|
Kuehneotherium
''Kuehneotherium'' is an early mammaliaform genus, previously considered a Holotheria, holothere, that lived during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Epochs and is characterized by reversed-triangle pattern of Molar (tooth), molar Cusp (anatomy), cusps. Although many fossils have been found, the fossils are limited to teeth, dental fragments, and mandible fragments. The genus includes ''Kuehneotherium praecursoris'' and all related species. It was first named and described by Doris M. Kermack, K. A. Kermack, and Frances Mussett in November 1967. The family Kuehneotheriidae and the genus ''Kuehneotherium'' were created to house the single species ''Kuehneotherium praecursoris''. Modeling based upon a comparison of the ''Kuehneotherium'' jaw with other mammaliaforms indicates it was about the size of a modern-day shrew between 4 and 5.5 g at adulthood. ''Kuehneotherium'' is thought to be an insectivore that could consume only soft-bodied insects such as moths. Its teeth were shaped f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuehneotheriidae
Kuehneotheriidae is an extinct family of mammaliaforms traditionally placed within 'Symmetrodonta', though now generally considered more basal than true symmetrodonts. All members of Kuehneotheriidae which have been found so far are represented only by teeth, but these teeth have features which have led paleontologists to classify kuehneotheriids as very close relatives of the first true mammals. But fossil clades based solely on teeth often lead to difficulties ( Ausktribosphenidae being a good example), and it is not possible to draw significant conclusions about mammalian evolution from Kuehneotheriidae unless some more complete skeletons are found. See also * Evolution of mammals The evolution of mammals has passed through many stages since the first appearance of their synapsid ancestors in the Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian sub-period of the late Carboniferous period. By the mid-Triassic, there were many synaps ... References Mammaliaformes Prehistoric t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotheria
Holotheria is a diverse group of mammals that are descendants of the last common ancestor of ''Kuehneotherium'' (now known to be a non-mammalian cynodont) and Theria (the group that includes marsupials and placental mammals).Wible, J. R., Rougier, G. W., Novacek, M. J. & McKenna, M. C. (2001). "Earliest eutherian ear region: A petrosal referred to ''Prokennalestes'' from the Early Cretaceous of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 3322. The group is characterized by the beginning of the triangulation of a typical triconodont dentition in morganucodonts, towards a symmetrodonta. This triangulation occurs convergently in Docodontiformes although Shuotheriidae was formerly considered sister to Australosphenida. There are studies that place Docodonta as sister to Monotreme, Monotremata, which would make Docodontiformes fall within Pan-Monotremata instead of being a clade outside Holotheria. Holotheria fell into disuse and was widely considered invalid by the early 2000s, but Mao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinnetherium
''Dinnetherium'' is an extinct genus of mammaliaforms from the Early Jurassic of Arizona. The type species, ''D. nezorum'', was named in 1983. It was discovered in a Sinemurian layer of the Kayenta Formation, within the Gold Spring Quarry 1. The holotype is MNA V3221, which is a partial right mandible. ''Dinnetherium'' has sometimes been placed in the family Megazostrodontidae, but in 2011 the monotypic In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unisp ... family Dinnetheriidae and order Dinnetheria were erected for the genus. Classification The phylogenetic position of ''Dinnetherium'' within mammaliaforms is shown in the cladogram below: References Morganucodonta Sinemurian life Early Jurassic synapsids of North America Jurassic Arizona Fossils of the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
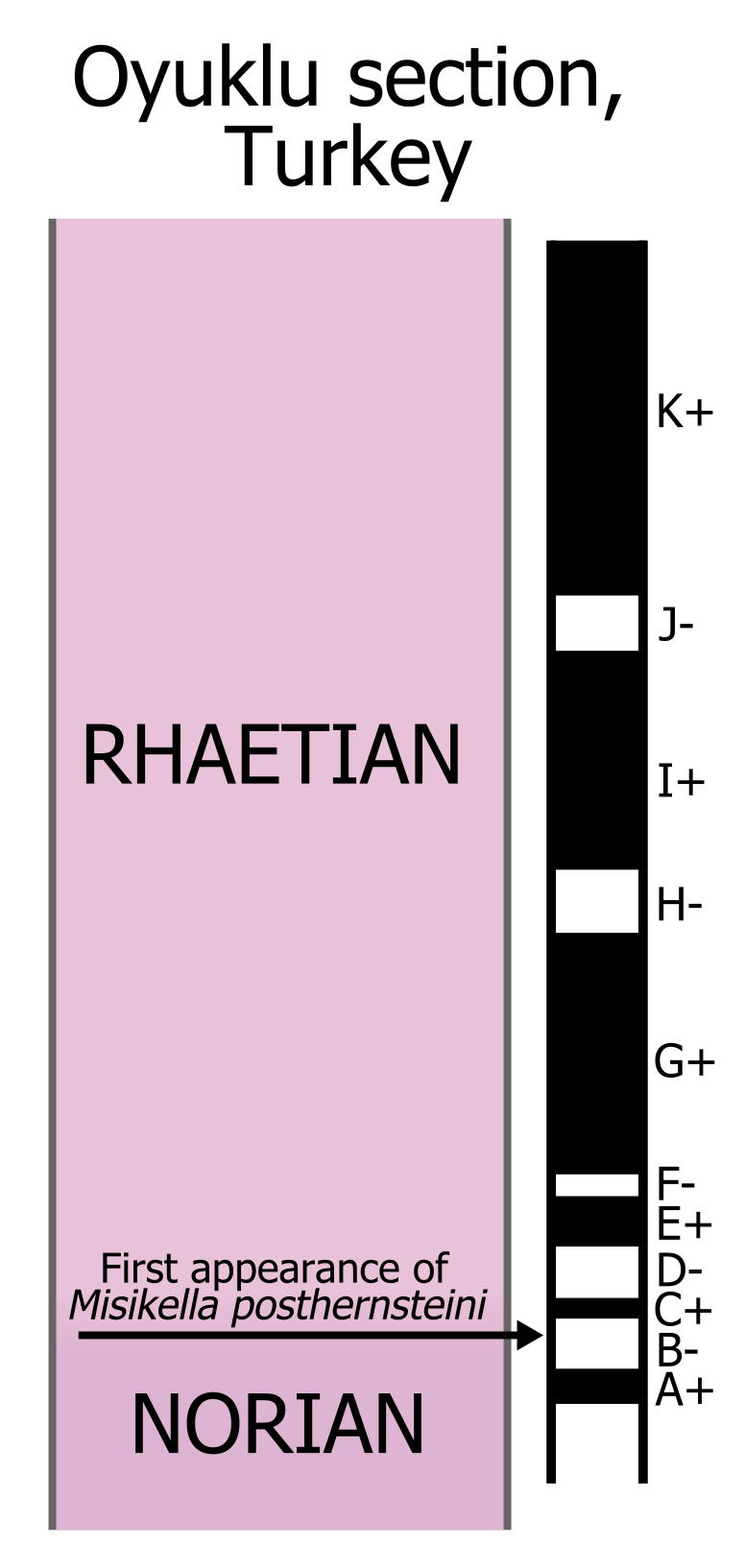
Rhaetian
The Rhaetian is the latest age (geology), age of the Triassic period (geology), Period (in geochronology) or the uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage of the Triassic system (stratigraphy), System (in chronostratigraphy). It was preceded by the Norian and succeeded by the Hettangian (the lowermost stage or earliest age of the Jurassic). The base of the Rhaetian lacks a formal Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point, GSSP, though candidate sections include Steinbergkogel section, Steinbergkogel in Austria (since 2007) and Pignola-Abriola section, Pignola-Abriola in Italy (since 2016). The end of the Rhaetian (and the base of the overlying Hettangian Stage) is more well-defined. According to the current International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS (International Commission on Stratigraphy) system, the Rhaetian ended ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). In 2010, the base of the Rhaetian (i.e. the Norian-Rhaetian boundary) was voted to be defined based on the first appearance of ''Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theria
Theria ( or ; ) is a scientific classification, subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the Placentalia, placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes and various extinct mammals evolving prior to the common ancestor of placentals and marsupials. Characteristics Therians give birth to live young without a shelled egg (biology), egg. This is possible thanks to key proteins called Syncytin-1, syncytins which allow exchanges between the mother and its offspring through a placenta, even Marsupial#Reproductive system, rudimental ones such as in marsupials. Genetic studies have suggested a viral origin of syncytins through the Endogenous retrovirus, endogenization process. The marsupials and the placentals evolved from a common therian ancestor that gave live birth by suppressing the mother's immune system. While the marsupials continued to give birth to an underdeveloped fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woutersia
''Woutersia'' was a Triassic genus of ' symmetrodont' and the only representative of the family Woutersiidae. It was originally classified as a kuehneotheriid, but it has been suggested that it may be related to Docodonta. Remains of ''W. mirabilis'' and ''W. butleri'' have been found in the Gres à Avicula contorta Formation at Saint-Nicolas-de-Port, France, while ''W. mirabilis'' has been found in Varangéville, France; remains have been dated to the Late Triassic The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ..., 205.6 to 201.6 Ma. References Mammaliaformes Rhaetian life Late Triassic synapsids of Europe Triassic France Fossils of France Fossil taxa described in 1983 Taxa named by Denise Sigogneau-Russell {{paleo-cynodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalia
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals). Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and birds), constitut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrocodium
''Hadrocodium wui'' is an extinct mammaliaform that lived during the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic approximately in the Lufeng Formation in what is now the Yunnan province in south-western China (, paleocoordinates ). It is considered as the closest relative of the class Mammalia. The fossil of this mouse-like, paper-clip sized animal was discovered in 1985 but was then interpreted as a juvenile morganucodontid. ''Hadrocodium'' remained undescribed until 2001; since then its large brain and advanced ear structure have greatly influenced the interpretation of the earliest stages of mammalian evolution, as these mammalian characters could previously be traced only to some . ''Hadrocodium'' is known only from a skull long, and its body would have measured long in total and weighed up to , making it one of the smallest Mesozoic mammaliaforms. The specimen is thought to have been that of a mature adult. The name ''Hadrocodium'' alludes to its large cranial cavity, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haldanodon
''Haldanodon'' is an extinct docodont mammaliaform which lived in the Upper Jurassic (Kimmeridgian, about 145 million years ago). Its fossil remains have been found in Portugal, in the well-known fossil locality of Guimarota, which is in the Alcobaça Formation. It may have been a semi-aquatic burrowing insectivore, similar in habits to desmans and the platypus. Several specimens are known, include a partial skeleton and well-preserved skulls. Description ''Haldanodon'' was about as long as a desman, and may have had a similar ecology. The skull was low and triangular when seen from above. For many years it had the best-known skull material of any docodont, making it vital for understanding the taxonomic position of that mammaliaform group. It was the first Mesozoic mammaliaform discovered to possess Nasal concha, turbinal plates, a complex feature of mammalian Nasal cavity, nasal cavities. However, it also retained some curiously primitive traits in common with non-mammaliaform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megazostrodon
''Megazostrodon'' is an extinct genus of basal mammaliaforms belonging to the order Morganucodonta. It is approximately 200 million years old.Fur and Fangs: Mammal Origins . Palaeobiology and Biodiversity Research Group, University of Bristol. Two species are known: ''M. rudnerae'' from the Early Jurassic of Lesotho and South Africa, and ''M. chenali'' from the Late Triassic of France. Discovery The type species ''M. rudnerae'' was first discovered in 1966 in the Elliot Formation of Lesotho, southern Africa, by palaeontologist and archaeologist Ione Rudner. It was first described by Alfred W. Crompton, A. W. Crompton and Farish Jenkins, F. A. Jenkins Jr. in 1968. The generic name ''Mega ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinoconodon
''Sinoconodon'' is an extinct genus of mammaliamorphs that appears in the fossil record of the Lufeng Formation of China in the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic period, about 193 million years ago. While sharing many plesiomorphic traits with other non-mammaliaform cynodonts, it possessed a special, secondarily evolved jaw joint between the dentary and the squamosal bones, which in more derived taxa would replace the primitive tetrapod one between the articular and quadrate bones. The presence of a dentary-squamosal joint is a trait historically used to define mammals. Description This animal had skull of which suggest a presacral body length of and weight about due to the similar parameters to the European hedgehog. ''Sinoconodon'' closely resembled early mammaliaforms like ''Morganucodon'', but it is regarded as more basal, differing substantially from ''Morganucodon'' in its dentition and growth habits. Like most other non-mammalian tetrapods, such as reptiles and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammaliaformes
Mammaliaformes ("mammalian forms") is a clade of synapsid tetrapods that includes the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent common ancestor of Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals; the latter is the clade originating with the most recent common ancestor of extant Monotremata, Marsupialia and Placentalia. Besides Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals, Mammaliaformes also includes Docodonta and ''Hadrocodium''. Mammaliaformes is a term of phylogenetic nomenclature. In contrast, the assignment of organisms to class Mammalia has traditionally been founded on traits and, on this basis, Mammalia is slightly more inclusive than Mammaliaformes. In particular, trait-based taxonomy generally includes ''Adelobasileus'' and '' Sinoconodon'' in Mammalia, though they fall outside the Mammaliaformes definition. These ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |