|
LBT-3627
LBT-3627 is an experimental peptide drug derived from vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) intended to modulate the behavior of immune cells in cases of neurodegenerative disease such that they protect dopamine-producing cells rather than attack them. The drug is currently being studied for its potential use in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Function LBT-3627 specifically targets the VIP2 receptor. The drug may also have an effect on microglia. LBT-3627 has been shown to be more stable in the body as compared to VIP. History and development Researchers at the University of Nebraska Medical Center and Longevity Biotech, Inc. in Philadelphia first demonstrated the use of the drug in mouse models. A phase I trial for humans was planned for 2017, but as of 2018 it was still in the preclinical development In drug development, preclinical development, also termed preclinical studies or nonclinical studies, is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials (testing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the ligand of class II G protein–coupled receptors. VIP is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas, and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain. VIP stimulates contractility in the heart, causes vasodilation, increases glycogenolysis, lowers arterial blood pressure and relaxes the smooth muscle of trachea, stomach and gallbladder. In humans, the vasoactive intestinal peptide is encoded by the ''VIP'' gene. VIP has a half-life (t½) in the blood of about two minutes. Function In the body VIP has an effect on several tissues: In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation ( lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic jui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
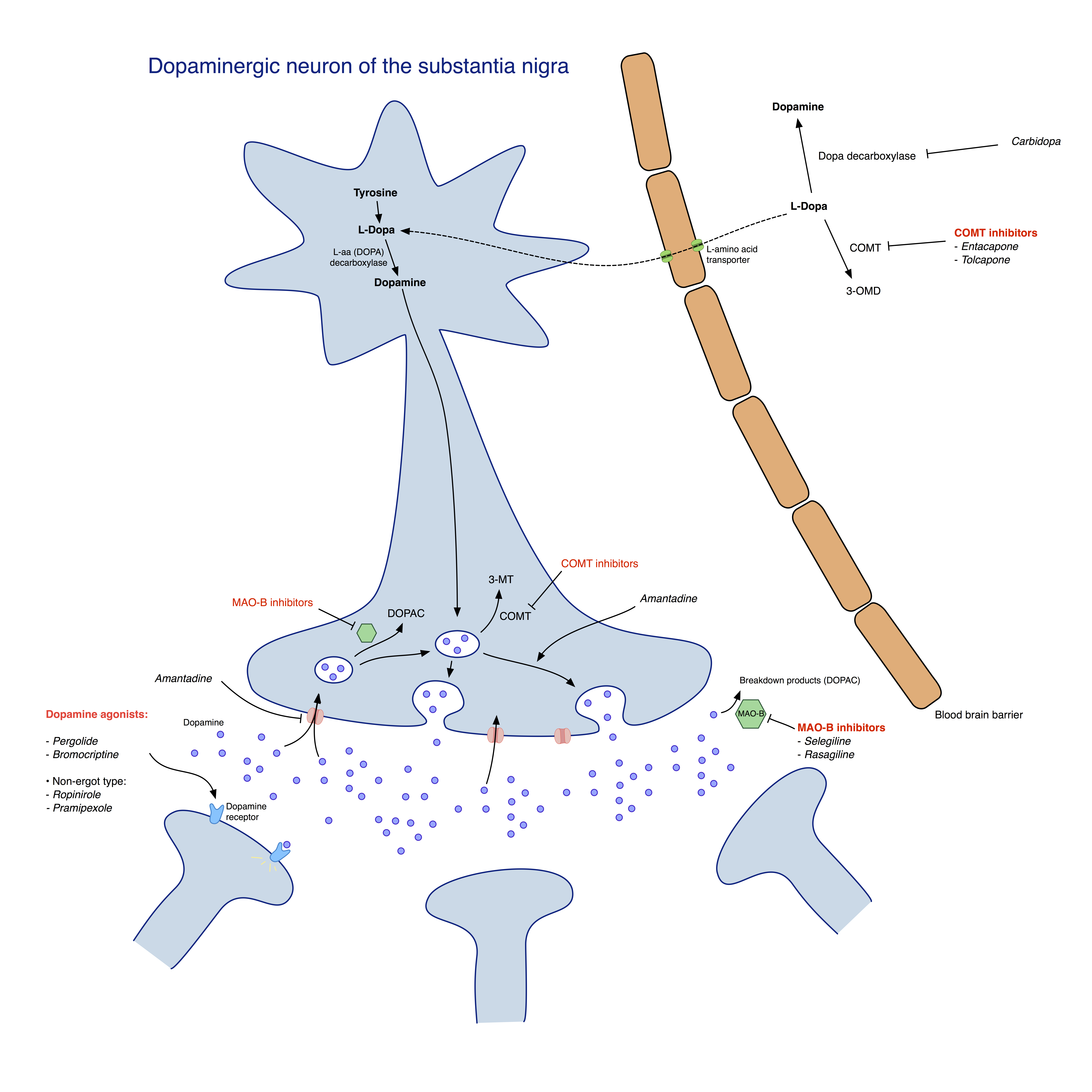
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward-motivated behavior. The anticipation of most types of rewards increases the level of dopamine in the brain, and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with Depression (mood), depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of protein, misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Receptor
There are two known receptors for the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) termed VPAC1 and VPAC2. These receptors bind both VIP and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) to some degree. Both receptors are members of the 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor family. VPAC1 is distributed widely in the CNS, liver, lung, intestine and T-lymphocytes. VPAC2 is found in the CNS, pancreas, skeletal muscle Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ..., heart, kidney, adipose tissue, testis, and stomach. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) receptors are activated by the endogenous peptides VIP, PACAP-38, PACAP-27, peptide histidine isoleucineamide (PHI), peptide histidine methionineami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenance—they are constantly scavenging the CNS for plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular potassium. Recent evidence shows that microglia are also key players in the sustainment of normal brain functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Nebraska Medical Center
The University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) is a public academic health science center in Omaha, Nebraska. Founded in 1869 and chartered as a private medical college in 1881, UNMC became part of the University of Nebraska System in 1902. Rapidly expanding in the early 20th century, the university founded a hospital, dental college, pharmacy college, college of nursing, and college of medicine. It later added colleges of public health and allied health professions. One of Omaha's top employers, UNMC has an annual budget of $841.6 million for 2020 to 2021, and an economic impact of $4.8 billion. History A private medical college was founded in Omaha by the state legislature in 1869 and chartered in 1881 as the Omaha Medical College. It became part of the University of Nebraska system in 1902. A university hospital opened in 1917. In 1968, the University of Nebraska united its health sciences, forming the University of Nebraska Medical Center campus. In 1991, a technology trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase I Trial
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants (potentially tens of thousands) to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays. Summary Clinical trials testing potential medical products are commonly classified into four phases. The drug development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory authority for use in the general population. Phase IV trials are 'post-marketing' or 'surveillance' studies conducted to monitor safety over se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preclinical Development
In drug development, preclinical development, also termed preclinical studies or nonclinical studies, is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials (testing in humans) and during which important feasibility, iterative testing and drug safety data are collected, typically in laboratory animals. The main goals of preclinical studies are to determine a starting, safe dose for first-in-human study and assess potential toxicity of the product, which typically include new medical devices, prescription drugs, and diagnostics. Companies use stylized statistics to illustrate the risks in preclinical research, such as that on average, only one in every 5,000 compounds that enters drug discovery to the stage of preclinical development becomes an approved drug. Types of preclinical research Each class of product may undergo different types of preclinical research. For instance, drugs may undergo pharmacodynamics (what the drug does to the body) (PD), pharmacokinetics (wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiparkinsonian Agents
In the management of Parkinson's disease, due to the chronic nature of Parkinson's disease (PD), a broad-based program is needed that includes patient and family education, support-group services, general wellness maintenance, exercise, and nutrition. At present, no cure for the disease is known, but medications or surgery can provide relief from the symptoms. While many medications treat Parkinson's, none actually reverses the effects of the disease. Furthermore, the gold-standard treatment varies with the disease state. People with Parkinson's, therefore, often must take a variety of medications to manage the disease's symptoms. Several medications currently in development seek to better address motor fluctuations and nonmotor symptoms of PD. However, none is yet on the market with specific approval to treat Parkinson's. Medication The main families of drugs useful for treating motor symptoms are levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors. The most commonly used treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Therapeutics
Peptide therapeutics are peptides or polypeptides (oligomers or short polymers of amino acids) which are used to for the treatment of diseases. Naturally occurring peptides may serve as hormones, growth factors, neurotransmitters, ion channel ligands, and anti-infectives; peptide therapeutics mimic such functions. Peptide Therapeutics are seen as relatively safe and well-tolerated as peptides can be metabolized by the body. Examples The current highest selling marketed diabetic drug Liraglutide, incorporates a lipid chain to extent plasma circulation and ensures prolonged bioavailability. Liraglutide is a GLP-1 agonist drug that self-assembles into an alpha-helical structure, and it requires once a day administration. Lipid conjugation of a palmitoyl chain to a lysine residue at position 26 of Liraglutide results in an extended half-life (around 13–14 hours) in the blood. This is due to the palmitoyl chain allowing non covalent binding to albumin, which delays proteolytic att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |