|
Kurchatov Institute
The Kurchatov Institute (, National Research Centre "Kurchatov Institute") is Russia's leading research and development institution in the field of nuclear power, nuclear energy. It is named after Igor Kurchatov and is located at 1 Kurchatov Square, Moscow. In the Soviet Union it was known as I. V. Kurchatov Institute of Atomic Energy (), abbreviated KIAE (). Between 1991 and 2010, it was known as the Russian Scientific Centre "Kurchatov Institute" () before its name was changed to National Research Centre "Kurchatov Institute". History Until 1955 known under a secret name "Laboratory No. 2 of the USSR Academy of Sciences", the Kurchatov Institute was founded in 1943 with the initial purpose of developing nuclear weapons. The majority of Soviet nuclear reactors were designed in the institute, including the on-site F-1 (nuclear reactor), F-1, which was the first nuclear reactor outside North America to sustain criticality. Since 1955, it was also the host for major scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear ''fission'' of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear ''decay'' processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as ''Voyager 2''. Reactors producing controlled fusion power, ''fusion'' power have been operated since 1958 but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future. The first nuclear power plant was built in the 1950s. The global installed nuclear capacity grew to 100GW in the late 1970s, and then expanded during the 1980s, reaching 300GW by 1990. The 1979 Three Mile Island accident in the United States and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union resulted in increased regulation and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
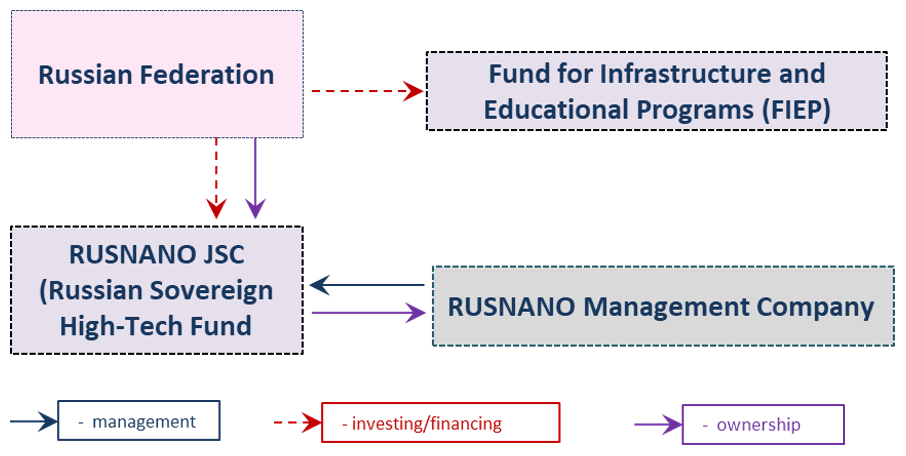
Nanotechnology In Russia
Rusnano Group () is a Russian state-established and funded company. The Rusnano Group's mission is to create competitive nanotechnology-based industry in Russia. Rusnano invests directly and through indirect funds into all major knowledge-based areas where nanotechnology is widely implemented: electronics, optics, telecom, classic and renewable energy, healthcare and biotechnology, materials and metallurgy, engineering and chemistry. In 2020 the government of Russia has merged it with VEB.RF. As of 2017 100% shares of Rusnano were owned by the Russian government. In 2015 Rusnano had 16 investment projects. It invested into about 97 plants and R&D companies in 37 regions of Russia. In 2016 many such enterprises were either dissolved, bankrupted or repurposed (see. below). In 2016 the company was on the verge of bankruptcy significantly devaluating below the equity levels but managed to recover. In November 2021 trade of company's securities trade was suspended on Moscow Sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosatom
State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom (commonly referred to as Rosatom rus, Росатом, p=rosˈatəm}), also known as Rosatom State Nuclear Energy Corporation, (), or Rosatom State Corporation, is a Russian State corporation (Russia), state corporation headquartered in Moscow that specializes in Nuclear power in Russia, nuclear energy, nuclear non-energy goods and high-tech products. It was established in 2007 and comprises more than 350 enterprises, including scientific research organizations, a Nuclear weapon, nuclear weapons complex, and the world's only Nuclear-powered icebreaker, nuclear icebreaker fleet. The organization is the largest electricity generating company in Russia, producing 217.4 TWh of electricity, 20.28% of the country's total electricity production. The corporation ranks first in overseas nuclear power plant construction, responsible for 90% of global nuclear technology exports: 22 nuclear power plant units, at different stages of development, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Government
The Russian Government () or fully titled the Government of the Russian Federation () is the highest federal executive governmental body of the Russian Federation. It is accountable to the president of the Russian Federation and controlled by the State Duma. The status and procedure of its activities are determined by chapter 6 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the provisions of the federal constitutional law "On the Government of the Russian Federation". The Government's terms of reference include the development and enforcement of the federal budget and the implementation of socially oriented government policies in various cultural areas of Russian society. Although the Government of the Russian Federation does not adopt laws, its responsibilities include issuing federal by-laws (resolutions) based on federal laws passed by the Federal Assembly. According to the 1991 amendment to the 1978 constitution, the president of Russia was the head of the executi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolution Of The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. Declaration No. 142-Н of the Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union, formally establishing the dissolution of the Soviet Union as a state and subject of international law. It also brought an end to the Soviet Union's federal government and General Secretary (also President) Mikhail Gorbachev's effort to reform the Soviet political and economic system in an attempt to stop a period of political stalemate and economic backslide. The Soviet Union had experienced internal stagnation and ethnic separatism. Although highly centralized until its final years, the country was made up of 15 top-level republics that served as the homelands for different ethnicities. By late 1991, amid a catastrophic political crisis, with several republics al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet In Russia
Internet in Russia, or Russian Internet (, which means "Russia-related Internet"), and sometimes Runet (a portmanteau of "Russian" and "Internet"), is the part of the Internet that is related to Russia. , Internet access in Russia is available to businesses and home users in various forms, including dial-up, cable, DSL, FTTH, mobile, wireless and satellite. , 122,488,468 Russians (85% of the country's total population) were Internet users. , Russia ranked 47th among the world's countries by the fixed broadband Internet access speed, with an average download speed of 75.91 mbit/s, and 88th by mobile network Internet access speed, with 22.83 mbit/s. According to Freedom House, the Internet in Russia is "Not Free" . In September 2011, Russia overtook Germany on the European market with the highest number of unique visitors online. In March 2013, a survey found that Russian had become the second-most commonly used language on the web after English. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEMOS
Demos may refer to: Computing * DEMOS, a Soviet Unix-like operating system * DEMOS (ISP), the first internet service provider in the USSR * Demos Commander, an Orthodox File Manager for Unix-like systems * Plural for Demo (computer programming) Organizations * Demos (UK think tank), London-based public policy research organisation and publisher * Demos (U.S. think tank), a public policy research and advocacy organization * DEMOS (Republika Srpska), a political party in Republika Srpska * DEMOS (Montenegro), a parliamentary political party in Montenegro * DEMOS (Slovenia), a coalition of democratic political parties in Slovenia * Demos Helsinki, a think tank in Finland * Demos Medical Publishing, a publisher of books on medical subjects * Solidary Democracy, a political party in Italy * Democracy and Solidarity Party, a political party in Romania Arts and entertainment * ''Demos'' (film), a 1921 silent film * ''Demos'' (novel), an 1886 novel by George Gissing Music * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siberia and the list of cities and towns in Russia by population, third-most populous city in Russia after Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Additionally, it is the largest city in the Asian part of Russia and the most populous city in the country that does not have the status of a Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject. Novosibirsk is located in southwestern Siberia, on the banks of the Ob River. Novosibirsk was founded in 1893 on the Ob River crossing point of the future Trans-Siberian Railway, where the Novosibirsk Rail Bridge was constructed. Originally named Novonikolayevsk ("New Nicholas") in honor of Nicholas II of Russia, Emperor Nicholas II, the city rapidly grew into a major transport, commercial, and industrial hub. Novosibirsk was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-4 (tokamak)
T4 or T-4 may refer to: Airports and airlines * Heathrow Terminal 4 * Tiyas Military Airbase, also known as the T-4 Airbase Biology and medicine * T4 phage, a bacteriophage * Thyroxine (T4), a form of thyroid hormone * the T4 spinal nerve * the fourth thoracic vertebrae of the vertebral column * A non-small cell lung carcinoma staging for a type of tumour * A CD4 + T lymphocyte * T4: an EEG electrode site according to the 10-20 system Entertainment * ''T4'' (Channel 4), the former daytime teen-aimed slot on Channel 4 in the UK * '' Terminator Salvation'', sometimes referred to as ''Terminator 4'' * '' Transformers: Age of Extinction'', the fourth film in the live-action ''Transformers'' film series Software and video games * Text Template Transformation Toolkit, a technology developed by Microsoft * ''Tekken 4'', a 2001 fighting game Rail transport * Eastern Suburbs & Illawarra Line, a Sydney Trains railway service * Île-de-France tramway Line 4 * T4 (Istanbul Tram) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-3 (tokamak)
T3 or T-3 may refer to: Entertainment * '' T3: Alliance'', an investigative-public affairs TV program in the Philippines * ''T3'' (magazine), focusing on new and hi-tech gadgets * '' Terminator 3: Rise of the Machines'', the third film in the ''Terminator'' series * ''Tekken 3'', a 1997 fighting game in the ''Tekken'' franchise * '' Tiger 3'', a 2023 Indian action thriller film in the YRF Spy Universe Places * Fletcher's Ice Island or T-3, an iceberg and scientific research station * T3 (skyscraper), an office building in Taichung, Taiwan * Tokyo Teleport Town, a planned city on Odaiba, reclaimed land in Tokyo Bay Science, mathematics and technology * Axiom T3, or T3 space, regular space in topology and related fields of mathematics * T3 Technion Technology Transfer, the technology transfer office of the Technion Israel Institute of Technology * T3 line, or Digital Signal 3, a 44.736 Mbit/s telecommunications channel standard * T-3, a Palomar–Leiden survey Jupiter T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |