|
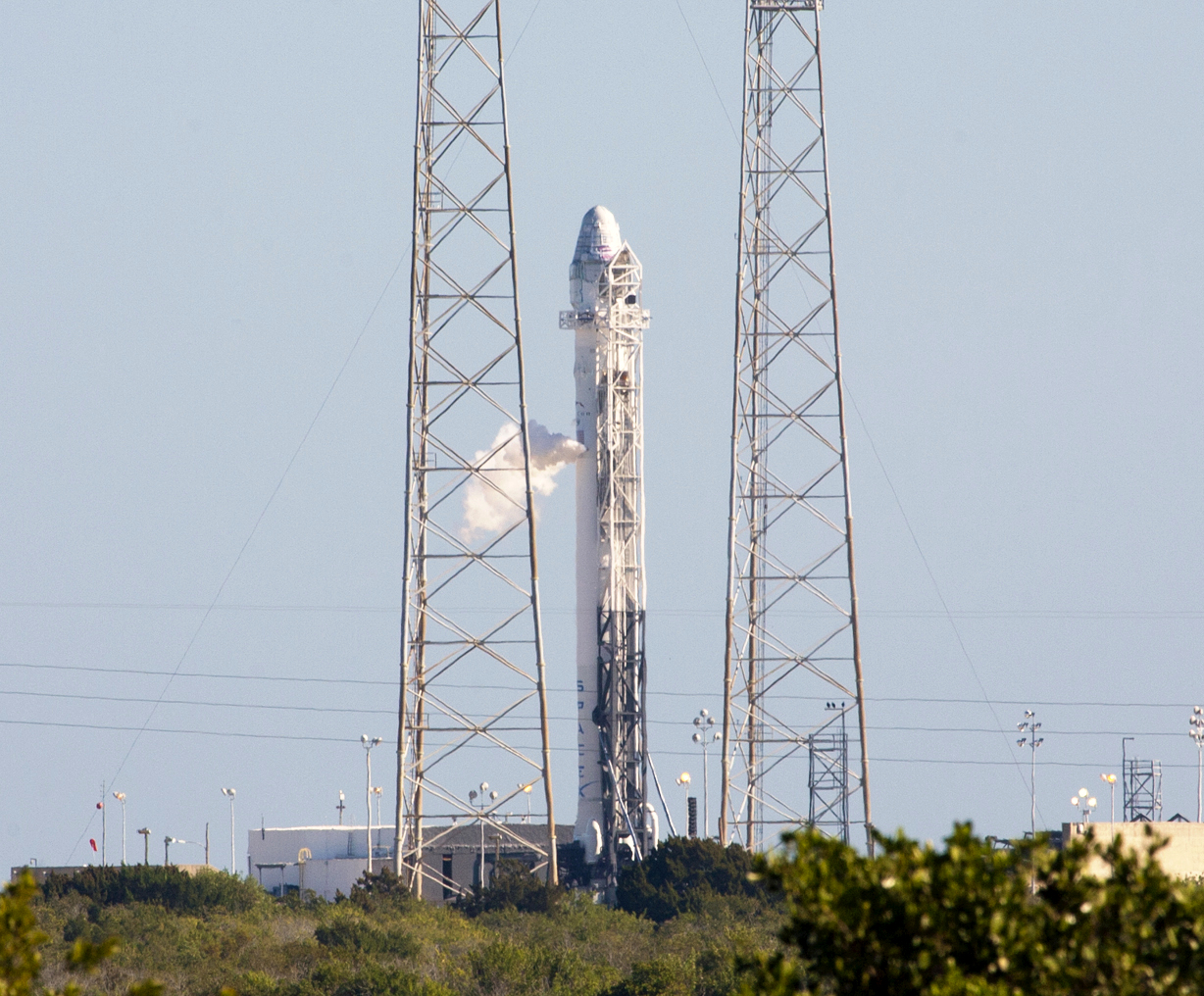
LC-40
Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40), previously Launch Complex 40 (LC-40) is a launch pad for rockets located at the north end of Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. The launch pad was used by the United States Air Force for 55 Titan III and Titan IV launches between 1965 and 2005. The facility underwent multiple upgrades including the design and construction of towers with retractable and foldable platforms for vehicle assembly, instrumentation and monitoring. After 2007, the US Air Force leased the complex to SpaceX to launch the Falcon 9 rocket. As of August 2022, there have been 93 launches of the Falcon 9 from the complex. The site was heavily damaged following the September 2016 Falcon 9 flight 29 incident, due to a catastrophic failure during a static fire test. The complex was repaired and returned to operational status in December 2017 for the CRS-13 mission. Launch history Rocket launches Titan The first launch from SLC-40 (initially nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan IIIC
The Titan IIIC was an expendable launch system used by the United States Air Force from 1965 until 1982. It was the first Titan booster to feature large solid rocket motors and was planned to be used as a launcher for the Dyna-Soar, though the spaceplane was cancelled before it could fly. The majority of the launcher's payloads were DoD satellites, for military communications and early warning, though one flight ( ATS-6) was performed by NASA. The Titan IIIC was launched exclusively from Cape Canaveral while its sibling, the Titan IIID, was launched only from Vandenberg AFB. History The Titan rocket family was established in October 1955 when the Air Force awarded the Glenn L. Martin Company (later Martin Marietta and now Lockheed Martin) a contract to build an intercontinental ballistic missile (SM-68). It became known as the Titan I, the nation's first two-stage ICBM, and replaced the Atlas ICBM as the second underground, vertically stored, silo-based ICBM. Both stages o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan III-C
The Titan IIIC was an expendable launch system used by the United States Air Force from 1965 until 1982. It was the first Titan booster to feature large solid rocket motors and was planned to be used as a launcher for the Dyna-Soar, though the spaceplane was cancelled before it could fly. The majority of the launcher's payloads were DoD satellites, for military communications and early warning, though one flight (ATS-6) was performed by NASA. The Titan IIIC was launched exclusively from Cape Canaveral while its sibling, the Titan IIID, was launched only from Vandenberg AFB. History The Titan rocket family was established in October 1955 when the Air Force awarded the Glenn L. Martin Company (later Martin Marietta and now Lockheed Martin) a contract to build an intercontinental ballistic missile (SM-68). It became known as the Titan I, the nation's first two-stage ICBM, and replaced the Atlas ICBM as the second underground, vertically stored, silo-based ICBM. Both stages of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan IV
Titan IV was a family of heavy-lift space launch vehicles developed by Martin Marietta and operated by the United States Air Force from 1989 to 2005. Launches were conducted from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida and Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The Titan IV was the last of the Titan family of rockets, originally developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company in 1958. It was retired in 2005 due to their high cost of operation and concerns over its toxic hypergolic propellants, and replaced with the Atlas V and Delta IV launch vehicles under the EELV program. The final launch (B-30) from Cape Canaveral occurred on 29 April 2005, and the final launch from Vandenberg AFB occurred on 19 October 2005. Lockheed Martin Space Systems built the Titan IVs near Denver, Colorado, under contract to the US government. Two Titan IV vehicles are currently on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio and the Evergreen Aviation and Space Museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan 34D
The Titan 34D was a United States expendable launch vehicle used to launch a number of satellites for military applications. Service history Derived from the Titan III, the Titan 34D featured Stage 1 and Stage 2 stretched with more powerful UA1206 solid motors. A variety of upper stages were available, including the Inertial Upper Stage, the Transfer Orbit Stage, and the Transtage. The Titan 34D made its maiden flight in the year of 1982 on the 30th of October with two DSCS defense communications satellites for the United States Department of Defense (DOD). All of the launches were conducted from either LC-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station or SLC-4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base. Overall, fifteen launches were carried out, of which three failed. 1985 failure, Titan 34D-7 The first failure was a launch of a KH-11 photoreconnaissance satellite in the year 1985 on the 28th of August. The core stage suffered a propulsion system malfunction and was destroyed by Range Safety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with three launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 37B, 40, and 41). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. unmanned lunar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falcon 9
Falcon 9 is a partially reusable medium lift launch vehicle that can carry cargo and crew into Earth orbit, produced by American aerospace company SpaceX. The rocket has two stages. The first (booster) stage carries the second stage and payload to a certain altitude, after which the second stage lifts the payload to its ultimate destination. The rocket evolved through several versions. V1.0 flew from 2010–2013, V1.1 flew from 2013–2016, while V1.2 Full Thrust first launched in 2015, encompassing the Block 5 variant, flying since May 2018. The booster is capable of landing vertically to facilitate reuse. This feat was first achieved on flight 20 in December 2015. Since then, SpaceX has successfully landed boosters over 100 times. Individual boosters have flown as many as 15 flights. Both stages are powered by SpaceX Merlin engines, using cryogenic liquid oxygen and rocket-grade kerosene ( RP-1) as propellants. The heaviest payloads flown to geostationary transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars. The company manufactures the Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy, and Starship launch vehicles, several rocket engines, Cargo Dragon and Crew Dragon spacecraft, and Starlink communications satellites. SpaceX is developing a satellite internet constellation named Starlink to provide commercial internet service. In January 2020, the Starlink constellation became the largest satellite constellation ever launched, and as of December 2022 comprises over 3,300 small satellites in orbit. The company is also developing Starship, a privately funded, fully reusable, super heavy-lift launch system for interplanetary and orbital spaceflight. It is intended to become SpaceX's prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Titan III
The Commercial Titan III, also known as CT-3 or CT-III, was an American expendable launch system, developed by Martin Marietta during the late 1980s and flown four times during the early 1990s. It was derived from the Titan 34D, and was originally proposed as a medium-lift expendable launch system for the US Air Force, who selected the Delta II instead. Development was continued as a commercial launch system, and the first rocket flew in 1990. Due to higher costs than contemporary rockets such as the Ariane 4, orders were not forthcoming, and the CT-3 was retired in 1992. The Commercial Titan III differed from the Titan 34D in that it had a stretched second stage, and a larger payload fairing to accommodate dual satellite payloads. All four launches occurred from LC-40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The first carried two communications satellites, Skynet 4A and JCSAT-2, and was launched at 00:07 UTC on 1 January 1990, which was 19:07 local time on 31 December 1989, making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
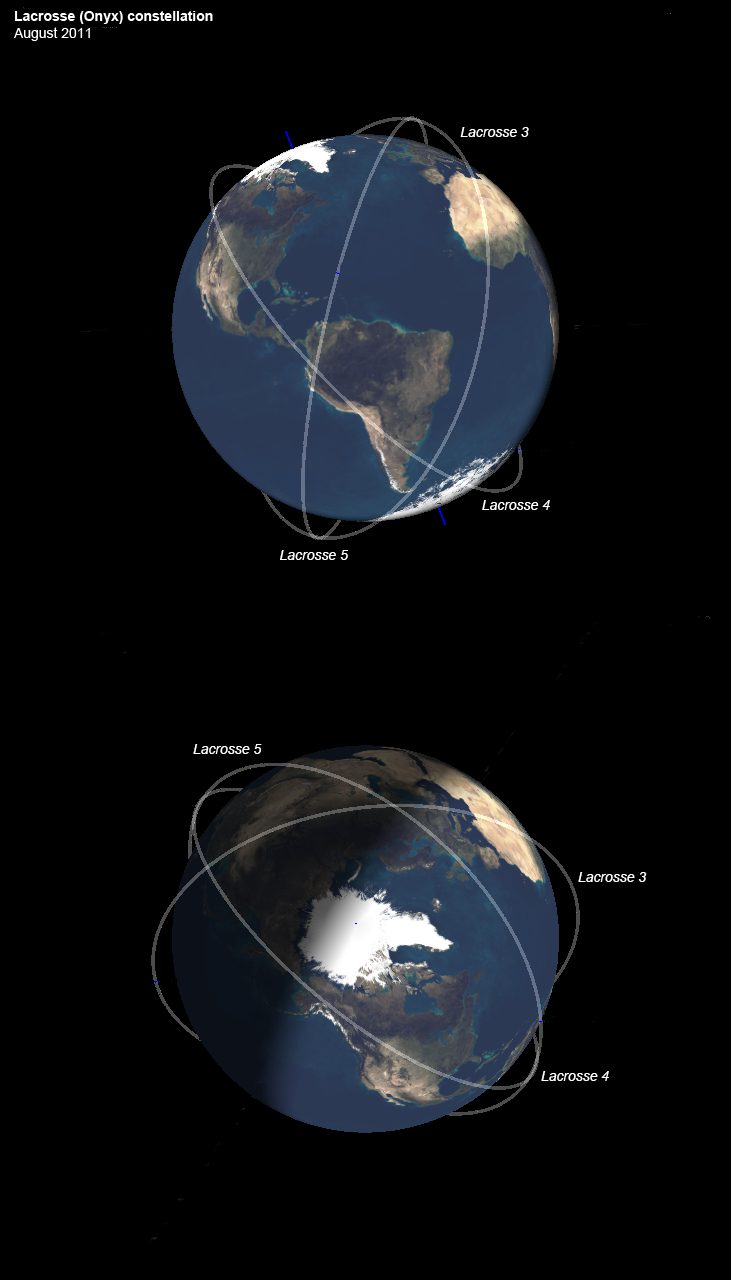
Lacrosse (satellite)
Lacrosse or Onyx is a series of terrestrial radar imaging reconnaissance satellites operated by the United States National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). While not officially confirmed by the NRO or the Government of the United States prior to 2008, there was widespread evidence pointing to its existence, including one NASA website. In July 2008, the NRO itself declassified the existence of its synthetic aperture radar (SAR) satellite constellation. According to former Director of Central Intelligence Admiral Stansfield Turner, Lacrosse had its origins in 1950 (1980?) when a dispute between the Central Intelligence Agency and the U.S. Air Force as to whether a combined optical/radar reconnaissance satellite (the CIA proposal) or a radar-only one (the USAF proposal) should be developed was resolved in favor of the USAF. Lacrosse uses synthetic aperture radar as its prime imaging instrument. It is able to see through cloud cover and also has some ability to penetrate soil, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRS-13
SpaceX CRS-13, also known as SpX-13, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station launched on 15 December 2017. The mission was contracted by NASA and is flown by SpaceX. It was the second mission to successfully reuse a Dragon capsule, previously flown on CRS-6. The first stage of the Falcon 9 Full Thrust rocket was the previously flown, "flight-proven" core from CRS-11. The first stage returned to land at Cape Canaveral's Landing Zone 1 after separation of the first and second stage. Mission overview In early 2015, NASA awarded a contract extension to SpaceX for three CRS additional missions (CRS-13 to CRS-15). , a NASA Inspector General report had this mission manifested for September 2017. The flight has been delayed from 13 September, 1 November, 4 December, 12 December, and 13 December 2017. SpaceX pushed off the launch to 15 December due to the detection of particulates in the second stage fuel system, taking the time to completely f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Fire
Launch vehicle system tests assess the readiness of a launch system to safely reach orbit. Launch vehicles undergo system tests before they launch. A wet dress rehearsal (WDR) and a more extensive static fire tests a fully assembled launch vehicle and its associated ground support equipment (GSE) prior to launch. The spacecraft/payload may or may not be attached to the launch vehicle during the WDR or static fire, but sufficient elements of the rocket and all relevant ground support equipment are in place to help verify that the rocket is ready for flight. Propellant load tests and static fire tests may also be done on prototype rocket stages as well, in which case no fully assembled launch vehicle is involved. Wet dress rehearsal A wet dress rehearsal is called "wet" because the liquid propellant components (such as liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, etc.) are loaded into the rocket during the test. In a pure wet dress rehearsal the rocket engines are not ignited. Wet dress rehea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX CRS-13
SpaceX CRS-13, also known as SpX-13, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station launched on 15 December 2017. The mission was contracted by NASA and is flown by SpaceX. It was the second mission to successfully reuse a Dragon capsule, previously flown on CRS-6. The first stage of the Falcon 9 Full Thrust rocket was the previously flown, "flight-proven" core from CRS-11. The first stage returned to land at Cape Canaveral's Landing Zone 1 after separation of the first and second stage. Mission overview In early 2015, NASA awarded a contract extension to SpaceX for three CRS additional missions (CRS-13 to CRS-15). , a NASA Inspector General report had this mission manifested for September 2017. The flight has been delayed from 13 September, 1 November, 4 December, 12 December, and 13 December 2017. SpaceX pushed off the launch to 15 December due to the detection of particulates in the second stage fuel system, taking the time to completely f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
