|
LIII Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
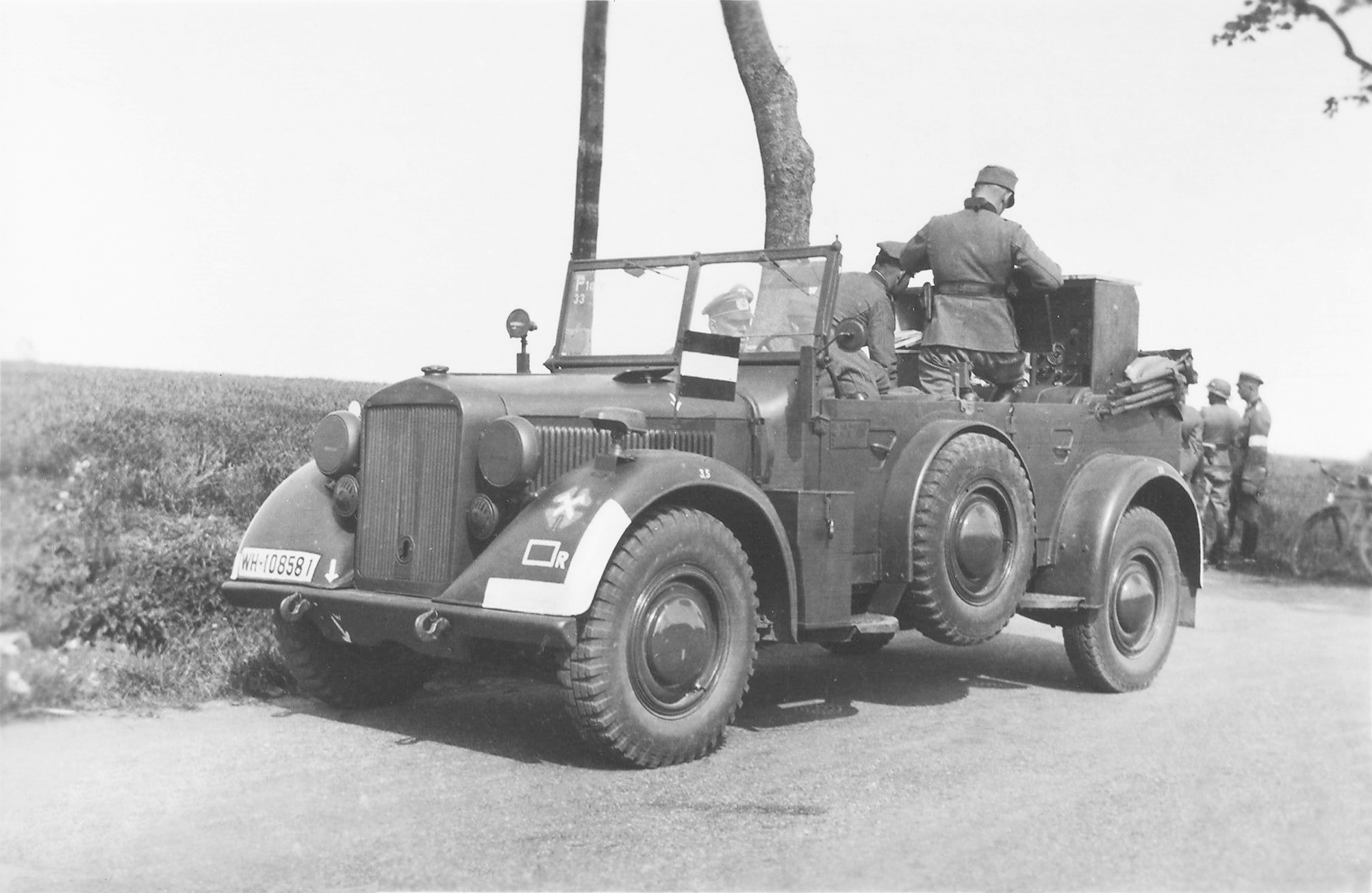
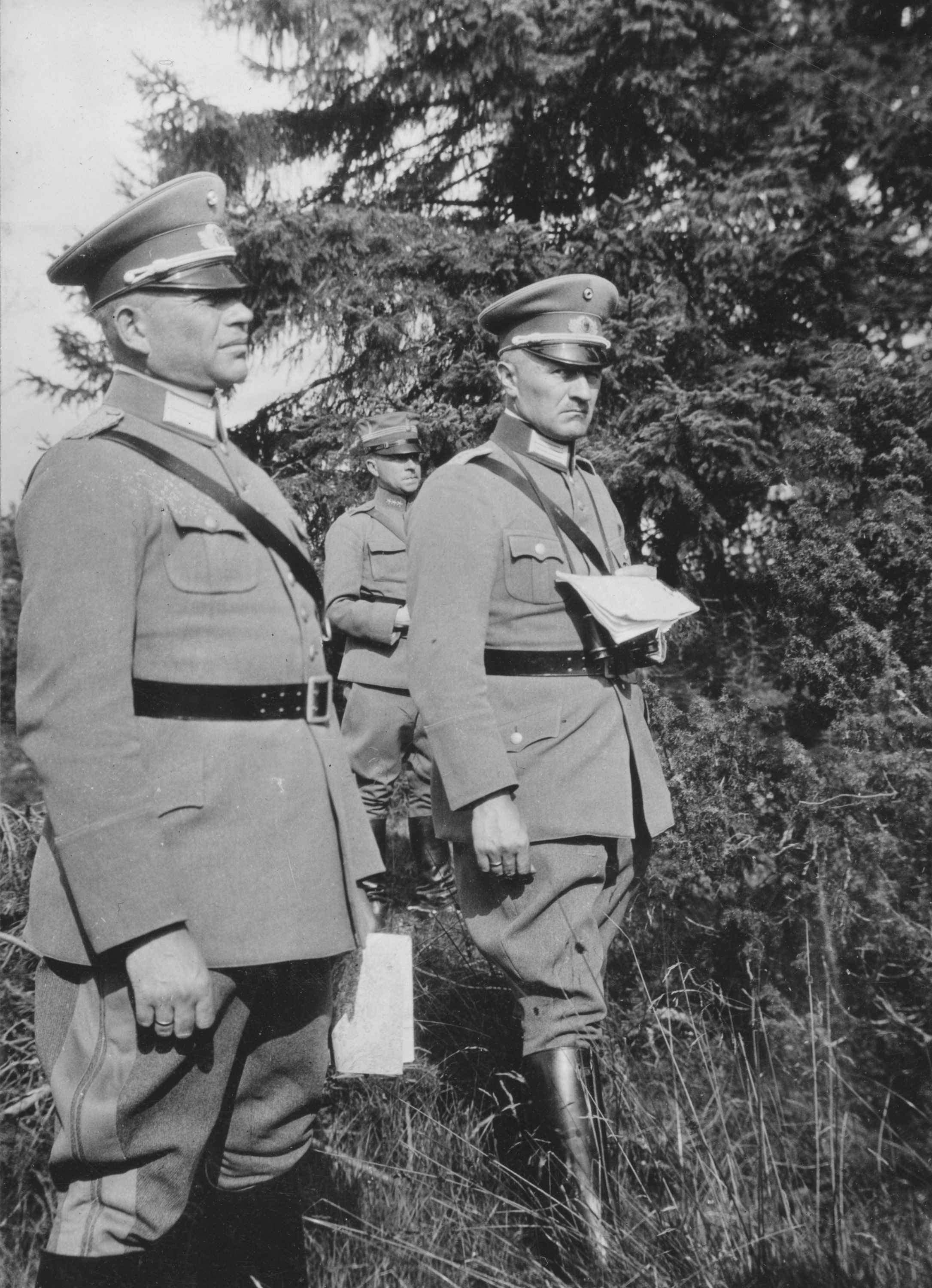
The LIII Army Corps (53rd Army Corps, ) was a corps of the German Army during World War II. It was first deployed in 1941 and was active as part of various armies under Army Group Centre until 1944, when it was destroyed during the Soviet Red Army operations Bagration and Kutuzov in June and July 1944. The corps suffered enormous casualties as a result of the Soviet attacks. All of its divisions were destroyed and all but a few of the soldiers were killed or captured by the Soviet Union. A new formation named LIII Army Corps was subsequently deployed in December 1944, when it was assigned to Seventh Army and fought on the western front until surrendering to United States Army forces in April 1945. History First Deployment, 1941—1944 1941 The ''Generalkommando'' of LIII Army Corps was first deployed on 15 February 1941, in Wehrkreis XVIII (Salzburg). The initial commander was Karl Weisenberger, formerly the commander of 71st Infantry Division. LIII Corps was put under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corps
Corps (; plural ''corps'' ; from French , from the Latin "body") is a term used for several different kinds of organization. A military innovation by Napoleon I, the formation was formally introduced March 1, 1800, when Napoleon ordered General Jean Victor Marie Moreau to divide his command into four corps. The size of a corps varies greatly, but two to five divisions and anywhere from 40,000 to 80,000 are the numbers stated by the US Department of Defense. Within military terminology a corps may be: *an military organization, operational formation, sometimes known as a field corps, which consists of two or more division (military), divisions, such as the I Corps (Grande Armée), , later known as ("First Corps") of Napoleon I's ); *an administrative corps (or Muster (military), mustering) – that is a #Administrative corps, specialized branch of a military service (such as an artillery corps, an armoured corps, a signal corps, a medical corps, a marine corps, or a corps of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
71st Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 71st Infantry Division ''Kleeblatt'' ("Cloverleaf Division", "Lucky One") () was an infantry Division (military), division of the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army, raised on 26 August 1939, shortly before the outbreak of World War II, as a division of the 2nd wave of deployment by Infantry Commander 19 (''Infanterie-Kommandeur 19'') in Hildesheim. It fought in Verdun, Battle of Stalingrad, Stalingrad and Battle of Monte Cassino, Monte Cassino, among others. The division's symbol was the four-leaf clover and after congratulations on the victory in Verdun in June 1940, the division was henceforth called the "lucky one". The same action also earning Generalleutnant Karl Weisenberger the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 29 June 1940 by Generalfeldmarschall Ernst Busch (field marshal), Ernst Busch. Divisional history In the divisional history of the 71st Infantry Division, a distinction is made between the line-up and personnel composition up to the Battle of Stalingrad as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yepifan
Yepifan () is an urban locality (a work settlement) in Kimovsky District of Tula Oblast, Russia, located on the left bank of the Don River about southeast of Kimovsk and southeast of Tula, in the proximity of the Kulikovo Field. Population: Yepifan was founded by Prince Ivan Mstislavsky (Ivan the Terrible's cousin) as a fort against the Crimean Tatars (see Great Abatis Border). The people of Yepifan supported Ivan Bolotnikov during the Time of Troubles. The town was ravaged by Ivan Zarutsky and the Tatars on several occasions. The last Tatar raid on Yepifan was recorded in 1659. Peter the Great Peter I (, ; – ), better known as Peter the Great, was the Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Tsar of all Russia from 1682 and the first Emperor of Russia, Emperor of all Russia from 1721 until his death in 1725. He reigned j ... intended to connect the Volga and the Don Rivers through a system of waterways and sluices centred on Yepifan. It soon beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oka River
The Oka (, ; ) is a river in central Russia, the largest right tributary of the Volga. It flows through the regions of Oryol, Tula, Kaluga, Moscow, Ryazan, Vladimir and Nizhny Novgorod and is navigable over a large part of its total length, as far upstream as the town of Kaluga. Its length is and its catchment area .«Река Ока» Russian State Water Registry The Russian capital sits on one of the Oka's tributaries—the Moskva, from which the capital's name is thought to be derived. Name and history The Oka river was the homeland of the Easter ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XXXXIII Army Corps (Wehrmacht)
XXXXIII Army Corps (XXXXIII. Armeekorps) was a corps in the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army during World War II. Operations The XXXXIII. Army Corps was created on 15 April 1940 in military district XI (Weimar). It participated in the Battle of France, where it played only a secondary role. After the French capitulation it occupied the Channel coast in the area of Rouen. In June 1941, it participated in Operation Barbarossa as part of the 4th Army (Wehrmacht), 4th Army. It fought in the Battle of Białystok–Minsk and Battle of Kiev (1941). In November 1941, it reached the city of Aleksin on the Oka River but was pushed back towards Spas-Demensk by the Soviet counter offensive in the Battle of Moscow. It stayed in Spa-Demansk during 1942 and was moved to Velikiye Luki in 1943, where it was involved in the Battle of Nevel (1943). In March 1944, it became part of ''Armee-Abteilung Narwa'' and fought in the Battle of Narva (1944). In Autumn 1944, the Corps was locke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
112th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 112th Infantry Division (German: ''112. Infanteriedivision'') was a German Army infantry division active in World War II World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo .... History The division was formed in December 1940 from elements of 34th Infantry division and 33rd infantry division, as part of the 12th wave of German mobilization.George F. Nafziger, German Order of Battle: Infantry in World War II, pp. 152–153 The 112th Infantry Division remained in OKH reserve during the opening phase of operation Barbarossa, and was committed to the southern wing in the second half of July during the battle of Smolensk. Here elements of the Soviet 21st Army had pushed back forward German elements and advanced up to 80 kilometers in to the German rear. At the beginning of Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinz Guderian
Heinz Wilhelm Guderian (; 17 June 1888 – 14 May 1954) was a German general during World War II who later became a successful memoirist. A pioneer and advocate of the "blitzkrieg" approach, he played a central role in the development of the panzer division concept. After serving in the military since leaving school, including in World War I, in 1936, he became the Inspector of Motorized Troops. At the beginning of World War II, Guderian led an Panzer corps, armoured corps in the Invasion of Poland. During the Battle of France, Invasion of France, he commanded the armoured units that attacked through the Ardennes forest and overwhelmed the Allied defenses at the Battle of Sedan (1940), Battle of Sedan. He led the 2nd Panzer Army during Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union. The campaign ended in failure after the German offensive Operation Typhoon failed to capture Moscow, and after a disagreement with Hitler, Guderian was dismissed. In early 1943, Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Panzer Army
The 2nd Panzer Army () was a German armoured formation during World War II, formed from the 2nd Panzer Group on October 5, 1941. Organisation Panzer Group Guderian () was formed on 5 June 1940 and named after its commander, general Heinz Guderian. In early June 1940, after reaching the English Channel following the breakthrough in the Ardennes, the ''Panzergruppe Guderian'' was formed from the XIX Army Corps, and thrust deep into France, cutting off the Maginot Line. In November 1940, it was upgraded into ''Panzergruppe 2''. The 2nd Panzer Group () was formed in November 1940 from Panzer Group Guderian. In October 1941 it was renamed the 2nd Panzer Army. Panzer Group 2 played a significant role in the early stages of the German invasion of the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa in 1941 when it was a constituent part of Army Group Centre. Operational history 2nd Panzer Group was part of the Army Group Centre during Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Unio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaryta
Malaryta or Malorita is a town in Brest Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative centre of Malaryta District. The name of the city comes from the Ryta, Ryta River. As of 2025, it has a population of 12,593. History Within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Malaryta was part of Brest Litovsk Voivodeship. In 1795, Malaryta was acquired by the Russian Empire as a result of the Third Partition of Poland. From 1921 to 1939, Malaryta (''Małoryta'') was part of the Second Polish Republic, administratively located in the Polesie Voivodeship. In September 1939, Malaryta was Soviet invasion of Poland, occupied by the Red Army and, on 14 November 1939, incorporated into the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR. From 22 June 1941 to 20 July 1944, Malaryta was German occupation of Byelorussia during World War II, occupied by Nazi Germany and administered as a part of the Generalbezirk Wolhynien-Podolien of Reichskommissariat Ukrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
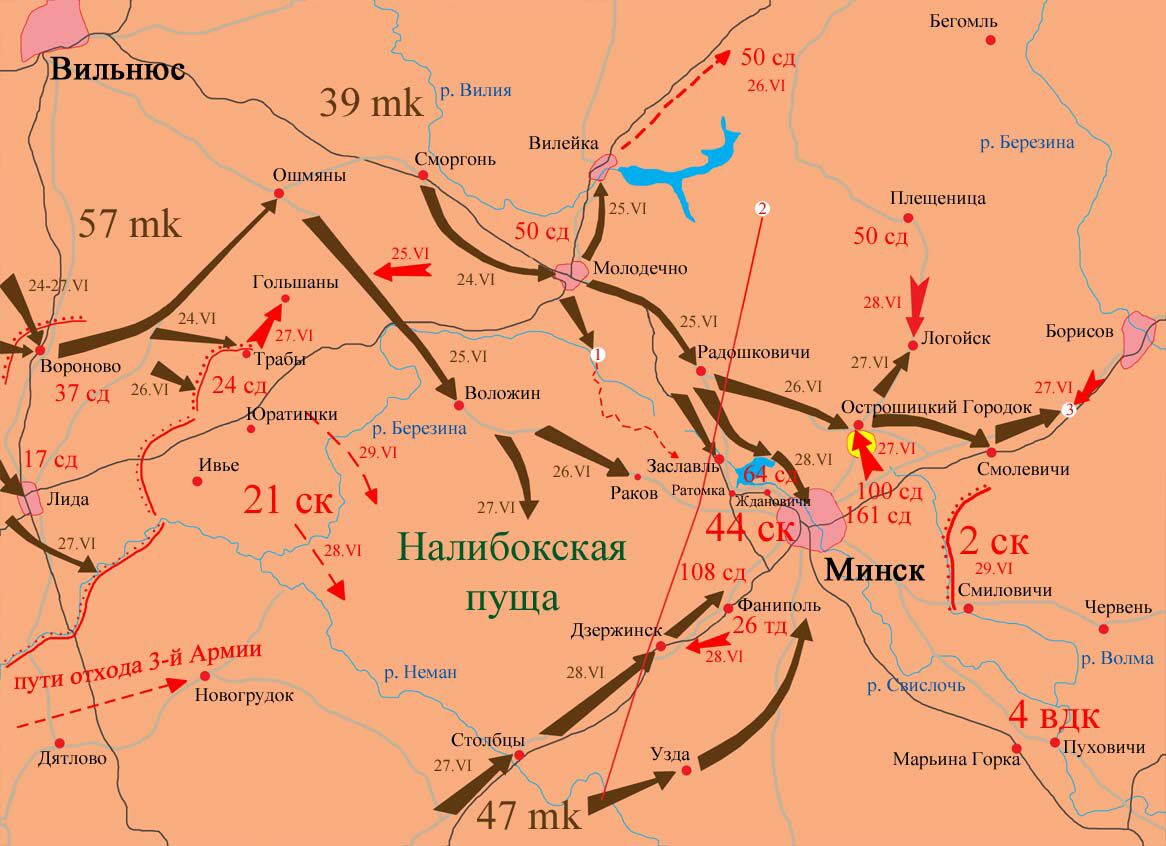
Battle Of Białystok–Minsk
The Battle of Białystok–Minsk was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre under Field Marshal Fedor von Bock during the penetration of the Soviet border region in the opening stage of Operation Barbarossa, lasting from 22 June to 9 July 1941. The Army Group's 2nd Panzer Group under Colonel General Heinz Guderian and the 3rd Panzer Group under Colonel General Hermann Hoth decimated the Soviet frontier defenses, defeated all Soviet counter-attacks and encircled four Soviet Armies of the Red Army's Western Front near Białystok and Minsk by 30 June. The majority of the Western Front was enclosed within, and the pockets were destroyed by 9 July. The Red Army lost from 420,000 to 474,000 men, against Wehrmacht casualties estimated between 12,157 and 67,244. The Germans destroyed the Soviet Western Front in 18 days and advanced 460 kilometers into the Soviet Union, causing many to believe that the Germans had effectively won the war aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of with a population of . The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into Regions of Belarus, six regions. Minsk is the capital and List of cities and largest towns in Belarus, largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status. For most of the medieval period, the lands of modern-day Belarus was ruled by independent city-states such as the Principality of Polotsk. Around 1300 these lands came fully under the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth; this period lasted for 500 years until the Partitions of Poland, 1792-1795 partitions of Poland-Lithuania placed Belarus within the Belarusian history in the Russian Empire, Russian Empire for the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
167th Volksgrenadier Division (Wehrmacht)
The 167th Volksgrenadier Division (German: ''167. Volksgrenadierdivision''), formerly the 167th Infantry Division (German: ''167. Infanteriedivision'') was a German Army infantry division in World War II. Operational history Formation and France The 167th Infantry Division was formed in the Bavarian capital of Munich in November 1939, absorbing the 7th; 27th and 34th Field-Replacement Battalions from their respective divisions in January. It was also at this point that its commanding officer, Colonel Gilbert, was promoted to major general, shortly before his replacement by Lieutenant General Oskar Vogl. The division took part in the initial 1940 invasion of France with Army Group C, capturing Ouvrage Kerfent and Ouvrage Bambesch - two components of the Maginot Line - between 20–21 June. The division remained in occupied France until February 1941, when it returned to its garrison in Bavaria. In August 1940, Major General Hans Schönhärl took over as commanding officer, bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |