|
L. Peter Deutsch
L Peter Deutsch (born Laurence Peter Deutsch on August 7, 1946, in Boston, Massachusetts) is an American computer scientist and composer. He is the founder of Aladdin Enterprises and creator of Ghostscript, a free software PostScript and PDF interpreter. Deutsch's other work includes the Smalltalk implementation that inspired Java (software platform), Java just-in-time compilation technology about 15 years later. Name Deutsch changed his legal first name from "Laurence" to "L" on September 12, 2007. His published work and other public references before that time generally use the name ''L. Peter Deutsch'' (with a dot after the ''L''). Early life Deutsch's father was the physicist Martin Deutsch, a professor at MIT. Contributions to computer science Deutsch wrote the PDP-1 Lisp (programming language), Lisp 1.5 implementation and first REPL, Basic PDP-1 LISP, "while still in short pants" and finished it in 1963, when he was 17 years old. He collaborated with Calvin Mooers on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeastern United States. It has an area of and a population of 675,647 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the third-largest city in the Northeastern United States after New York City and Philadelphia. The larger Greater Boston metropolitan statistical area has a population of 4.9 million as of 2023, making it the largest metropolitan area in New England and the Metropolitan statistical area, eleventh-largest in the United States. Boston was founded on Shawmut Peninsula in 1630 by English Puritans, Puritan settlers, who named the city after the market town of Boston, Lincolnshire in England. During the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, Boston was home to several seminal events, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles P
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in '' Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (James (wikt:Appendix:Proto-Indo-European/ǵerh₂-">ĝer-, where the ĝ is a palatal consonant, meaning "to rub; to be old; grain." An old man has been worn away and is now grey with age. In some Slavic languages, the name ''Drago (given name), Drago'' (and variants: ''Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, Reduced instruction set computer, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualization, virtualized computing. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California (part of Silicon Valley), on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center. Sun products included computer servers and workstations built on its own Reduced instruction set computer, RISC-based SPARC processor architecture, as well as on x86-based AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors. Sun also developed its own computer storage, storage systems and a suite of software products, including the Unix-based SunOS and later Solaris operating system, Solaris operating s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PARC (company)
Future Concepts division (formerly Palo Alto Research Center, PARC and Xerox PARC) is a research and development company in Palo Alto, California. It was founded in 1969 by Jack Goldman, Jacob E. "Jack" Goldman, chief scientist of Xerox Corporation, as a division of Xerox, tasked with creating computer technology-related products and hardware systems. Xerox PARC has been foundational to numerous revolutionary computer developments, including laser printing, Ethernet, the modern personal computer, graphical user interface (GUI) and desktop metaphor–paradigm, object-oriented programming, ubiquitous computing, electronic paper, amorphous silicon (a-Si) applications, the computer mouse, and very-large-scale integration (VLSI) for semiconductors. Unlike Xerox's existing research laboratory in Rochester, New York, which focused on refining and expanding the company's copier business, Goldman's "Advanced Scientific & Systems Laboratory" aimed to pioneer new technologies in advanced ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
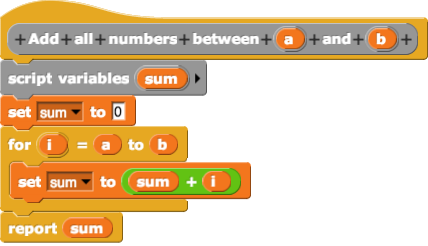
Visual Programming Language
In computing, a visual programming language (visual programming system, VPL, or, VPS), also known as diagrammatic programming, graphical programming or block coding, is a programming language that lets users create computer program, programs by manipulating program elements rather than by specifying them . A VPL allows programming with visual expressions, spatial arrangements of text and graphic symbols, used either as elements of syntax or secondary notation. For example, many VPLs are based on the idea of "boxes and arrows", where boxes or other screen objects are treated as entities, connected by arrows, lines or arcs which represent relations. VPLs are generally the basis of low-code development platforms. Definition VPLs may be further classified, according to the type and extent of visual expression used, into icon-based languages, form-based languages, and diagram languages. Visual programming environments provide graphical or iconic elements which can be manipulated by u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsch Limit
The Deutsch limit is an aphorism about the Information design, information density of visual programming languages originated by L Peter Deutsch, L. Peter Deutsch that states: :The problem with visual programming is that you can't have more than 50 visual primitives on the screen at the same time. The term was coined by Fred Lakin, after Deutsch made the following comment at a talk on visual programming by Scott Kim and Warren Robinett: "Well, this is all fine and well, but the problem with visual programming languages is that you can't have more than 50 visual primitives on the screen at the same time. How are you going to write an operating system?" The language primitive, primitives in a visual language are the separate graphical elements used to build a program, and having more of them available at the same time enables the programmer to read more information. This ''limit'' is sometimes cited as an example of the advantage of textual over visual languages, pointing out the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallacies Of Distributed Computing
The fallacies of distributed computing are a set of assertions made by L Peter Deutsch and others at Sun Microsystems describing false assumptions that programmers new to distributed applications invariably make. The fallacies The originally listed fallacies are # The network is reliable; # Latency is zero; # Bandwidth is infinite; # The network is secure; # Topology doesn't change; # There is one administrator; # Transport cost is zero; # The network is homogeneous; The effects of the fallacies # Software applications are written with little error-handling on networking errors. During a network outage, such applications may stall or infinitely wait for an answer packet, permanently consuming memory or other resources. When the failed network becomes available, those applications may also fail to retry any stalled operations or require a (manual) restart. # Ignorance of network latency, and of the packet loss it can cause, induces application- and transport-layer developer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Request For Comments
A Request for Comments (RFC) is a publication in a series from the principal technical development and standards-setting bodies for the Internet, most prominently the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). An RFC is authored by individuals or groups of engineers and computer scientists in the form of a memorandum describing methods, behaviors, research, or innovations applicable to the working of the Internet and Internet-connected systems. It is submitted either for peer review or to convey new concepts, information, or, occasionally, engineering humor. The IETF adopts some of the proposals published as RFCs as Internet Standards. However, many RFCs are informational or experimental in nature and are not standards. The RFC system was invented by Steve Crocker in 1969 to help record unofficial notes on the development of ARPANET. RFCs have since become official documents of Internet specifications, communications protocols, procedures, and events. According to Crocker, the docu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community Memory
Community Memory (CM) was the first public computerized bulletin board system. Established in 1973 in Berkeley, California, it used an SDS 940 timesharing system in San Francisco connected via a 110 baud link to a teleprinter at a record store in Berkeley to let users enter and retrieve messages. Individuals could place messages in the computer and then look through the memory for a specific notice. While initially conceived as an information and resource sharing network linking a variety of counter-cultural economic, educational, and social organizations with each other and the public, Community Memory was soon generalized to be an information flea market, by providing unmediated, two-way access to message databases through public computer terminals.Schuler, D. (1994). Community networks: Building a new participatory medium. Communications of the ACM, 37(1), 38 Once the system became available, the users demonstrated that it was a general communications medium that could be used f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NLS (computer System)
NLS (oN-Line System) was a revolutionary computer collaboration system developed in the 1960s. It was designed by Douglas Engelbart and implemented by researchers at the Augmentation Research Center (ARC) at the SRI International, Stanford Research Institute (SRI). It was the first computer system to employ the practical use of hypertext links, a computer mouse, raster scan, raster-scan computer monitor, video monitors, information organized by relevance, GUI, screen windowing, presentation programs, and other modern computing concepts. It was funded by ARPA (the predecessor to DARPA, Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency), NASA, and the United States Air Force, US Air Force. The NLS was demonstrated in "The Mother of All Demos". Development Douglas Engelbart developed his concepts while supported by the US Air Force from 1959 to 1960 and published a framework in 1962. The strange acronym, NLS (rather than OLS), was an artifact of the evolution of the system. Engelbart's f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tymshare
Tymshare, Inc was a time-sharing service and third-party hardware maintenance company. Competing with companies such as CompuServe, Service Bureau Corporation and National CSS. Tymshare developed and acquired various technologies, such as data networking, electronic data interchange (EDI), credit card and payment processing, and database technology. It was headquartered in Cupertino in California, from 1964 to 1984. In 1984, Tymshare was acquired by McDonnell Douglas, to which Tymshare had sold its hospital accounting service in 1982. Tymshare was restructured, split up and portions were resold, spun off, and merged with other companies from 1984 through 2004 when most of its legacy network was eventually shut down. Islands of its network technology continued as part of EDI, into 2008. McDonnell Douglas was acquired by Boeing. Consequently, rights to use technology developed by Tymshare are currently held by Boeing, British Telecom (BT), Verizon Communications, and AT&T Inc. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |