|
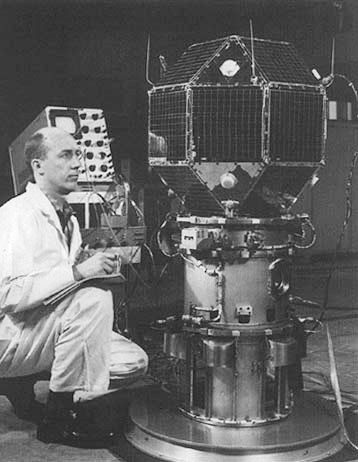
LES-2
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 2, also known as LES-2, was a communications satellite, the second of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on 6 May 1965, it demonstrated many then-advanced technologies including active use of the military's SHF (super high frequency) band (7 to 8 GHz) to service hundreds of users. Background After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink problem including improved antennas, better stabilizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LES-3
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 3, also known as LES-3, was a communications satellite, the third of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on 21 Dec 1965, it was stranded in a Geostationary Transfer Orbit rather than its planned circular high orbit. Despite this, LES-3 returned good data on communications propagation in the UHF band. Background After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites (" downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink problem including improved antennas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Experimental Satellite
The Lincoln Experimental Satellite series was designed and built by Lincoln Laboratory at Massachusetts Institute of Technology between 1965 and 1976, under USAF sponsorship, for testing devices and techniques for satellite communication. Development After the successful development and deployment of Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles, MIT's Lincoln Laboratory turned to improving active-satellite space communications. In particular, Lincoln aimed to increase the transmission capability of communications satellites ("downlink"), which was necessarily constrained by their limited size. After receiving a charter in 1963 to build and demonstrate military space communications, Lincoln focused on a number of engineering solutions to the downlink problem including improved antennas, better stabilization of satellites in orbit (which would benefit both downlink and "uplink"—communications from the ground), high-efficiency systems of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Calibration Sphere 1
The Lincoln Calibration Sphere 1, or LCS-1, is a large aluminium sphere in Earth orbit since 6 May 1965. It is still in use, having lasted for over 50 years. The sphere was launched along with the Lincoln Experimental Satellite-2 on a Titan IIIA. It is technically the oldest operational spacecraft , but it has no power supply or fuel; it is merely a passive metal sphere. LCS-1 has been used for radar calibration since its launch. It was built by Rohr. Corp. for the MIT Lincoln Laboratory The MIT Lincoln Laboratory, located in Lexington, Massachusetts, is a United States Department of Defense federally funded research and development center chartered to apply advanced technology to problems of national security. Research and d .... LCS-1 is a hollow sphere in diameter with a wall thickness of . The sphere was constructed from two hemispheres, made by spinning sheet metal over a mold. These hemispheres were fastened to an internal, circumferential hoop by 440 countersunk s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan IIIA
The Titan IIIA or Titan 3A was an American expendable launch system, launched four times in 1964 and 1965, to test the Transtage upper stage which was intended for use on the larger Titan IIIC. The Transtage was mounted atop two core stages derived from the Titan II The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space la .... The Titan IIIA was also used as the core of the Titan IIIC. The Titan IIIA made its first flight on 1 September 1964. However, the Transtage failed to pressurize, resulting in a premature cutoff and failure to reach orbit. A second test on 10 December was successful. Two further launches occurred in 1965 with Lincoln Experimental Satellites, before the Titan IIIA was retired. Launch history References * * External links Titan (rocket family) {{rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LES-1
Lincoln Experimental Satellite 1, also known as LES-1, was a communications satellite, the first of nine in the Lincoln Experimental Satellite program. Launched by the United States Air Force (USAF) on February 11, 1965, it pioneered many then-advanced technologies including active use of the military's SHF (super high frequency) band (7 to 8 GHz) to service hundreds of users. LES-1 did not have a successful operational life due to being placed in a suboptimal orbit, and it ceased transmissions in 1967. After 45 years of inactivity, LES-1 spontaneously resumed transmissions in 2012 making it one of the oldest zombie satellites. Background The Lincoln Experimental Satellite (LES) series was MIT's Lincoln Laboratory's first active communications satellite project. Lincoln had previously successfully developed and deployed Project West Ford, a passive communications system consisting of orbiting copper needles. The goal of LES was to increase the transmission capability of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The high frequency radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by line of sight and so are obstructed by the curve of the Earth. The purpose of communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project West Ford
Project West Ford (also known as Westford Needles and Project Needles) was a test carried out by Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory on behalf of the United States military in 1961 and 1963 to create an artificial ionosphere above the Earth. This was done to solve a major weakness that had been identified in military communications. History At the height of the Cold War, all international communications were either sent through submarine communications cables or bounced off the natural ionosphere. The United States military were concerned that the Soviets might cut those cables, forcing the unpredictable ionosphere to be the only means of communication with overseas forces. To mitigate the potential threat, Walter E. Morrow started Project Needles at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory in 1958. The goal of the project was to place a ring of 480,000,000 (Abstract) copper dipole antennas in orbit to facilitate global radio communication. The dipoles collectivel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen engine with his own steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one newton, the rate at which work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potential difference of one volt (V), meaning the watt is equivalent to the volt-ampere (the latter unit, however, is used for a different quantity from the real power of an electrical circuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Electronics
Solid-state electronics means semiconductor electronics: electronic equipment using semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used as an adjective for devices in which semiconductor electronics that have no moving parts replace devices with moving parts, such as the solid-state relay in which transistor switches are used in place of a moving-arm electromechanical relay, or the solid-state drive (SSD) a type of semiconductor memory used in computers to replace hard disk drives, which store data on a rotating disk. History The term "solid-state" became popular at the beginning of the semiconductor era in the 1960s to distinguish this new technology based on the transistor, in which the electronic action of devices occurred in a solid state, from previous electronic equipment that used vacuum tubes, in which the electronic action occurred in a gaseous state. A semiconductor device works by controlling an electric curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error Detection And Correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunication, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels. Many communication channels are subject to channel noise, and thus errors may be introduced during transmission from the source to a receiver. Error detection techniques allow detecting such errors, while error correction enables reconstruction of the original data in many cases. Definitions ''Error detection'' is the detection of errors caused by noise or other impairments during transmission from the transmitter to the receiver. ''Error correction'' is the detection of errors and reconstruction of the original, error-free data. History In classical antiquity, copyists of the Hebrew Bible were paid for their work according to the number of stichs (lines of verse). As the prose books of the Bible were hardly ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downlink
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links. A telecommunications link is generally based on one of several types of information transmission paths such as those provided by communication satellites, terrestrial radio communications infrastructure and computer networks to connect two or more points. The term ''link'' is widely used in computer networking to refer to the communications facilities that connect nodes of a network. Sometimes the communications facilities that provide the communication channel that constitutes a link are also included in the definition of ''link''. Types Point-to-point A point-to-point link is a dedicated link that connects exactly two communication facilities (e.g., two nodes of a network, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |