|
Krum
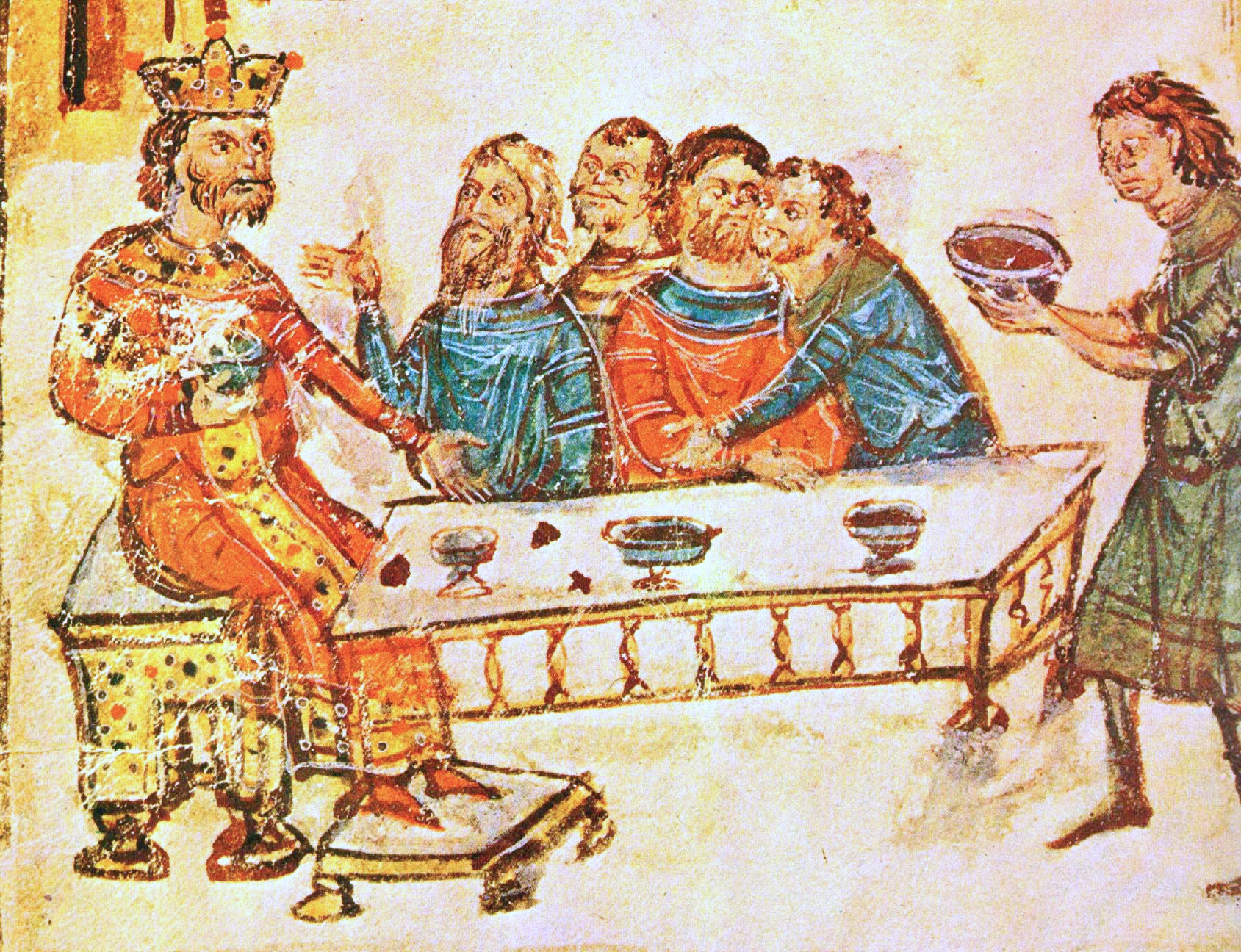
Krum (, ), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome () was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territory doubled in size, spreading from the middle Danube to the Dnieper and from Odrin to the Tatra Mountains. His able and energetic rule brought law and order to Bulgaria and developed the rudiments of state organization. Biography Origins Krum was a Bulgar chieftain from Pannonia. His family background and the surroundings of his accession are unknown. It has been speculated that Krum might have been a descendant of Khan Kubrat through his son Kuber. The Bulgar name Krum comes from the Old Turkic ''qurum'' and means "ruler". Establishment of new borders Around 805, Krum defeated the Avar Khaganate to destroy the remainder of the Avars and to restore Bulgar authority in Ongal again, the traditional Bulgar name for the area north of the Danube across the Carpathians covering Transylvania and along t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Bulgarian Empire
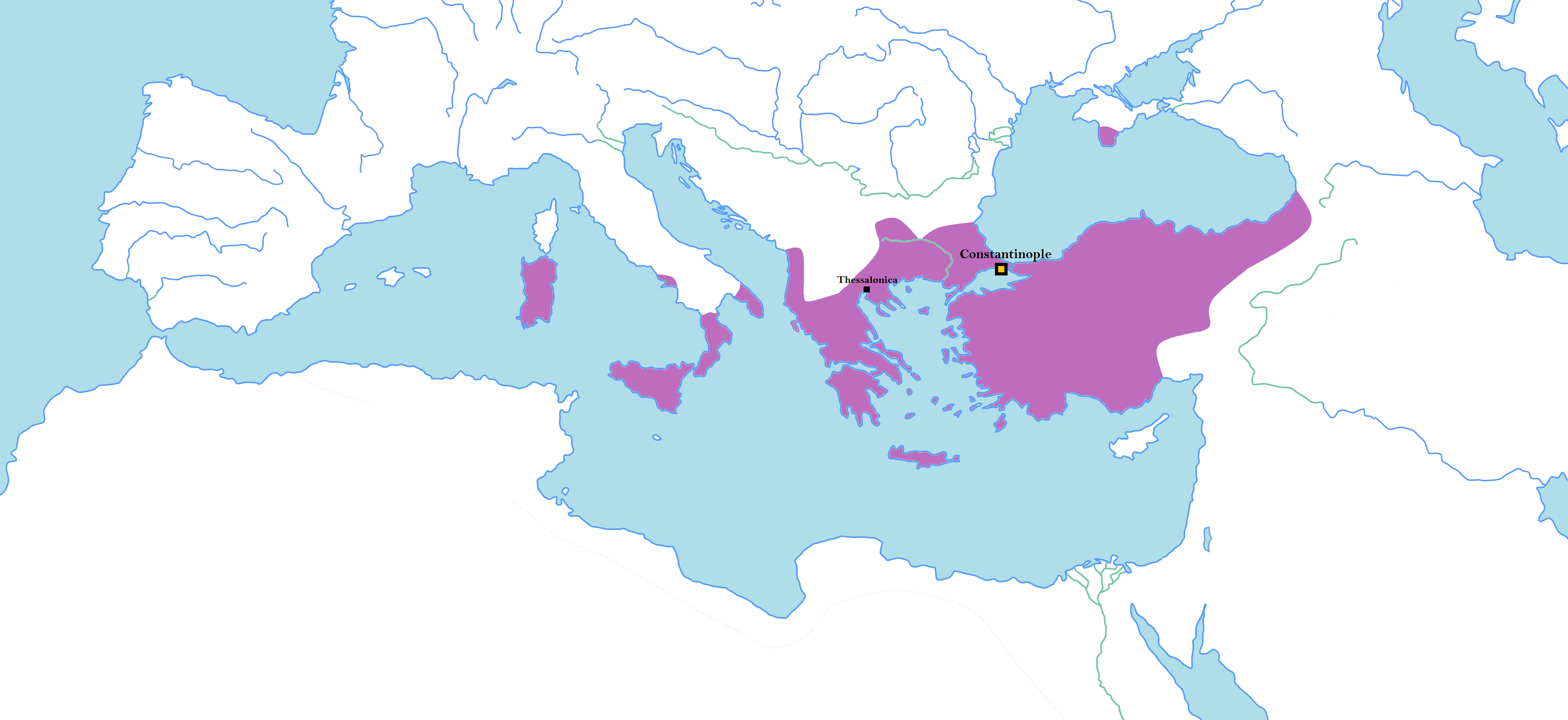
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led by Asparuh of Bulgaria, Asparuh, moved south to the northeastern Balkans. There they secured Byzantine Empire, Byzantine recognition of their right to settle south of the Danube by Battle of Ongal, defeatingpossibly with the help of Seven Slavic tribes, local South Slavic tribesthe Byzantine army led by Constantine IV. During the 9th and 10th century, Bulgaria at the height of its power spread from the Danube Bend to the Black Sea and from the Dnieper River to the Adriatic Sea and became an important power in the region competing with the Byzantine Empire. As the state solidified its position in the Balkans, it entered into a centuries-long interaction, sometimes friendly and sometimes hostile, with the Byzantine Empire. Bulgaria emerged as Byzantium's chief antagonist to its north, resulting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan Of Bulgaria
The monarchs of Bulgaria ruled Bulgaria during the medieval First Bulgarian Empire, First ( 681–1018) and Second Bulgarian Empire, Second (1185–1422) Bulgarian empires, as well as during the modern Principality of Bulgaria, Principality (1879–1908) and Kingdom of Bulgaria, Kingdom (1908–1946) of Bulgaria. This list includes monarchs from the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire until modern times, omitting earlier mythical rulers as well as rulers of separate states such as Old Great Bulgaria and Volga Bulgaria. Various titles have been used by the rulers of Bulgaria. The only recorded title, used before Bulgaria's conversion to Christianity, is ''kanasubigi'', likely meaning "Khan (title), Khan, Lord of the Army" or "the sublime Khan (title), Khan". When Bulgaria converted to Christianity in the ninth century, the ruler Boris I of Bulgaria, Boris I (852–889) was using the title ''knyaz'' (prince). For much of its later history under the first and second empires, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omurtag Of Bulgaria
Omurtag (or Omortag) (died 831) also known as Murtag or Murtagon (; Веселин Бешевлиев, Първобългарски надписи. 2ed. София 1992. Chapter: VI. Възспоменателни надписи, Inscriptio) was a Great Khan (''Kanasubigi'') of First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria from 814 to 831. He is known as "the Builder". In the very beginning of his reign he signed a Byzantine–Bulgarian Treaty of 815, 30-year peace treaty with the neighboring Byzantine Empire which remained in force to the end of his life. Omurtag successfully coped with the aggressive policy of the Frankish Empire to take Bulgaria's north-western lands and suppressed the unrest among several Early Slavs, Slavic tribes. He made administrative reforms which increased the power and the authority of the central government. His reign was marked with a strong development of Bulgarian architecture with a number of significant construction projects. Rise to the throne After the death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krum's Dynasty
Krum's dynasty () was the royal and later imperial family founded by the Khan of Bulgaria Krum (r. 803–814), producing the monarchs of First Bulgarian Empire between 803 and 991. During this period Bulgaria adopted Christianity, reached its greatest territorial extent and triggered a golden age of culture and literature. Under the patronage of these monarchs Bulgaria became the birthplace of the Cyrillic alphabet; Old Bulgarian became the ''lingua franca'' of much of Eastern Europe and it came to be known as Old Church Slavonic. As a result of the victory in the Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 913–927 the Byzantine Empire recognized the imperial title of the Bulgarian rulers and the Bulgarian Orthodox Church as an independent Patriarchate. The last representative of the dynasty, Tsar Roman (r. 977–991), was succeeded by Tsar Samuel (r. 997–1014) of the Cometopuli dynasty, upon the former's death in Byzantine captivity in 997, after spending six years in prison. Samuel had ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey to the south, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, and Romania to the north. It covers a territory of and is the tenth largest within the European Union and the List of European countries by area, sixteenth-largest country in Europe by area. Sofia is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city; other major cities include Burgas, Plovdiv, and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Karanovo culture (6,500 BC). In the 6th to 3rd century BC, the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I
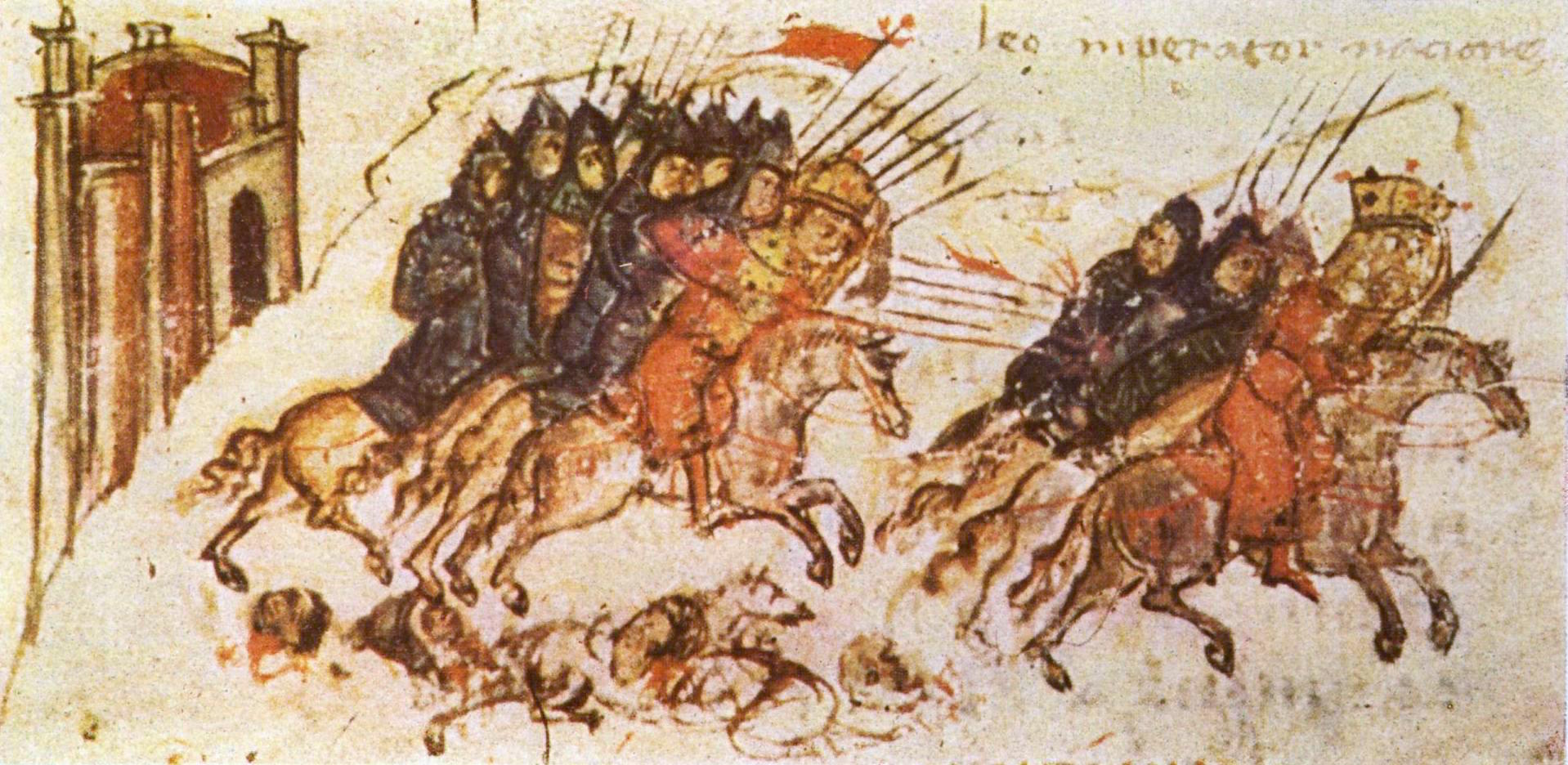
Nikephoros I (; 750 – 26 July 811), also known as Nicephorus I, was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. He was General Logothete (finance minister) under Empress Irene, but later overthrew her to seize the throne for himself. Prior to becoming emperor, he was sometimes referred to as "the Logothete" () and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (), in recognition of his previous role as General Logothete. During his reign, Nikephoros engaged in military campaigns against both the Arabs and the Bulgarians, although the outcomes were varied. While leading an invasion into Bulgaria, he suffered a defeat and was killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background According to several sources outside the Byzantine context, such as Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, there is a tradition that suggests Nikephoros had Ghassanid Arab origins and that he descended from the final Ghassanid ruler Jabala ibn al-Ayham. Al-Tabari assets that he obtained this information from Byzantine sources, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kardam Of Bulgaria
Kardam () was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire (777 – after 796/before 803).''A Concise History of Bulgaria'', R. J. Crampton, Cambridge University Press, 2005, p. 270./ref> Life The name of Kardam is first encountered in the Byzantine sources in 791, when Emperor Constantine VI embarked on an expedition against Bulgaria, in retaliation for Bulgarian incursions in the Struma valley since 789. Kardam pre-empted the Byzantine invasion and met the enemy near Adrianople in Thrace. The Byzantine army was defeated and turned to flight. In 792 Constantine VI led another army against the Bulgarians and encamped at Marcellae (near Karnobat), which he proceeded to fortify. Kardam arrived with his army on July 20 and occupied the neighboring heights. After some time passed with the two forces sizing up, Constantine VI gave in to the reassuring advice of a "false prophet" and ordered the attack. But the Byzantine forces lost formation and once again were defeated and turned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centuries. They became known as Eurasian nomads, nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers trace Bulgar ethnic roots to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian Steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian peoples, Iranic, Finno-Ugric peoples, Finno-Ugric, and Huns, Hunnic tribes. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic languages, Turkic language, the Bulgar language of the Oghur languages, Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization, and customs of Eurasian steppes as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tengri, Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary during the 7th century in the Pontic- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan Mountains
The Balkan mountain range is located in the eastern part of the Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It is conventionally taken to begin at the peak of Vrashka Chuka on the border between Bulgaria and Serbia. It then runs for about , first in a south-easterly direction along the border, then eastward across Bulgaria, forming a natural barrier between the northern and southern halves of the country, before finally reaching the Black Sea at Cape Emine. The mountains reach their highest point with Botev Peak at . In much of the central and eastern sections, the summit forms the watershed between the drainage basins of the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea, Aegean. A prominent gap in the mountains is formed by the predominantly narrow Iskar Gorge, a few miles north of the Bulgarian capital, Sofia. The karst relief determines the large number of caves, including Magura Cave, Magura, featuring the most important and extended European post-Palaeolithic cave painting, Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan (, , ) is a historic Turkic peoples, Turkic and Proto-Mongols, Mongolic title originating among nomadic tribes in the Eurasian Steppe#Divisions, Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a king. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, Seljük Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a Orda (organization), horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. It is a title commonly used to signify the head of a Pashtun Pashtun tribes, tribe or clan. The title subsequently declined in importance. During the Safavid Iran, Safavid and Qajar Iran, Qajar dynasty it was the title of an army general high noble rank who was ruling a province, and in Mughal Empire, Mughal India it was a high noble rank restricted to courtiers. After the downfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karnobat
Karnobat ( ) is a town in the Burgas Province, Southeastern Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Karnobat Municipality. According to the 2021 census, the town had a population of 16,483. Geography Karnobat municipality is situated in the southeastern part of Bulgaria, and it falls within the administrative boundaries of Burgas region. Rishki Passage links the municipality to north Bulgaria. The Karnobat-Aitos range of the Balkan Mountains is located in the northern part of the municipality. Hisar Hill raise to the south of the town of Karnobat. The territory of Karnobat municipality is , 87.37% of which is agricultural land, 9.81% forest land and 2.82% residential areas. History The Karnobat region, located in front of the south approaches of the Rishki and Varbishki passes, features an ancient history, dating back to the Neolithic era. Villages and tumuli reveal traces of life from the Neolithic and the Iron Age, rich settlement life during the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The highest peaks in the Carpathians are in the Tatra Mountains, exceeding , closely followed by those in the Southern Carpathians in Romania, exceeding . The range stretches from the Western Carpathians in Austria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Poland, clockwise through the Eastern Carpathians in Ukraine and Romania, to the Southern Carpathians in Romania and Serbia.About the Carpathians – Carpathian Heritage Society [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |