|
Ku80
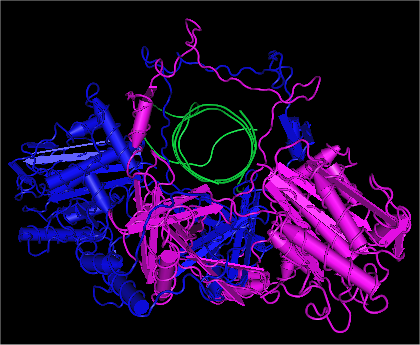
Ku80 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''XRCC5'' gene. Together, Ku70 and Ku80 make up the Ku heterodimer, which binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, which utilizes the NHEJ pathway to promote antigen diversity in the mammalian immune system. In addition to its role in NHEJ, Ku is required for telomere length maintenance and subtelomeric gene silencing. Ku was originally identified when patients with systemic lupus erythematosus were found to have high levels of autoantibodies to the protein. Nomenclature Ku80 has been referred to by several names including: * Lupus Ku autoantigen protein p80 * ATP-dependent DNA helicase 2 subunit 2 * X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 5 * X-ray repair cross-complementing 5 (XRCC5) Epigenetic repression The protein expression level of Ku80 can be repressed by e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ku (protein)
Ku is a dimeric protein complex that binds to DNA double-strand break DNA end, ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair. Ku is evolutionarily conserved from bacteria to humans. The ancestral bacterial Ku is a homodimer (two copies of the same protein bound to each other). Eukaryotic Ku is a heterodimer of two polypeptides, Ku70 (XRCC6) and Ku80 (XRCC5), so named because the molecular weight of the human Ku proteins is around 70 kDa and 80 kDa. The two Ku subunits form a basket-shaped structure that threads onto the DNA end. Once bound, Ku can slide down the DNA strand, allowing more Ku molecules to thread onto the end. In higher eukaryotes, Ku forms a complex with the DNA-PKcs, DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) to form the full DNA-dependent protein kinase, DNA-PK. Ku is thought to function as a molecular scaffold to which other proteins involved in NHEJ can bind, orienting the double-strand break for ligat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ku70
Ku70 is a heterodimeric protein made up of Ku70 and Ku80, which together form Ku. In humans, is encoded by the ''XRCC6'' gene. Ku70 plays a critical role in the DNA repair, maintenance and many other cellular processes. Function Together, Ku70 and Ku80 make up the Ku heterodimer form a quasi-symmetric structure, which encircles the double-stranded DNA. The DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) of the DNA repair pathway. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, which utilizes the NHEJ pathway to promote antigen diversity in the mammalian immune system. Ku70 is key for sensing and responding to cytosolic DNA, which is essential for the indication of infection. Within the heterodimer, Ku70 specifically binds directly to broken ends of double-stranded DNA breaks, or DSBs. Then together, Ku70 and Ku80 will tightly form a ring-like structure around the DNA strand, preventing further degradation. These steps are essential for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Damage Theory Of Aging
The DNA damage theory of aging proposes that aging is a consequence of unrepaired accumulation of DNA damage (naturally occurring), naturally occurring DNA damage. Damage in this context is a DNA alteration that has an abnormal structure. Although both mitochondrion, mitochondrial and Cell nucleus, nuclear DNA damage can contribute to aging, nuclear DNA is the main subject of this analysis. Nuclear DNA damage can contribute to aging either indirectly (by increasing apoptosis or Hayflick limit, cellular senescence) or directly (by increasing cell dysfunction). Several review articles have shown that deficient DNA repair, allowing greater accumulation of DNA damage, causes premature aging; and that increased DNA repair facilitates greater longevity, e.g. Mouse models of nucleotide-excision–repair syndromes reveal a striking correlation between the degree to which specific DNA repair pathways are compromised and the severity of accelerated aging, strongly suggesting a causal relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-homologous End Joining
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. It is called "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homology directed repair (HDR), which requires a homologous sequence to guide repair. NHEJ is active in both non-dividing and proliferating cells, while HDR is not readily accessible in non-dividing cells. The term "non-homologous end joining" was coined in 1996 by Moore and Haber. NHEJ is typically guided by short homologous DNA sequences called microhomologies. These microhomologies are often present in single-stranded overhangs on the ends of double-strand breaks. When the overhangs are perfectly compatible, NHEJ usually repairs the break accurately. Imprecise repair leading to loss of nucleotides can also occur, but is much more common when the overhangs are not compatible. Inappropriate NHEJ can lead to translocations and telomere fusion, hallmarks of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA-PKcs
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit, also known as DNA-PKcs, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in repairing DNA double-strand breaks and has a number of other DNA housekeeping functions. In humans it is encoded by the gene designated as ''PRKDC'' or ''XRCC7''. DNA-PKcs belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. The DNA-Pkcs protein is a serine/threonine protein kinase consisting of a single polypeptide chain of 4,128 amino acids. Function DNA-PKcs is the catalytic subunit of a nuclear DNA-dependent serine/threonine protein kinase called DNA-PK. The second component is the autoimmune antigen Ku. On its own, DNA-PKcs is inactive and relies on Ku to direct it to DNA ends and trigger its kinase activity. DNA-PKcs is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA repair, which rejoins double-strand breaks. It is also required for V(D)J recombination, a process that utilizes NHEJ to promote immune system diversit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-small-cell Lung Carcinoma
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively ( neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively ( adjuvant chemotherapy). Types The most common types of NSCLC are squamous-cell carcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, but several other types occur less frequently. A few of the less common types are pleomorphic, carcinoid tumor, salivary gland carcinoma, and unclassified carcinoma. All types can occur in unusual histologic variants and as mixed cell-type combinations. Non-squamous-cell carcinoma almost occupies the half of NSCLC. In the tissue classification, the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TERF2IP
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2-interacting protein 1 also known as repressor activator protein 1 (Rap1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TERF2IP'' gene. Interactions TERF2IP has been shown to interact with Ku80, Rad50 DNA repair protein RAD50, also known as RAD50, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAD50'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is highly similar to ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' Rad50, a protein involved in DNA double- ... and TERF2. Upon interaction, TERF2IP/TERF2 complex has been shown to bind to telomeric junction sites with higher affinity References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-16-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GCN5L2
__NOTOC__ Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''KAT2A'' gene. Interactions GCN5L2 has been shown to interact with: * DDB1, * Ku70, * Ku80 Ku80 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''XRCC5'' gene. Together, Ku70 and Ku80 make up the Ku heterodimer, which binds to DNA double-strand break ends and is required for the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway of DNA rep ..., * TADA2L, * TAF9, and * Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCOA6
Nuclear receptor coactivator 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCOA6'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional coactivator that can interact with nuclear hormone receptors to enhance their transcriptional activator functions. The encoded protein has been shown to be involved in the hormone-dependent coactivation of several receptors, including prostanoid, retinoid, vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and steroid receptors. The encoded protein may also act as a general coactivator since it has been shown to interact with some basal transcription factors, histone acetyltransferases, and methyltransferases. Interactions NCOA6 has been shown to interact with: * ASCL2 and * Activating transcription factor 2, * Androgen receptor, * CREB-binding protein, * DNA-PKcs, * E2F1, * EP300, * Estrogen receptor alpha, * Estrogen receptor beta, * HBXIP, * HIST2H3C, * HSF1, * Ku70, * Ku80, * Liver X receptor beta, * MLL3, * R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCNA
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase delta, DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cell (biology), cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, where it acts as a scaffold to recruit proteins involved in DNA replication, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling and epigenetics. Many proteins interact with PCNA via the two known PCNA-interacting motifs PCNA-interacting peptide (PIP) box and AlkB homologue 2 PCNA interacting motif (APIM). Proteins binding to PCNA via the PIP-box are mainly involved in DNA replication whereas proteins binding to PCNA via APIM are mainly important in the context of genotoxic stress. Function The protein encoded by this gene is found in the nucleus and is a cofactor of DNA polymerase delta. The encoded protein acts as a homotrimer and helps increase the processivity of leading strand synthesis during DNA replication. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POU2F1
POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POU2F1'' gene. Interactions POU2F1 has been shown to interact with: * EPRS, * Glucocorticoid receptor, * Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, * Host cell factor C1, * Ku80, * MNAT1 * NPAT, * Nuclear receptor co-repressor 2, * POU2AF1, * RELA, * Retinoid X receptor alpha, * SNAPC4, * Sp1 transcription factor, and * TATA binding protein. See also * Octamer transcription factor Octamer transcription factors are a family of transcription factors which binds to the "ATTTGCAT" DNA sequence. Their DNA-binding domain is a POU domain. There are eight Octamer proteins in humans (Oct1–11),Oct-5 and Oct-10 are not found in hu ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{Transcription factors, g3 POU-domain proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |