer storage preserves the distinction between upper and lower case * Digital preservation, endeavor to ensure that digital information of continuing value remains accessible and usable Arts and entertainment * ''Preservation'' (2018 novel), historical fiction by Jock Serong about the wreck of the '' Sydne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Eastern Railway Locomotives
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the Lord M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNER D49 Hunt Class Loco In 1948
LNER may refer to: *London and North Eastern Railway, a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1923 until 1947 *London North Eastern Railway, a train operating company in the United Kingdom since 2018 * Liquid neutral earthing resistor, a type of Liquid resistor A liquid resistor is an electrical resistor in which the resistive element is a solution. Fixed-value liquid resistors are typically used where very high power dissipation is required. They are used in the rotor circuits of large slip ring inductio ... See also *, including articles about LNER locomotives * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
62712 Morayshire At Hawick
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number. In mathematics Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second smallest composite number, behind 4; its proper divisors are , and . Since 6 equals the sum of its proper divisors, it is a perfect number; 6 is the smallest of the perfect numbers. It is also the smallest Granville number, or \mathcal-perfect number. As a perfect number: *6 is related to the Mersenne prime 3, since . (The next perfect number is 28.) *6 is the only even perfect number that is not the sum of successive odd cubes. *6 is the root of the 6-aliquot tree, and is itself the aliquot sum of only one other number; the square number, . Six is the only number that is both the sum and the product of three consecutive positive numbers. Unrelated to 6's being a perfect number, a Golomb ruler of length 6 is a "perfect ruler". Six is a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Riding Of Yorkshire
The East Riding of Yorkshire, or simply East Riding or East Yorkshire, is a ceremonial county and unitary authority area in the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England. It borders North Yorkshire to the north and west, South Yorkshire to the south-west, and Lincolnshire to the south. The coastal towns of Bridlington, Hornsea and Withernsea are popular with tourists, the town of Howden contains Howden Minster, Market Weighton, Pocklington, Brough, Hedon and Driffield are market towns with markets held throughout the year and Hessle and Goole are important port towns for the county. The port city of Kingston upon Hull is an economic, transport and tourism centre which also receives much sea freight from around the world. The current East Riding of Yorkshire came into existence in 1996 after the abolition of the County of Humberside. The county's administration is in the ancient market town of Beverley. The landscape is mainly rural, consisting of rolling hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlisle, Cumberland
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers Eden, Caldew and Petteril. It is the administrative centre of the City of Carlisle district which, (along with Cumbria County Council) will be replaced by Cumberland Council in April 2023. The city became an established settlement during the Roman Empire to serve forts on Hadrian's Wall. During the Middle Ages, the city was an important military stronghold due to its proximity to the Kingdom of Scotland. Carlisle Castle, still relatively intact, was built in 1092 by William Rufus, served as a prison for Mary, Queen of Scots in 1568 and now houses the Duke of Lancaster's Regiment and the Border Regiment Museum. In the early 12th century, Henry I allowed a priory to be built. The priory gained cathedral status with a diocese in 1133, the city status rules at the time meant the settlement became a city. From t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion". Purpose In the simple case, this can be a relatively simple task as in the internal combustion engine in which the valves always open and close at the same points. This is not the ideal arrangement for a steam engine, though, because greatest power is achieved by keeping the inlet valve open throughout the power stroke (thus having full boiler pressure, minus transmission losses, against the piston throughout the stroke) while peak efficiency is achieved by only having the inlet valve open for a short time and then letting the steam expand in the cylinder (expansive working). The point at which steam stops being admitted to the cylinder is known as the '' cutoff'', and the optimal positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephenson Valve Gear
The Stephenson valve gear or Stephenson link or shifting link is a simple design of valve gear that was widely used throughout the world for various kinds of steam engines. It is named after Robert Stephenson but was invented by his employees. Historical background During the 1830s, the most popular valve drive for steam locomotives was known as '' gab motion'' in the United Kingdom and'' V-hook motion'' in the United States. The gab motion incorporated two sets of eccentrics and rods for each cylinder; one eccentric was set to give forward and the other backwards motion to the engine and one or the other could accordingly engage with a pin driving the distribution valve by means of the gabs: - vee-shaped ends to the eccentric rods supposed to catch the rocker driving the valve rod whatever its position. It was a clumsy mechanism, difficult to operate, and only gave fixed valve events. In 1841, two employees of Robert Stephenson and Company, draughtsman William Howe and patt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)