|
Kuvikal Point
Kuvikal Point ( bg, нос Кувикъл, ‘Nos Kuvikal’ \'nos 'ku-vi-k&l\) is the point on the east side of the entrance to Transmarisca Bay and the west side of the entrance to Suregetes Cove on the north coast of Krogh Island in Biscoe Islands, Antarctica. The eponymous group of small ''Kuvikal Islands'', centred off the point at , extends in southwest-northeast direction and in south-southeast to north-northwest direction.Kuvikal Point. Composite Antarctic Gazetteer The point is named after Kuvikal Peak in the , Bulgaria. Location Kuvikal Point is located at , which is east-southeast of |
Transmarisca Bay
Transmarisca Bay ( bg, залив Трансмариска, ‘Zaliv Transmarisca’ \'za-liv trans-ma-'ri-ska\) is the 4.3 km wide bay indenting for 3.2 km the north coast of Krogh Island in Biscoe Islands, Antarctica. It is entered east of Edholm Point and west of Kuvikal Point. The bay is named after the ancient Roman town of Transmarisca in Northeastern Bulgaria. Location Transmarisca Bay is centred at . British mapping in 1976. Maps British Antarctic Territory. Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Series, Sheet W 66 66. Directorate of Overseas Surveys, UK, 1976. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated. References Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer.Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suregetes Cove
Suregetes Cove ( bg, залив Сурегетес, zaliv Suregetes, ) is the 2.47 km wide cove indenting for 1.9 km the N coast of Krogh Island in Biscoe Islands, Antarctica. It is entered east of Kuvikal Point and west of Zagrade Point. The cove is named after the Thracian god Suregetes. Location Suregetes Cove is centred at . British mapping in 1976. Maps British Antarctic Territory. Scale 1:200000 topographic map. DOS 610 Series, Sheet W 66 66. Directorate of Overseas Surveys, UK, 1976. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR), 1993–2016. References Bulgarian Antarctic Gazetteer.Antarctic Place-names Commission The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in .... (details ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krogh Island
Krogh Island () is an ice-covered island about long lying close west of the southern part of Lavoisier Island in Biscoe Islands, Antarctica. The island is separated from Lavoisier Island on the east by Vladigerov Passage, from DuBois Island on the west by Papazov Passage and from Watkins Island to the south by Lewis Sound. Its north coast is indented by Transmarisca Bay and Suregetes Cove. The island was mapped from air photos taken by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (1956–57), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for August Krogh Schack August Steenberg Krogh (15 November 1874 – 13 September 1949) was a Danish professor at the department of zoophysiology at the University of Copenhagen from 1916 to 1945. He contributed a number of fundamental discoveries within several ..., a Danish physiologist who specialized in the functional activity of the capillaries, and was a pioneer of studies of human metabolism and blood circul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biscoe Islands
Biscoe Islands is a series of islands, of which the principal ones are Renaud, Lavoisier (named ''Serrano'' by Chile and ''Mitre'' by Argentina), Watkins, Krogh, Pickwick and Rabot, lying parallel to the west coast of Graham Land and extending between Southwind Passage on the northeast and Matha Strait on the southwest. Another group of islands are the Adolph Islands. The islands are named for John Biscoe, the commander of a British expedition which explored the islands in February 1832. See also * Bates Island * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Southwind Passage * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and st ... References * Archipelagoes of the Southern Ocean Islands of Anta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
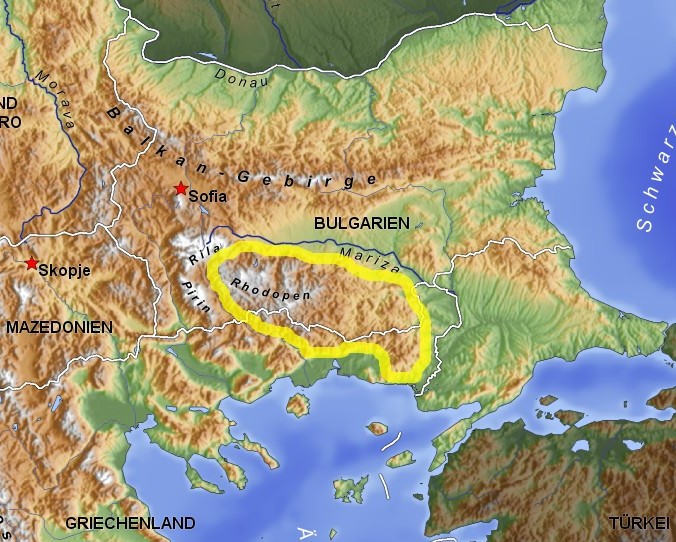
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edholm Point
Edholm Point () is the northwestern point of Krogh Island in the Biscoe Islands, Antarctica forming the west side of the entrance to Transmarisca Bay. The point was mapped from air photos by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (1956–57), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and ... for Otto Edholm, a British physiologist who was Head of the Division of Human Physiology of the National Institute for Medical Research since its foundation in 1949, and who specialized in studies of the effects of cold on man. In 2021 one of Otto Edholm's grandchildren set up an ice-cream company called Edholm Point Ice-Cream.www.edholmpointicecream.com References Headlands of the Biscoe Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burton Point
Burton Point () is the northeastern point of Krogh Island in the Biscoe Islands, Antarctica forming the north side of the northeast entrance to Vladigerov Passage. The point was mapped from air photos taken by the Falkland Islands and Dependencies Aerial Survey Expedition (1956–57), and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Alan C. Burton Alan C. Burton (April 18, 1904 – June 27, 1979) was an English-born Canadian physicist. He is considered a founding father of modern biophysics. He was born in London, received a BSc from University College London and taught high school phys ..., Canadian physiologist who has specialized in cold climate physiology and the problems of clothing for cold environments. References * Headlands of the Biscoe Islands {{Biscoes-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gaze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of The Biscoe Islands
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |