|
Kuiper (Mercurian Crater)
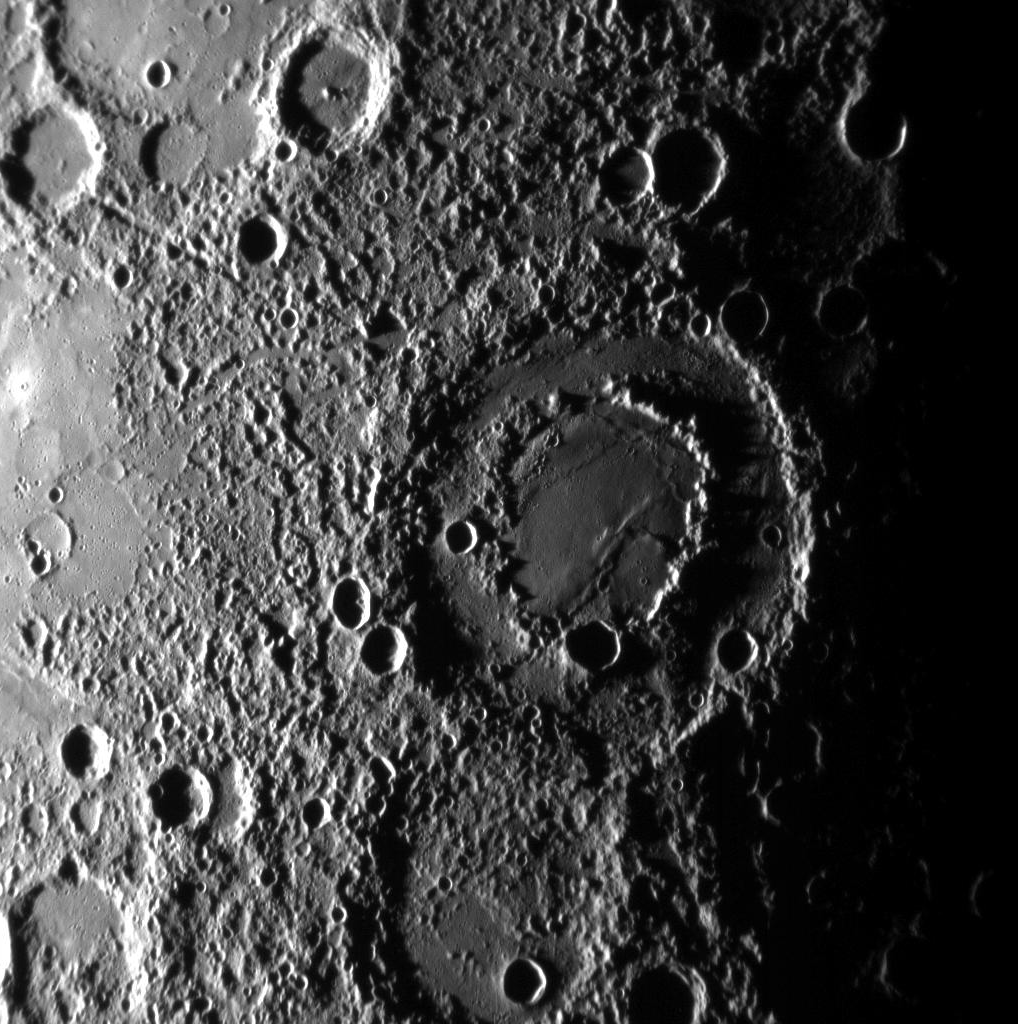
Kuiper is a moderate-size crater with a central peak cluster located at on Mercury. It is 62 kilometers in diameter and was named after Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper in 1976. It is one of only 2 Mercurian craters which are named not after artists, and one of very few cases when the same name is used for 3 craters (there are also Kuiper craters on Mars and on the Moon). Gerard Kuiper, being a leader of American planetary science, died shortly before the first images of Mercurian surface were made. Kuiper overlies the northern rim of the larger crater Murasaki. Kuiper crater has the highest recorded albedo of any region on the planet's surface and has a prominent ray system, suggesting that it is one of the youngest craters.Description Kuiper is one of the largest craters of the Kuiperian system on Mercury. The largest is Bartók crater.Denevi, B. W., Ernst, C. M., Prockter, L. M., and Robinson, M. S., 2018. The Geologic History of Mercury. In ''Mercury: The V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MESSENGER
Messenger, Messengers, The Messenger or The Messengers may refer to: People * Courier, a person or company that delivers messages, packages, or mail * Messenger (surname) * Bicycle messenger, a bicyclist who transports packages through cities * Messenger-at-arms, an officer of the Scottish Court of Session * Messenger of the Court, a court officer responsible for carrying communications and executing other orders * Prophets and messengers in Islam * Muhammad and other prophets in Islam, who were known as Messengers of Allah (God) Science and technology Biology and chemistry * Chemical messenger, such as a hormone or neurotransmitter, a molecule used for cellular signalling * Messenger RNA (mRNA), RNA that carries information from DNA to the ribosome sites of protein synthesis in a cell Electronics and computing *Instant messenger, a tool for online text communication **Facebook Messenger, an instant messaging service by Meta (Facebook) **Microsoft Messenger service, an instant me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper Quadrangle
The Kuiper quadrangle, located in a heavily cratered region of Mercury (planet), Mercury, includes the young, 55-km-diameter crater Kuiper (crater on Mercury), Kuiper (11° S., 31.5° ), which has the highest albedo recorded on the planet,Hapke, Bruce, Danielson, G. E., Jr., Klaasen, Kenneth, and Wilson, Lionel, 1975, Photometric observations of Mercury from Mariner 10: ''Journal of Geophysical Research'', v. 80, no. 17, pp. 2431–2443. and the small crater Hun Kal (crater), Hun Kal (0.6° S., 20.0° ), which is the principal reference point for Mercurian longitude (Davies and Batson, 1975). Impact craters and basins, their numerous secondary craters, and heavily to lightly cratered plains are the characteristic landforms of the region. At least six multiringed basins ranging from 150 km to 440 km in diameter are present. Inasmuch as multiringed basins occur widely on that part of Mercury photographed by ''Mariner 10'', as well as on the Moon and Mars, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the first planet from the Sun. It is a rocky planet with a trace atmosphere. While it is the List of Solar System objects by size, smallest and least massive planet of the Solar System, its surface gravity is slightly higher than that of Mars. The surface of Mercury is similar to Earth's Moon, heavily Impact crater, cratered, with expansive rupes system, generated from thrust faults, and bright ray systems, formed by ejecta. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of , which is about one-third the diameter of the planet (). Being the most inferior planet, inferior orbiting planet it appears in Earth's sky, always close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star". It stays most of the time the closest to all other planets and is the planet with the highest delta-v needed to travel to from all other planets of the Solar System. Mercury's sidereal year (88.0 Earth days) and sidereal day (58.65 Earth days) are in a 3:2 ratio. This relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerard Kuiper
Gerard Peter Kuiper ( ; born Gerrit Pieter Kuiper, ; 7 December 1905 – 23 December 1973) was a Dutch-American astronomer, planetary scientist, selenographer, author and professor. The Kuiper belt is named after him. Kuiper is considered by many to be the father of modern planetary science. Early life and education Kuiper, the son of a tailor in the village of Tuitjenhorn in North Holland, had an early interest in astronomy. He had extraordinarily sharp eyesight, allowing him to see with the naked eye Apparent magnitude, magnitude 7.5 stars, about four times fainter than those visible to normal eyes. He studied at Leiden University in 1924, where at the time a very large number of astronomers had congregated. He befriended fellow students Bart Bok and Pieter Oosterhoff, and was taught by Ejnar Hertzsprung, Antonie Pannekoek, Willem de Sitter, Jan Woltjer (astronomer), Jan Woltjer, Jan Oort, and the physicist Paul Ehrenfest. He received his Candidate (degree), c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters are typically circular, though they can be elliptical in shape or even irregular due to events such as landslides. Impact craters range in size from microscopic craters seen on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program to simple bowl-shaped depressions and vast, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury (planet), Mercury, Callisto (moon), Callisto, Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, and most small moons and asteroids. On other planet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper (Martian Crater)
Kuiper is a Dutch occupational surname meaning cooper. Common spelling variants include Kuyper, Kuipers, Kuijper, Kuijpers, Kuypers, and De Kuyper. Notable people with the name include: Kuiper * Adrian Kuiper (born 1959), South African cricketer * Barend Klaas Kuiper (1877–1961), Dutch-American historian * David Kuiper (born 1980), Dutch rower * Duane Kuiper (born 1950), American baseball player * Edith Kuiper (born 1960), Dutch economist * F. B. J. Kuiper (1907–2003), Dutch Indologist *Gerard Kuiper (1905–1973), Dutch-American astronomer after whom the Kuiper belt was named * Glen Kuiper (born 1963) American broadcaster * Hennie Kuiper (born 1949), Dutch cyclist * J. P. Kuiper (1922–1985), Dutch professor of social medicine * Michael Kuiper (born 1989), Dutch martial artist * Nick Kuiper (born 1982), Canadian ice hockey player * Nicky Kuiper (born 1989), Dutch footballer *Nicolaas Kuiper (1920–1994), Dutch mathematician, known for Kuiper's test, Kuiper's theorem, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper (lunar Crater)
Kuiper ( ) is a small lunar impact crater in a relatively featureless part of the Mare Cognitum. It is a circular, cup-shaped feature with only some minor wear. It was named after Dutch-American astronomer Gerard Kuiper in 1976. Kuiper was the Project Scientist for the Ranger program. This crater was previously identified as Bonpland E. The lava-flooded crater Bonpland lies to the east at the edge of the Mare Cognitum. To the east-southeast of Kuiper crater is the crash landing site of the Ranger 7 probe, the first American spacecraft to photograph the Moon. References * * * * * * * * * * * * External links Kuiper at The Moon WikiLTO-6D2 Kuiper— L&PI topographic map In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ... * {{cite web, last = Wood , first = Chuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariner 10
''Mariner 10'' was an American Robotic spacecraft, robotic space probe launched by NASA on 3 November 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury (planet), Mercury and Venus. It was the first spacecraft to perform flybys of multiple planets. ''Mariner 10'' was launched approximately two years after ''Mariner 9'' and was the last spacecraft in the Mariner program. (Mariner 11 and Mariner 12 were allocated to the Voyager program and redesignated ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''.) The mission objectives were to measure Mercury's environment, atmosphere, surface, and body characteristics and to make similar investigations of Venus. Secondary objectives were to perform experiments in the interplanetary medium and to obtain experience with a dual-planet gravity assist mission. ''Mariner 10''s science team was led by Bruce C. Murray at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Design and trajectory ''Mariner 10'' was the first mission to use a gravity assist from one planet (in this case, Venus) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murasaki (crater)
Murasaki is a impact crater, crater on Mercury (planet), Mercury located at 12 S, 31 W. It is 132 km in diameter. It was named after 10th-11th century Japanese writer Murasaki Shikibu. The name was approved by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature in 1976. To its east lies the slightly larger Hiroshige (crater), Hiroshige. The bright crater Kuiper (Mercurian crater), Kuiper overlays the rim of Murasaki. References Impact craters on Mercury Murasaki Shikibu {{Mercury-crater-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albedo
Albedo ( ; ) is the fraction of sunlight that is Diffuse reflection, diffusely reflected by a body. It is measured on a scale from 0 (corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation) to 1 (corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation). ''Surface albedo'' is defined as the ratio of Radiosity (radiometry), radiosity ''J''e to the irradiance ''E''e (flux per unit area) received by a surface. The proportion reflected is not only determined by properties of the surface itself, but also by the spectral and angular distribution of solar radiation reaching the Earth's surface. These factors vary with atmospheric composition, geographic location, and time (see position of the Sun). While directional-hemispherical reflectance factor is calculated for a single angle of incidence (i.e., for a given position of the Sun), albedo is the directional integration of reflectance over all solar angles in a given period. The temporal resolution may range from seconds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray System
In planetary geology, a ray system comprises radial streaks of fine '' ejecta'' thrown out during the formation of an impact crater, looking somewhat like many thin spokes coming from the hub of a wheel. The rays may extend for lengths up to several times the diameter of their originating crater, and are often accompanied by small secondary craters formed by larger chunks of ejecta. Ray systems have been identified on the Moon, Earth ( Kamil Crater), Mercury, and some moons of the outer planets. Originally it was thought that they existed only on planets or moons lacking an atmosphere, but more recently they have been identified on Mars in infrared images taken from orbit by '' 2001 Mars Odyssey''s thermal imager. Rays appear at visible, and in some cases infrared wavelengths, when ejecta are made of material with different reflectivity (i.e., albedo) or thermal properties from the surface on which they are deposited. Typically, visible rays have a higher albedo than th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Mercury
The geology of Mercury is the scientific study of the surface, crust (geology), crust, and interior of the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. Historically, Mercury has been the least understood of all the terrestrial planets in the Solar System. This stems largely from its proximity to the Sun which makes reaching it with spacecraft technically challenging and Earth-based observations difficult. For decades, the principal source of geologic information about Mercury came from the 2,700 images taken by the Mariner 10 spacecraft during three flybys of the planet from 1974 to 1975. These images covered about 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |