|
Kwase Benefo
Kwase Benefo, or Kwasi Benefo, is a mythic hero featured in the mythology of Ashanti people in Ghana. He is well known for his encounter with Amokye, the Ashanti psychopomp, during his journey to the underworld ''(asamando)'' to be reunited with his wives. Representation Kwase Benefo is depicted as a man who owns a fertile land. He became a farmer and rancher, and was successful in his endeavors. Prior to the tragedy which led him to travel to the underworld, Kwase Benefo was unmarried and lived alone. Role in myths Journey to the underworld Kwase Benefo had a relatively prosperous life as a farmer and a rancher, and was missing only a few things, which he greatly wanted: a wife and children. So, he set out to a nearby village to find himself a woman to marry. His efforts paid off, and he returned to his home with a beautiful woman, which he later married. Unfortunately, tragedy struck—his wife became sick and died soon after. Kwase Benefo grieved for her deeply; to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hero
A hero (feminine: heroine) is a real person or a main fictional character who, in the face of danger, combats adversity through feats of ingenuity, courage, or strength. Like other formerly gender-specific terms (like ''actor''), ''hero'' is often used to refer to any gender, though ''heroine'' only refers to women. The original hero type of classical epics did such things for the sake of glory and honor. Post-classical and modern heroes, on the other hand, perform great deeds or selfless acts for the common good instead of the classical goal of wealth, pride, and fame. The antonym of ''hero'' is '' villain''. Other terms associated with the concept of ''hero'' may include ''good guy'' or '' white hat''. In classical literature, the hero is the main or revered character in heroic epic poetry celebrated through ancient legends of a people, often striving for military conquest and living by a continually flawed personal honor code. The definition of a hero has changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashanti Mythology
Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom (from the Twi word ''akom'', meaning "prophecy"). Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups (including the Fanti, Ashanti, the Akuapem, the Wassa, the Abron, the Anyi, and the Baoulé, among others), so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans. Anansi the spider is a folk hero who is prominent in Ashanti folktales where he is depicted as a wise trickster. In other aspects of Akan spirituality, Anansi is also someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in Ghana–Ivory Coast border, the west, Burkina Faso in Burkina Faso–Ghana border, the north, and Togo in Ghana–Togo border, the east.Jackson, John G. (2001) ''Introduction to African Civilizations'', Citadel Press, p. 201, . Ghana covers an area of , spanning diverse biomes that range from coastal savannas to tropical rainforests. With nearly 31 million inhabitants (according to 2021 census), Ghana is the List of African countries by population, second-most populous country in West Africa, after Nigeria. The capital and List of cities in Ghana, largest city is Accra; other major cities are Kumasi, Tamale, Ghana, Tamale, and Sekondi-Takoradi. The first permanent state in present-day Ghana was the Bono state of the 11th century. Numerous kingdoms and empires emerged over the centuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
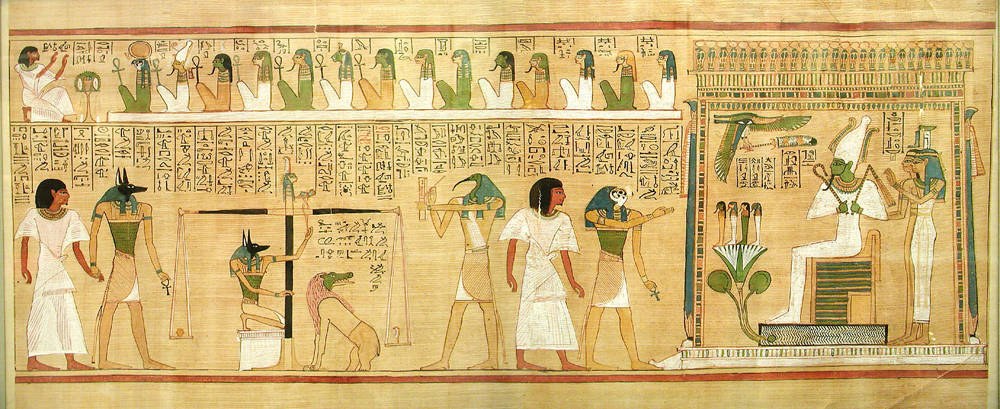
Amokye
In the religious traditions of the Akan people and the Ashanti people of Ghana, Amokye is the woman who guards the entrance to the other world, which is called 'Asamando' (the Land of the Dead). She is the woman who welcome the souls of dead women to the otherworld. According to the beliefs, Ashanti women were dressed for bury in amoasie (loincloths) and jewelry Jewellery (British English, UK) or jewelry (American English, U.S.) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment, such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be at ..., which they gave to Amokye as payment for allowing them to Asamando. References {{Portal bar, Traditional African religions African mythology Ashanti people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychopomp
Psychopomps (from the Greek word , , literally meaning the 'guide of souls') are supernatural creatures, spirits, entities, angels, demons or deities in many religions whose responsibility is to escort newly deceased souls from Earth to the afterlife. Their role is not to judge the deceased, but simply to guide them. Appearing frequently on funerary art, psychopomps have been depicted at different times and in different cultures as anthropomorphic entities, horses, deer, dogs, whip-poor-wills, ravens, crows, vultures, owls, sparrows, and cuckoos. In the case of birds, these are often seen in huge masses, waiting outside the home of the dying. Overview Ancient religion Classical examples of a psychopomp are the ancient Egyptian god Anubis, the deity Yama in Hinduism, the Greek ferryman Charon, the goddess Hecate, and god Hermes, the Roman god Mercury, the Norse Valkyries, the Aztec Xolotl, Slavic Morana and the Etruscan Vanth. Modern religion Heibai Wuchang, litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esoteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyame
Onyame, Nyankopon (Onyankapon) and Odomankoma are the trinity of the supreme god of the Akan people of Ghana, who is most commonly known as Nyame. His name means "He who knows and sees everything" and "omniscient, omnipotent sky deity" in the Akan language. Names Odomankoma The name Odomankoma means "Creator". Odomankoma is known by the name Odomankoma wuo, which has a double meaning. In one vein, it means "Father Death". On the other it means "The Creator's death". Both of these meanings are a reference to Odomankoma being the creator of Death, whose name is Owuo, and Death in return killed him. Odomankoma also goes by various other epithets: Oboade meaning Creator (an additional name of Creator), Oboo nkwa meaning the Creator of life and Oboo-wuo meaning the Creator of death, another name that is a call-back to Odomankoma creating Owuo (Death). Odomankoma also has the name Borebore, meaning Architect, and Ananse Kokuroko, meaning the great designer or, literally, the great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of African Mythological Figures
This is a list of African spirits as well as deities found within the traditional African religions. It also covers spirits as well as deities found within the Afro-American religions—which is mostly derived from traditional African religions. Additionally, prominent mythic figures including heroes and legendary creatures may also be included in this list. Akan *Abu-Mehsu * Amokye *Anansi *Asase Ya *Aso *Bia *Bobowissi *Bosomtwe *Intikuma *Katarwiri *Kwase Benefo *Kweku Tsin *Nyame * Owuo * Tano Alur * Jok Odudu Bambara * Bemba * Chiwara *Duga *Faro *Kontron *Muso Koroni *Ndomadyiri * Ninimini *Sanen *Suruku *Teliko Baganda * Katonda *Ggulu * Kibuka *Kitaka *Kiwanuka *Mukasa *Musisi *Nambi *Warumbe *Wanema *Wanga Bahumono *Owazi Boloki * Libanza * Njambe Dahomey *Agé *Ayaba *Da *Gbadu * Gleti *Gu *Lisa *Loko *Mawu *Nana Buluku *Salosteles * Sakpata * Xevioso *Zinsi *Zinsu Dinka * Abuk * Aiwel * Deng * Kejok * Nhialic Efik * Abassi *Atai Fang * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akan Religion
Akan religion comprises the traditional beliefs and religious practices of the Akan people of Ghana and eastern Ivory Coast. Akan religion is referred to as Akom (from the Twi word ''akom'', meaning "prophecy"). Although most Akan people have identified as Christians since the early 20th century, Akan religion remains practiced by some and is often syncretized with Christianity. The Akan have many subgroups (including the Fanti, Ashanti, the Akuapem, the Wassa, the Abron, the Anyi, and the Baoulé, among others), so the religion varies greatly by region and subgroup. Similar to other traditional religions of West and Central Africa such as West African Vodun, Yoruba religion, or Odinani, Akan cosmology consists of a senior god who generally does not interact with humans and many gods who assist humans. Anansi the spider is a folk hero who is prominent in Ashanti folktales where he is depicted as a wise trickster. In other aspects of Akan spirituality, Anansi is also som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Mythology
African or Africans may refer to: * Anything from or pertaining to the continent of Africa: ** People who are native to Africa, descendants of natives of Africa, or individuals who trace their ancestry to indigenous inhabitants of Africa *** Ethnic groups of Africa *** Demographics of Africa *** African diaspora ** African, an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the African Union ** Citizenship of the African Union ** Demographics of the African Union **Africanfuturism ** African art ** *** African jazz (other) ** African cuisine ** African culture ** African languages ** African music ** African Union ** African lion, a lion population in Africa Books and radio * ''The African'' (essay), a story by French author J. M. G. Le Clézio * ''The African'' (Conton novel), a novel by William Farquhar Conton * ''The African'' (Courlander novel), a novel by Harold Courlander * ''The Africans'' (radio program) Music * "African", a song by Peter Tosh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |